Field-programmable lab-on-a-chip based on microelectrode array architecture
A micro-electrode array, lab-on-a-chip technology, applied in the field of lab-on-a-chip microfluidic systems, can solve problems such as high one-time engineering costs and achieve low-cost effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
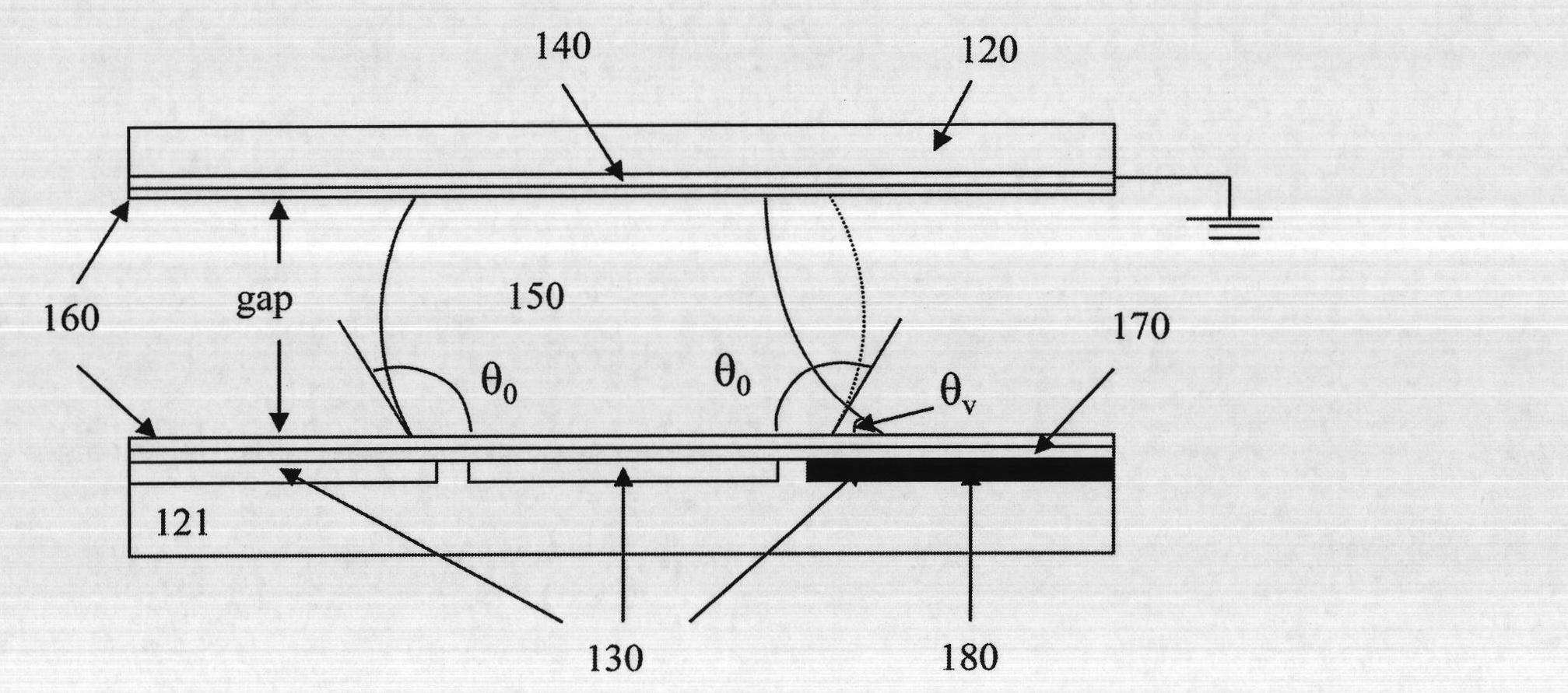
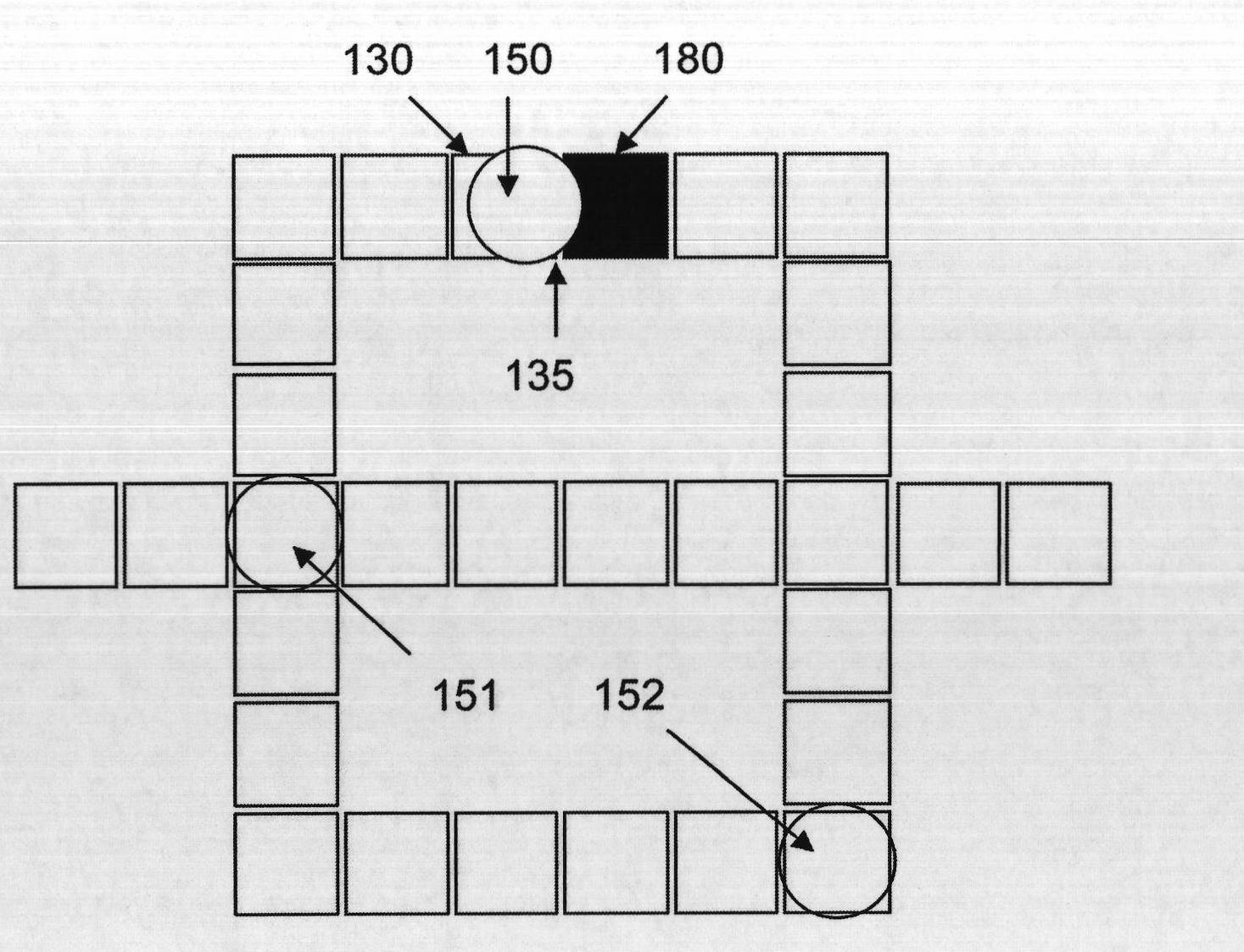
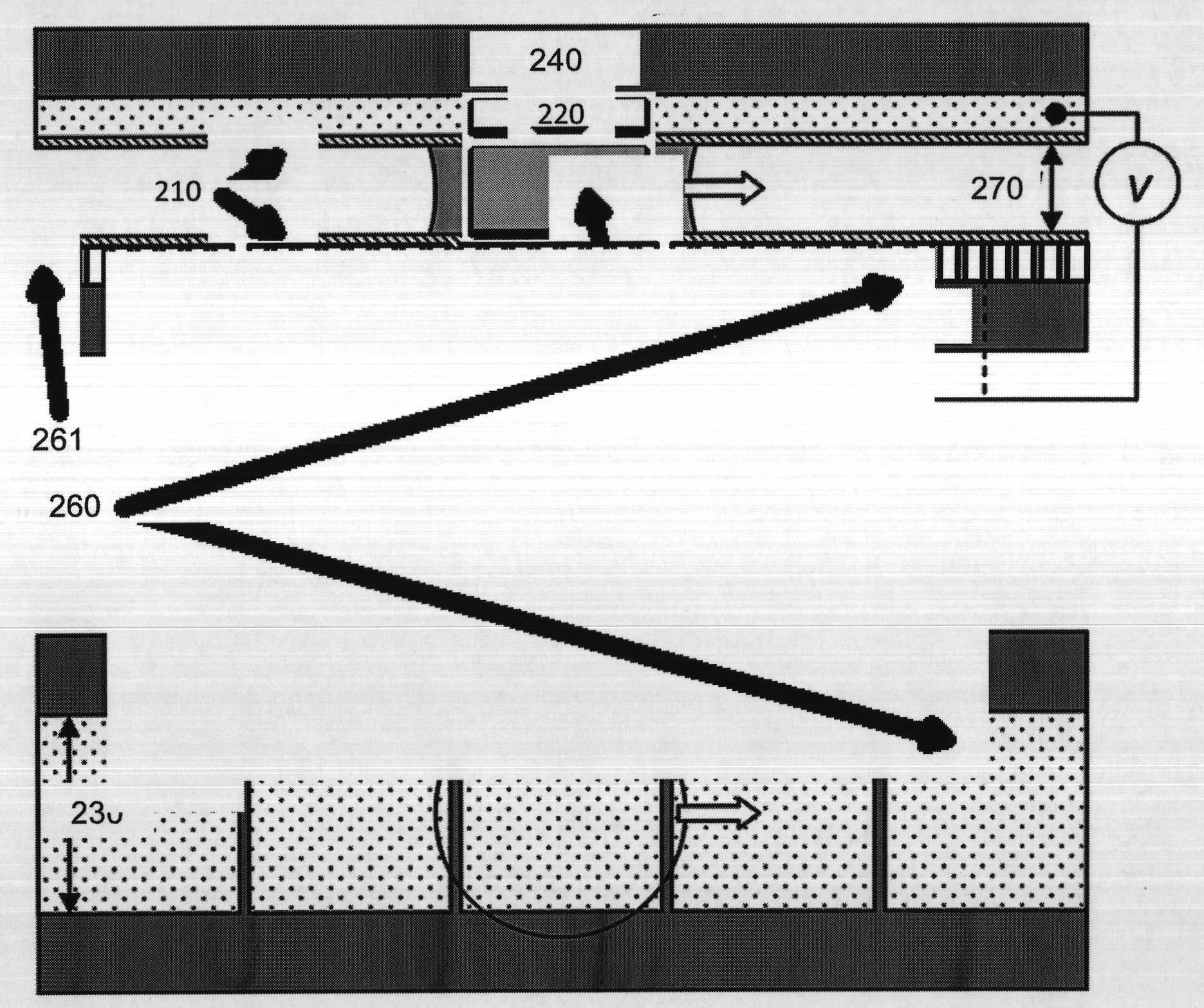
[0092] exist Figure 1A A conventional electrowetting microactuator structure is shown in (shown on a smaller scale for illustrative purposes only). The EWOD-based digital microfluidic device includes two glass plates 120 and 121 parallel to each other. The bottom plate 121 contains a patterned array of individually controllable electrodes 130 and the top plate 120 is coated with a continuous ground electrode 140 . The electrodes are preferably formed from a material such as indium tin oxide (ITO), which has the combined characteristics of electrical conductivity and light transmission in a thin layer. A dielectric insulator 170 (e.g. Parylene C) coated with a hydrophobic film 160 such as Teflon AF is added to the plate to reduce the wettability of the surface and increase the distance between the droplet and the control electrode. capacitance between. Droplets 150 containing biochemical samples and a fill medium such as silicone oil or air are sandwiched between plates to f...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com