Method of predicting risk of preterm birth
A risk, SE-CAD technology, applied in the direction of biochemical equipment and methods, biological testing, measuring devices, etc., can solve the problem of no reliable and clear markers of premature birth
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0064] Example 1. Premature delivery due to intrauterine infection results in decreased expression of E-cadherin in cervical tissue
[0065] In this example, a mouse model of intrauterine infection was used 16-18 , inject lipopolysaccharide (a component of the cell wall of Gram-negative bacteria, LPS) into its uterine horn. The female animals gave birth between 8-20 hours, most of them gave birth within 12 hours, and there were no deaths. 14,15,19-21 Intrauterine inflammation is associated with premature cervical ripening that occurs before clinical labor begins. 16 The cervix of dams exposed to intrauterine LPS had fewer collagen fibers, a less dense matrix, and increased mucin compared to controls. 16 Cervical ripening appears to be an initial event in the pathogenesis of inflammation-induced PTB.
[0066] Using the mouse model of intrauterine infection described above, cervical tissue was harvested from dams exposed to LPS or saline at 2, 4 and 6 hours. Using QPCR, it w...
Embodiment 2
[0067] Example 2. Full-term delivery is also associated with decreased E-cadherin mRNA expression, as this pathway in cervical remodeling is hypothesized to be common to all deliveries
[0068] Using QPCR, E-cadherin mRNA expression was measured in non-pregnant cervix, across gestation in time-pregnant mice, and postpartum. For this mouse strain, parturition occurred on a predictable time course as E19. "E#" refers to the date of the embryo used to determine the gestation period of the mouse, where the first 24 hours of gestation was recorded as E0. Thus, 12 hours earlier than E19 (E18.5) represents just before term labor. E-cadherin mRNA levels were significantly different between groups (P=0.001, one-way ANOVA). E-cadherin mRNA levels increased at E15 (preterm; second trimester) compared to non-pregnant levels (P=0.007, SNK). E-cadherin mRNA level decreased 4.3 times at E18.5 compared with E15 (P=<0.001, SNK), which supports the expression of E-cadherin also occurs in ful...
Embodiment 3
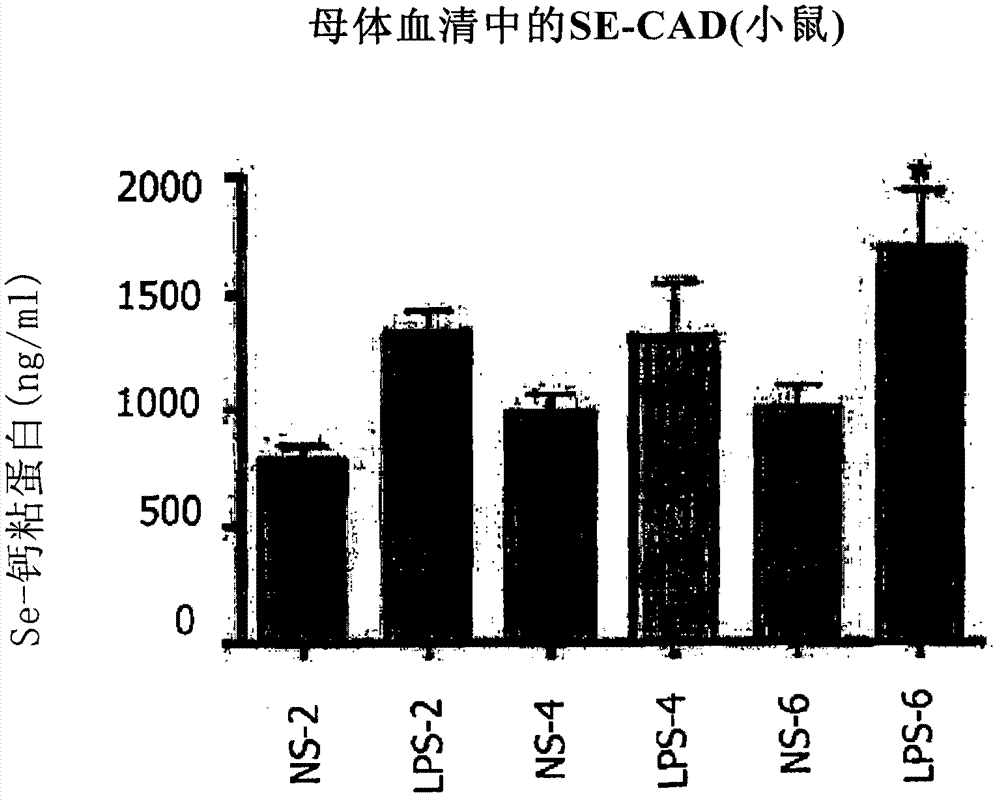
[0069] Example 3. Increased SE-Cadherin (SE-CAD) in Maternal Serum Before Parturition in an Inflammation-Induced Preterm Mouse Model
[0070] Using the mouse model of Example 1, SE-CAD was measured in maternal serum at 2, 4 and 6 hours after intrauterine infusion of LPS or saline. SE-CAD was measured using a commercially available ELISA (Human E-CAD Monoclonal Antibody ELISA Kit from R&D Biosystems). as figure 1 As noted, SE-CAD levels were significantly different between LPS- and saline-exposed dams (P=<0.001, one-way ANOVA). SE-CAD levels continued to rise for 6 hours (before the onset of clinical labor in this model). These data support that serum SE-CAD is a marker of E-cadherin breakdown, particularly at the cervical site, thereby enabling the systematic detection of cervical remodeling.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com