Sliding belt cooling machine
A cooling machine and conveyor belt technology, which is applied in the direction of processing discharged materials, furnace control devices, furnaces, etc., and can solve problems such as easy blockage of the chute of the conveyor belt cooler
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
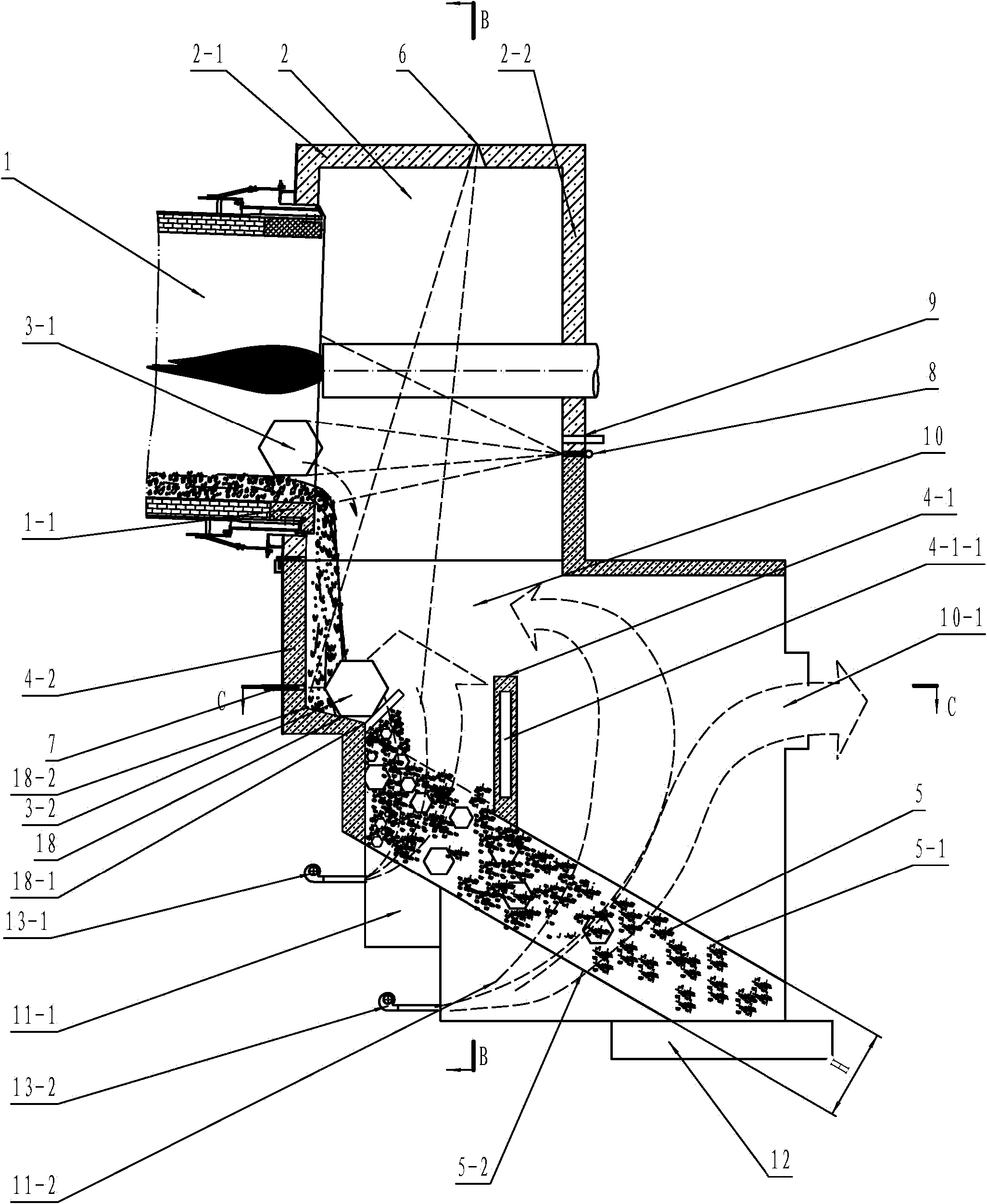
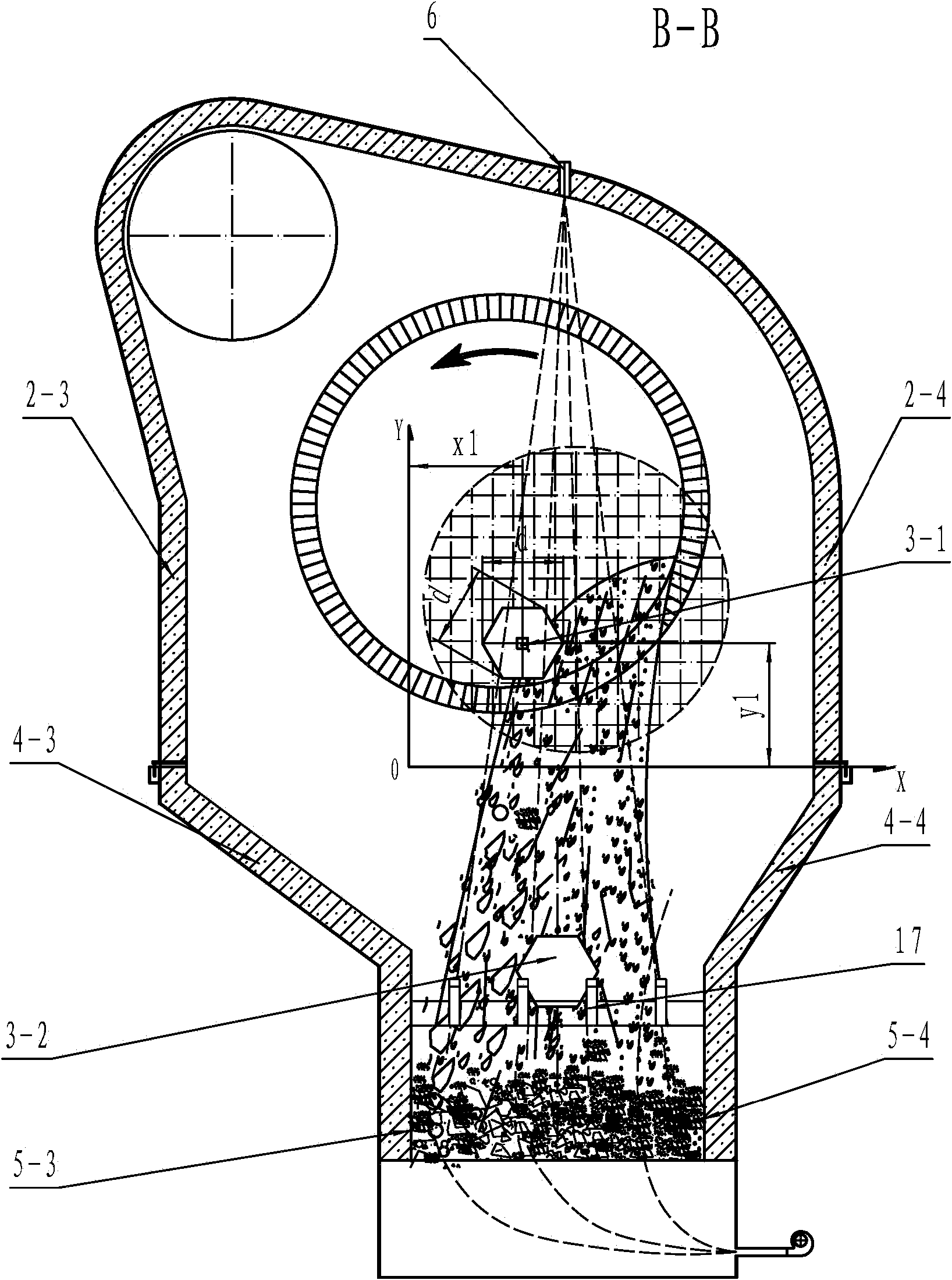
[0070] See figure 1 and figure 2 , is the front structural schematic diagram and the B-B structural schematic diagram of the belt cooler of the present invention. The material fired from the rotary kiln 1 is discharged into the chute 5 through the drainage of the drainage wall, and the material in the chute 5 slides from the inlet end of the chute to the outlet end of the chute by its own weight and is discharged through the unloader 12. When the material is falling, the cooling gas provided by the fan 13-1 and the fan 13-2 cools down the temperature of the material in the chute, so as to achieve the purpose of cooling the material. It can be seen that the entire conveyor belt cooler is a non-powered conveying system, and the conveying of materials depends entirely on the gravity of the materials. At the end, the belt cooling machine cannot handle it by itself, and it will only cause the consequence of blocking the chute, which seriously affects the production of the belt c...
