Method and device for synchronizing redundant array of independent disks (RAID)
A synchronization device and array technology, applied in the field of network storage, can solve problems such as high development cost of synchronization function, achieve the effect of reducing development and maintenance costs, and improving synchronization speed and performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach 1
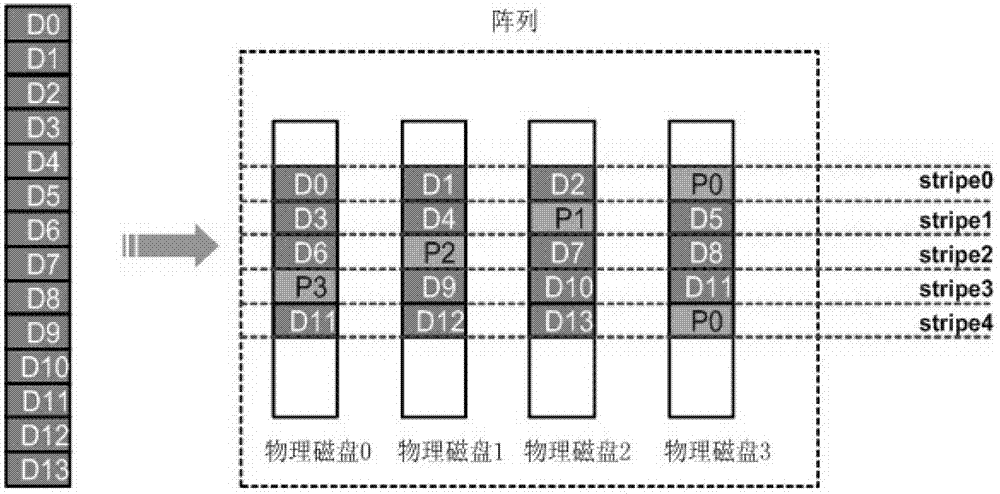
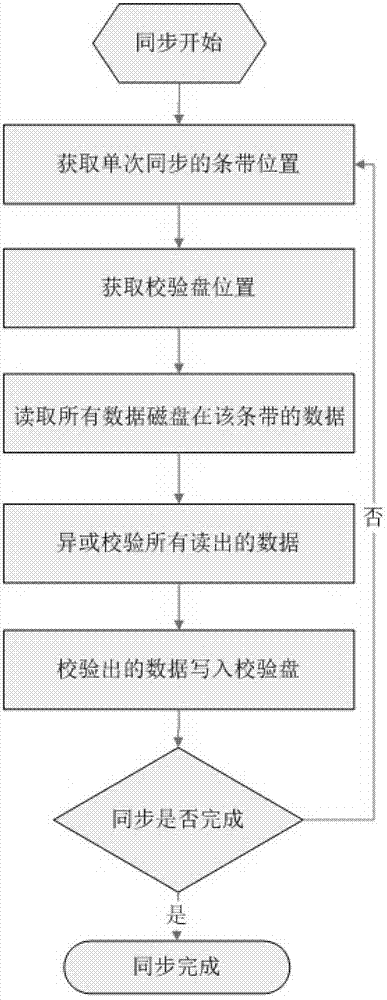
[0037] For implementation mode 1, please refer to Figure 6 , since the synchronization can be written to the specified synchronization check disk, the amount of data for each synchronization can break away from the size limit of the operation unit of the RAID array stripe, and as much data as possible can be used for synchronization, which will greatly improve the performance of the disk. Processing performance. For example, reading a 4K data volume on a disk and reading a 512KB data volume on a disk, the difference in performance consumption is very small, but the performance of RAID synchronization will be hundreds of times higher! Therefore, in a preferred embodiment, the sync block is larger than the stripe block, and accordingly the data capacity of the sync stripe formed by each disk sync block is larger than the stripe. Here are two better implementation methods in practice: a. The size of the synchronization block is N times the stripe block of the RAID array (N>=2),...
Embodiment approach 2
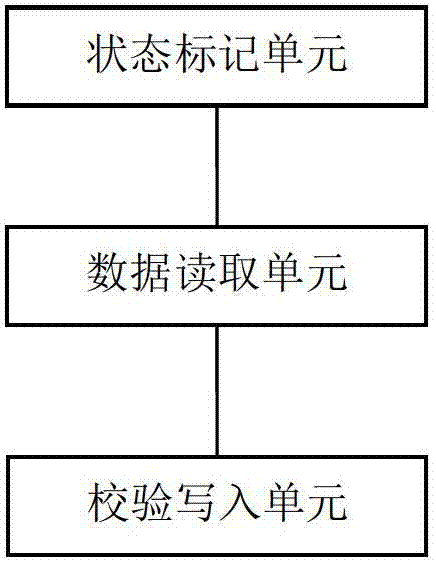
[0038] Embodiment 2. In the basic embodiment, it is not distinguished whether the read data in the synchronization block is already written business data. In order to improve the speed of synchronization, this distinction can be made. At this time, the synchronizing device may further include a writing flag unit, configured to modify the state of the data on the RAID array strip from unsynchronized to synchronized when the service data is written into the strip. Correspondingly, in this embodiment, when the data reading unit reads data, the corresponding reading status is unsynchronized data. In a preferred embodiment, the data state can be marked in the form of a Bitmap in units of stripes or stripe blocks.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com