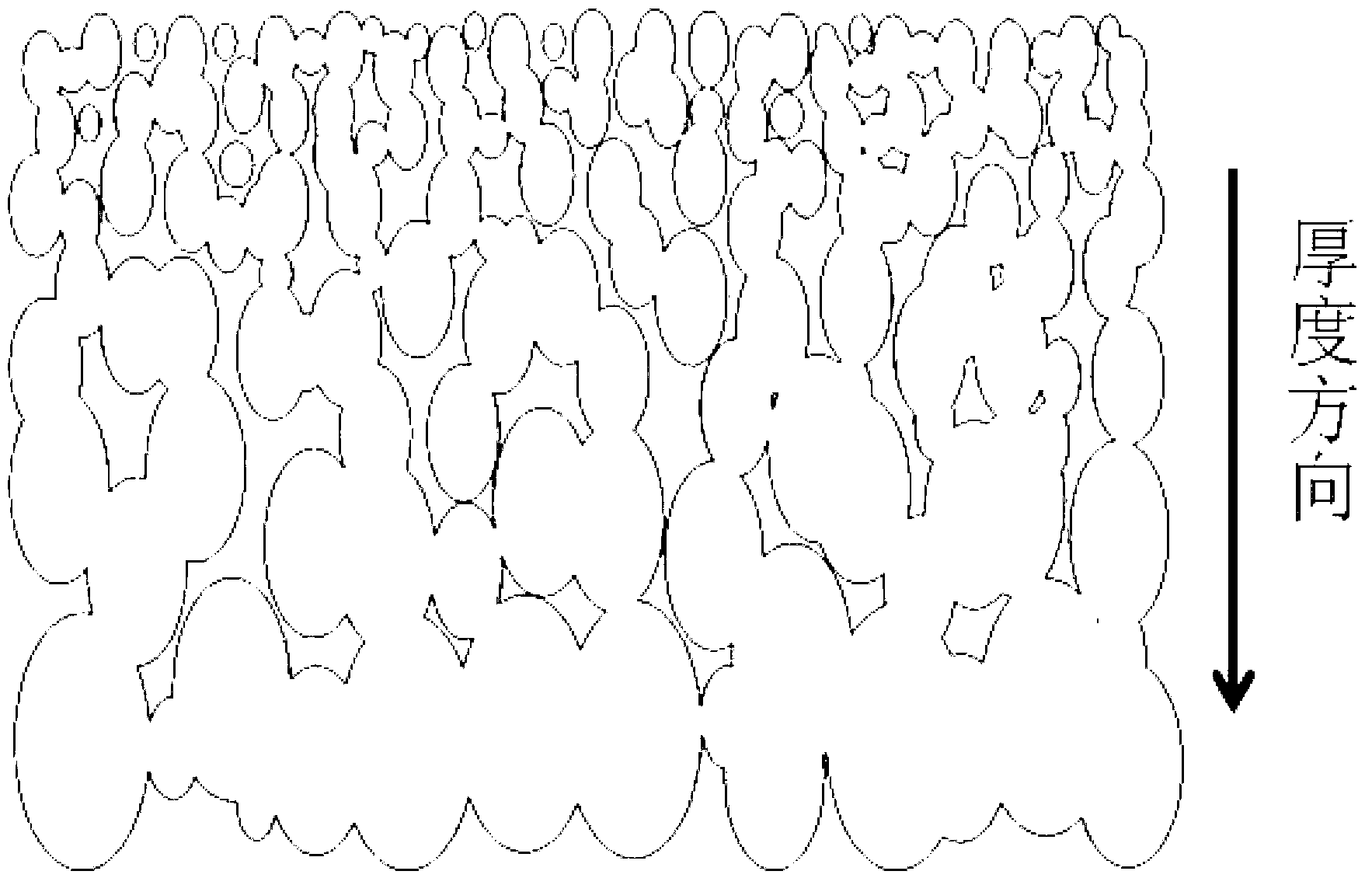
Gradient biocompatible polymer foaming material with opening structure and preparation method thereof
A technology of biocompatibility and open-cell structure, which is applied in the field of gradient biocompatible polymer foam materials and their preparation, can solve the problems of complicated operation, affecting performance, uneven distribution of cells in polymer materials, etc. , to achieve the effect of simplifying the process, uniform cells, and wide application
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0033] (1) Preparation of gradient parison
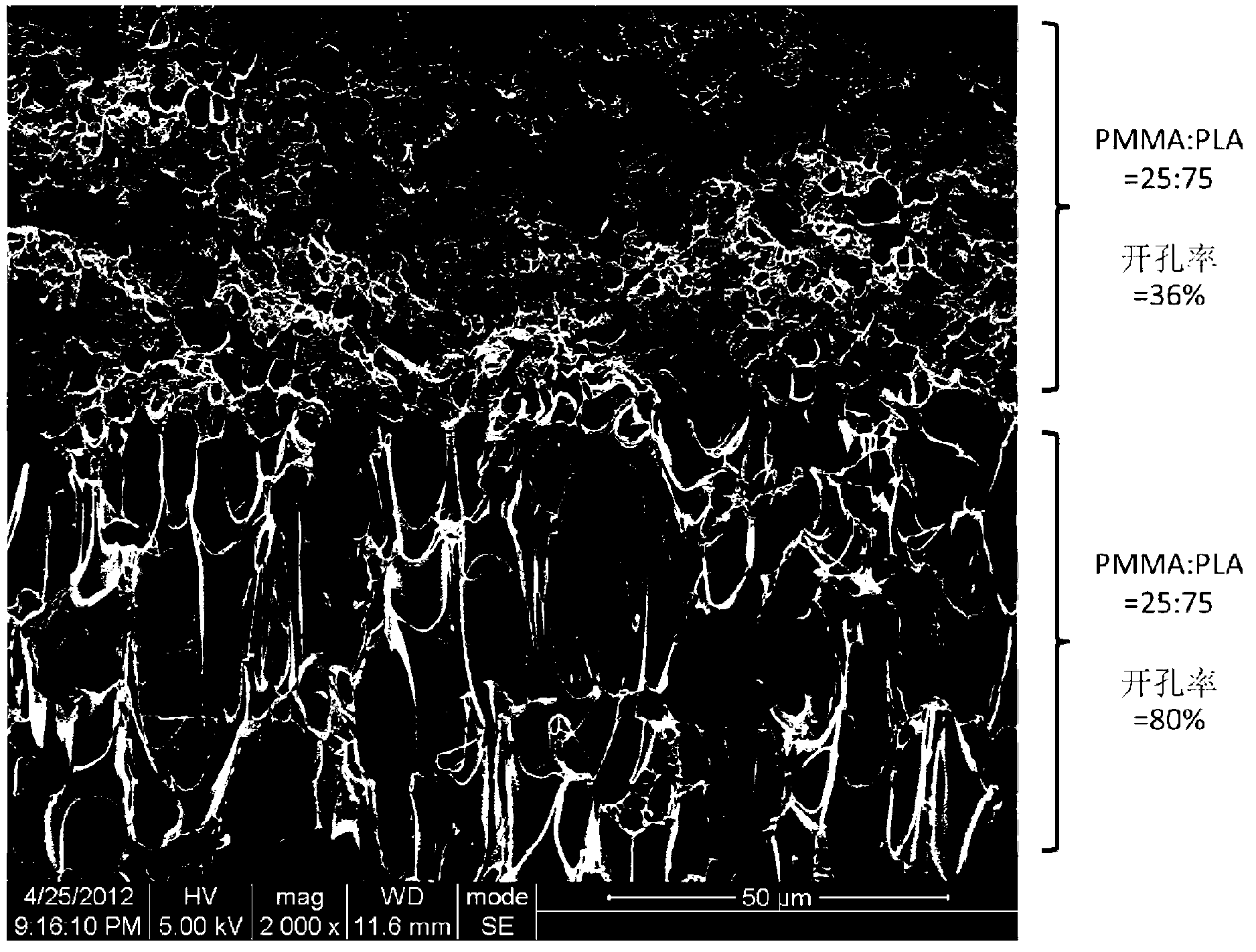
[0034]According to the mass ratio of polylactic acid (PLA): polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) = 75: 25, polylactic acid (PLA): polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) = 50: 50, weigh two groups of biocompatibility Polymers, the above two groups of biocompatible polymers were kneaded in a torque rheometer at normal pressure and 180 ℃ until the biocompatible polymers were mixed uniformly (8min), and two groups of biocompatible polymers with different compositions were obtained. Blend of compatible polymers.
[0035] The resulting two sets of blends of biocompatible polymers with different compositions were respectively molded on a press, and cooled rapidly in an ice-water bath to obtain two types of flakes with different mass ratios of PLA and PMMA and a thickness of 0.3 mm. Then two sheets of PLA and PMMA with different mass ratios are overlapped and molded into a flat gradient parison on a press. The molding temperature is 180°C and the holdin...
Embodiment 2
[0040] (1) Preparation of gradient parison