Embodiment 2
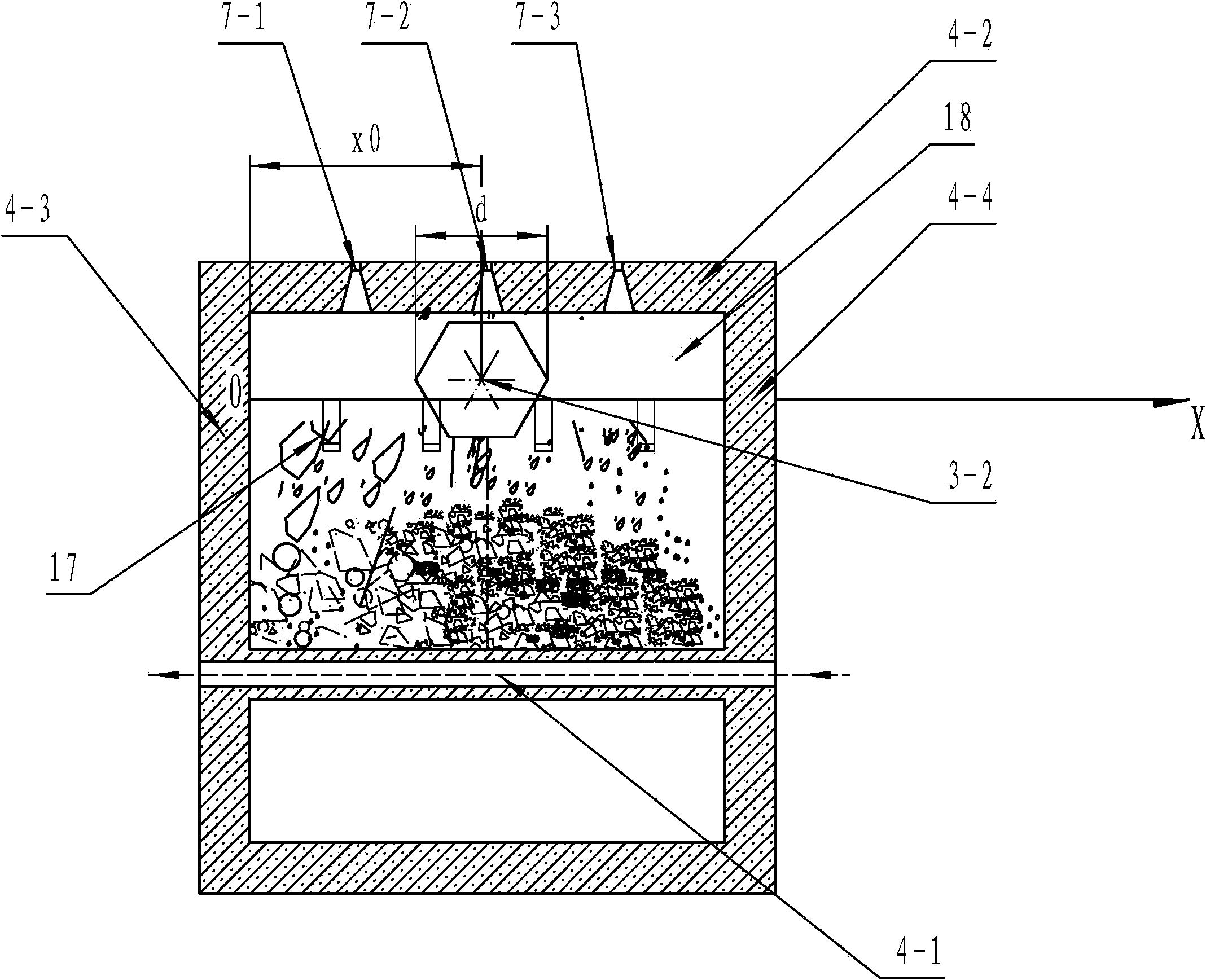
[0091] See Figure 4 and Figure 5 The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is that the filter material device in this embodiment is a grate 19, and the grate 19 is made up of a row of grate bars 19-1 arranged in the left and right direction, and one end of the grate bar 19-1 is fixed on On the front end of platform 18, the other end of grate bar 19-1 is fixed on the front drainage wall 4-1, and the distance between adjacent grate bar 19-1 is equal to size upper limit a, two grate bars at left rear two ends are respectively connected with The distance between the left drainage wall and the right drainage wall is equal to the upper limit a, so when the geometric size of the material is equal to or smaller than the upper limit a, the material can pass through the gap; when the geometric size of the material is greater than the upper limit a, that is, when the material When being a bulk material, the bulk material is grated out by the grate 19 and left on the platfo...
Embodiment 3
[0095] The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 and Embodiment 2 is that the belt cooler in this embodiment is also equipped with a material level detection device and a discharge controller on the basis of Embodiment 1 and Embodiment 2, such as Figure 9 and Figure 10 As shown, the material level detection device detects the material level at the inlet end of the chute in real time, and adjusts the material level at the inlet end of the chute by controlling the unloading speed of the unloader through the unloading controller, thereby preventing the material level at the inlet end of the chute from being too high. When the position is close to or equal to the height of the platform 18, the effect of the rake-shaped heat-resistant nails or the grate (filter) will be weakened or lost, resulting in the accumulation of materials on the platform and the filter, and small pieces of material cannot fall into the At the inlet end of the chute, when the filter material ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com