Variable-focus light emitting device
A light-emitting device and variable technology, which are applied to lighting devices, fixed lighting devices, components of lighting devices, etc., can solve the problem of large-accommodating space lens groups, difficult to miniaturize or thin design, and difficult to follow the user's needs. It is necessary to adjust the angle of the lighting direction and other issues to achieve the effect of changing the lighting range and changing the lighting angle.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 example
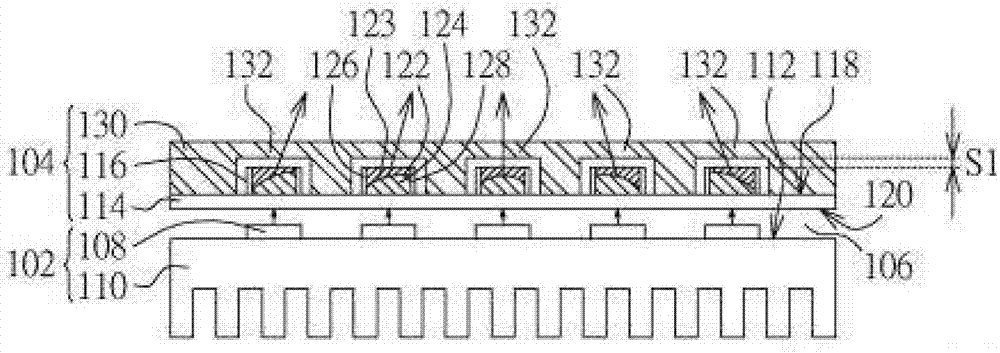
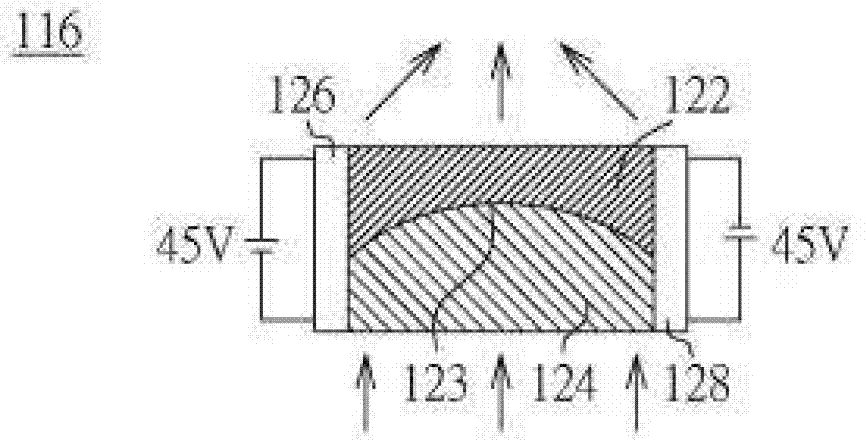
[0033] Figure 1A is a cross-sectional view of the variable-focus light emitting device according to the first embodiment. The variable-focus lighting device includes a light source module 102 and a zoom module 104 . The zoom module 104 is disposed on one side of the light source module 102 . For example, the space 106 between the light source module 102 and the zoom module 104 can be air or other fluids with different refractive indices.
[0034] Please refer to Figure 1A , the light source module 102 includes a plurality of semiconductor light emitting units 108 . The semiconductor light emitting unit 108 can be disposed on the first surface 112 of the plate heat sink 110 to quickly and efficiently dissipate the heat energy dissipated from the semiconductor light emitting unit 108 and improve the service life of the semiconductor light emitting unit 108 . The semiconductor light emitting unit 108 may include a light emitting diode (LED), a laser diode (LD), or an organic ...
no. 2 example
[0046] Figure 5 It is a cross-sectional view of the variable-focus light emitting device in the second embodiment. The difference between the second embodiment and the first embodiment is that the transparent material structure 232 of the solid transparent material layer 230 has a lens structure, for example, the lens structure is a convex lens structure or a concave lens structure. In this embodiment, the transparent material structure 232 is a spherical concave lens structure. In other embodiments, the transparent material structure 232 of the solid transparent material layer 230 may be a convex lens structure (not shown in the figure), such as a spherical convex lens. The light emitted from the liquid lens 116 enters the transparent material structure 232 having a lens structure, and then is emitted after being refracted by the transparent material structure 232 . Using the transparent material structure 232 with an optically designed lens structure can change the output...
no. 3 example
[0048] Figure 6 It is a cross-sectional view of the variable-focus light emitting device in the third embodiment. The difference between the third embodiment and the second embodiment is that the transparent material structure 332 of the solid transparent material layer 330 is an aspheric concave lens structure. In other embodiments, for example, the transparent material structure 332 of the solid transparent material layer 330 may be an aspheric convex lens structure (not shown in the figure).
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com