[0041] According to the mass ratio of polylactic acid (PLA): polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) = 75: 25, polylactic acid (PLA): polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) = 50: 50, weigh two groups of biocompatibility Polymer, at room temperature and normal pressure, the above two groups of biocompatible polymers were dissolved in dichloromethane and mixed evenly, then film was spread and vacuum-dried to constant weight at 50°C and -0.8MPa to obtain two groups with different compositions. The blend of biocompatible polymers, the amount of dichloromethane is limited to the complete dissolution of each group of biocompatible polymers.
[0042] The resulting two sets of blends of biocompatible polymers with different compositions were respectively molded on a press, and cooled rapidly in an ice-water bath to obtain two types of flakes with different mass ratios of PLA and PMMA and a thickness of 0.3 mm. Blend, and then two sheets of PLA and PMMA mas...
Embodiment 3
[0047] (1) Preparation of gradient parison
[0048] According to the mass ratio of polylactic acid (PLA): polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) = 75: 25, polylactic acid (PLA): polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) = 50: 50, weigh two groups of biocompatibility Polymers, the above two groups of biocompatible polymers were kneaded in a torque rheometer at normal pressure and 180 °C until the biocompatible polymers were mixed uniformly (8min), and two groups of different compositions were obtained. A blend of biocompatible polymers.
[0049] The resulting two sets of blends of biocompatible polymers with different compositions were respectively molded on a press, and cooled rapidly in an ice-water bath to obtain two types of flakes with different mass ratios of PLA and PMMA and a thickness of 0.3 mm. blend, and then overlap two pieces of PLA:PMMA=25:75 sheet-like blend, one piece of PLA:PMMA=50:50 sheet-like blend as follows: PLA:PMMA=25:75, PLA: PMMA = 50: 50, PLA: PMMA = 25: 75, placed on...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| porosity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| porosity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com