Compositions and methods for sequencing nucleic acids
A nucleic acid sequence, nucleotide sequence technology, applied in the field of nucleotide analogs and their use in nucleic acid sequencing, can solve problems such as expensive and time-consuming
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0203] Here and in the Examples below, exemplary nucleotide analogs may include base B 1 , B 2 and / or group L 1 , L 2 , Q, F, X 1 with X 2 , each having the identity as described herein, represent nucleotide analogs having the structure of Formula I above.
[0204] An exemplary dinucleotide triphosphate analog has the structure shown in Formula II:
[0205] Formula II
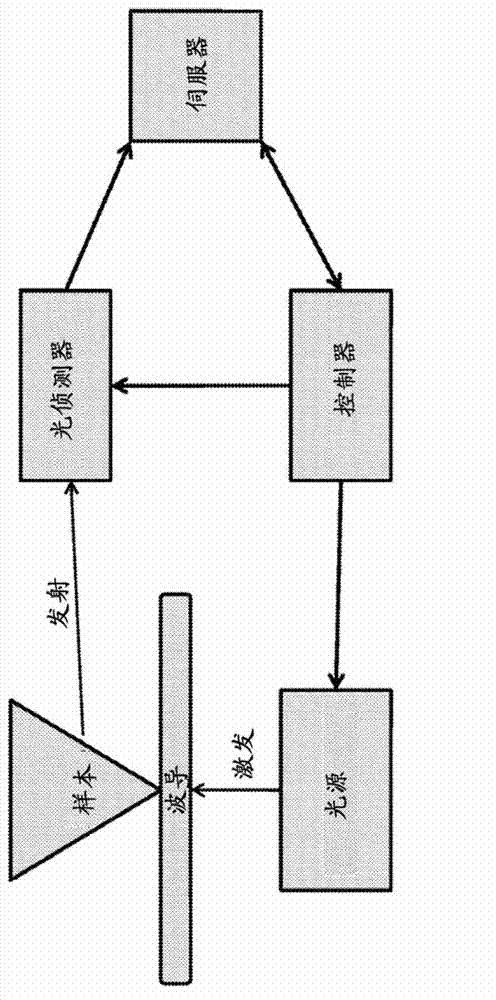
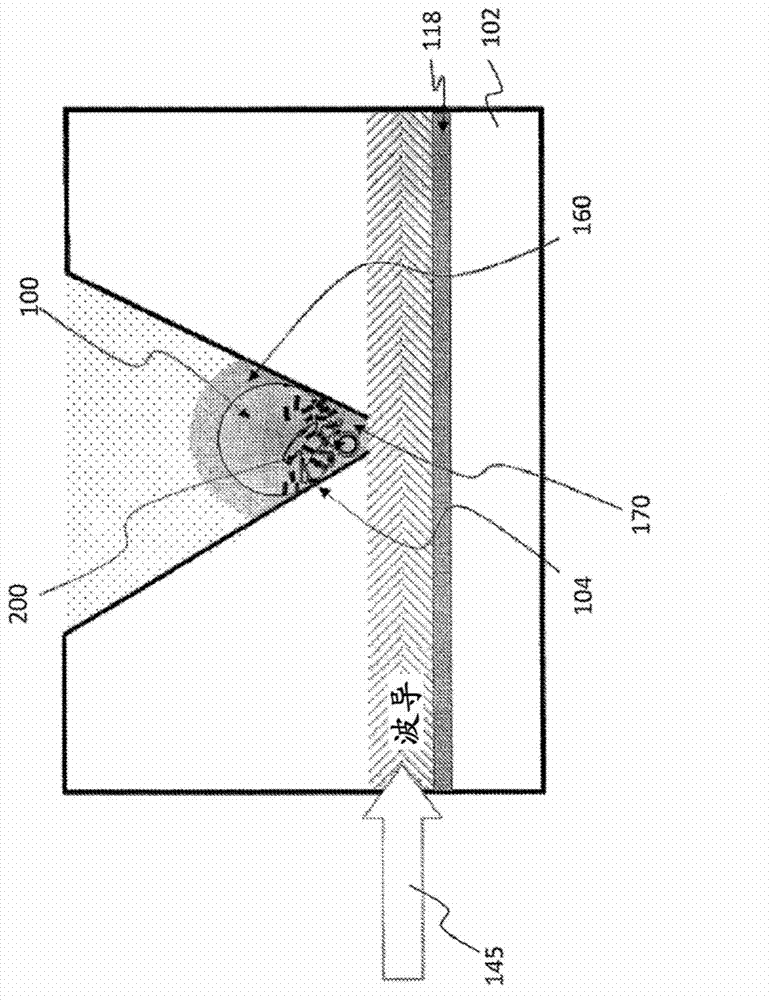
[0206] At image 3 A schematic scheme of a single cycle of proofread-dependent sequencing by synthesis using an analog having the structure of Formula II is provided in . A reaction complex comprising a proofreading polymerase, a target (template) strand, and a replicator strand is exposed to excitation light. An incoming nucleotide analog having as base B 1 An adenine that binds to the reactive site of the polymerase and base-pairs with a thymine in the target strand. By the polymerase, the dinucleotide analog is incorporated into the growing strand, whereupon the fluorescent label F is stimulated ...
