Wireless sensor-based detecting and positioning method for pollution source close to impervious boundary
A technology of wireless sensor and positioning method, which is applied in the direction of testing water, material inspection products, etc., and can solve the problems of high cost, long cycle, and poor operability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
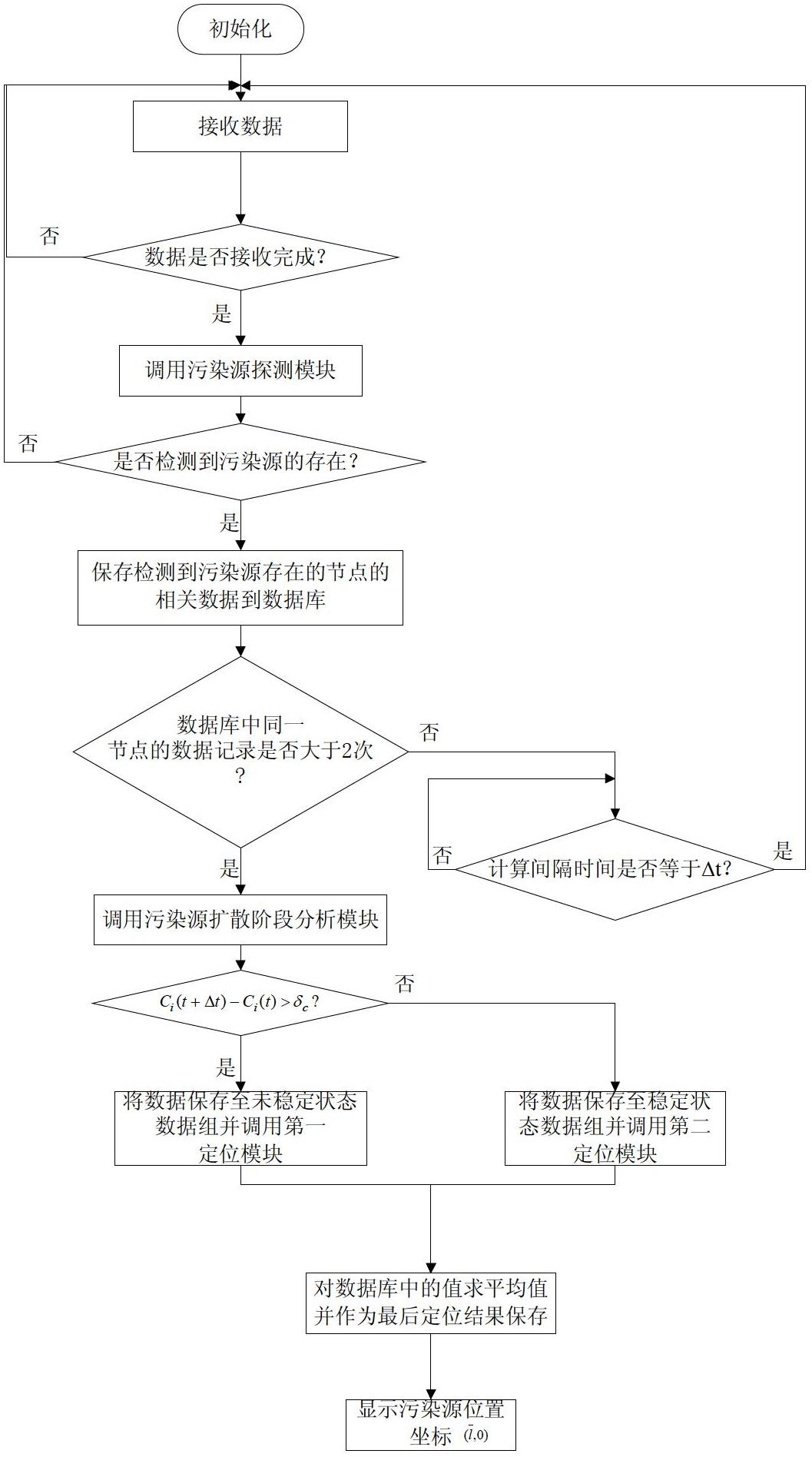
[0092] A method for detecting and locating pollution sources near impermeable boundaries based on wireless sensors, the steps of which are:
[0093] Step 1. Deploy wireless sensor nodes near the impervious boundary to be tested
[0094] Randomly distribute 10 sensor nodes near the impermeable boundary to be measured (that is, lake water within 1m from the shore or dam), and the coordinates of the sensor nodes are (x i ,y i )(i=1,2,3....10), sensor nodes (x i ,y i )(i=1,2,3....10) is connected with the terminal node by radio frequency, the terminal node is wirelessly connected with a gateway, and the gateway is connected with the PC through a serial line; the PC is equipped with a software management system, The software management system includes a pollution source detection module, a pollution source diffusion stage analysis module, a first positioning module and a second positioning module.
[0095] Step 2. Detection of water pollution sources near impermeable boundaries...
Embodiment 2
[0187] A method for detecting and locating pollution sources near impermeable boundaries based on wireless sensors, the steps of which are:
[0188] Step 1. Deploy wireless sensor nodes close to the impermeable boundary
[0189] With embodiment 1.
[0190] Step 2. Detection of water pollution sources near impermeable boundaries
[0191] Except following technical parameter, all the other are with embodiment 1.
[0192] 10 sensor nodes (x i ,y i )(i=1,2,3....10) there are 5 sensor nodes (x i ,y i )(i=1,5,6,7,10) detects that the concentration of ions in the water body is C i (t), the detected water ion concentration C i (t) As shown in Table 2.1, namely C i (t)-0.1mg / l≥10mg / l, then the sensor node (x i ,y i )(i=1,2,3....10) detects the presence of a pollution source close to an impervious boundary.
[0193] Table 2.1 Sensor nodes (xi ,y i )(i=1,5,6,7,10) the ion concentration of the water body detected at time t
[0194]
[0195] Step 3. Steady state judgment of...
Embodiment 3
[0244] A method for detecting and locating pollution sources near impermeable boundaries based on wireless sensors, the steps of which are:
[0245] Step 1. Deploy wireless sensor nodes
[0246] In addition to sensor nodes (x i ,y i ) (i=1, 2, 3....15) is 15, and the others are the same as in Embodiment 1.
[0247] Step 2. Detection of water pollution sources near impermeable boundaries
[0248] Except following technical parameter, all the other are with embodiment 1.
[0249] 15 sensor nodes (x i ,y i )(i=1,2,3....15) there are 6 sensor nodes (x i ,y i )(i=1,5,6,7,10,13) detects that the concentration of ions in the water body is C i (t), the detected water ion concentration C i (t) As shown in Table 3.1, namely C i (t)-01mg / l≥10mg / l, then the sensor node (x i ,y i ) (i = 1, 5, 6, 7, 10, 13) detects the presence of a pollution source close to an impervious boundary.
[0250] Table 3.1 Sensor nodes (x i ,y i )(i=1,5,6,7,10,13) detects the ion concentration of w...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com