Embodiment 2
[0208] An exemplary dinucleotide triphosphate analog comprising a fluorescence quenching moiety Q, the dinucleotide triphosphate analog has a structure as shown in Formula III:
[0209] Formula III
Embodiment 3
[0211] An exemplary dinucleotide triphosphate analog having a phosphorothioate that replaces the α-phosphate of the triphosphate chain, thus avoiding the persistent 3' to 5' exonuclease of the polymerase Active, this dinucleotide triphosphate analog has the structure shown in Formula IV:
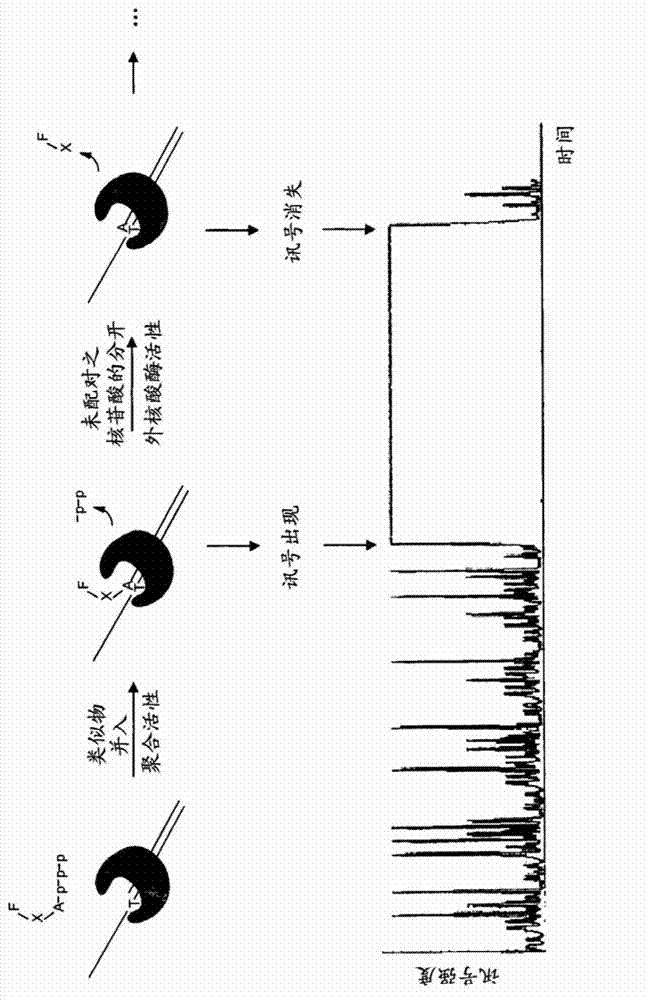
[0212] right. By the polymerase, the dinucleotide analog is incorporated into the growing strand, whereupon the fluorescent label F is stimulated by the excitation light and emits a signal which is picked up by a detector. as in Figure 4 As shown by the bar at the bottom showing the presence of a signal, the signal remains detectable when the dinucleotide is incorporated into the growing strand by the polymerase and persists until nuclease activity is increased from the polymerase by the polymerase. strand to cut off the unpaired portion of the analog (including the group X, which cannot base pair with the subsequent base in the target strand, and the fluorescent label F). When the lab...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com