Two-phase hollow-core compensation pulse generator and method for realizing pulse discharge
A technology for compensating pulses and pulse discharges, applied in the direction of controlling generators, electrical components, electromechanical devices, etc., can solve problems such as speed output current pulse width constraints, achieve the effect of miniaturization, increase energy density and power density
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
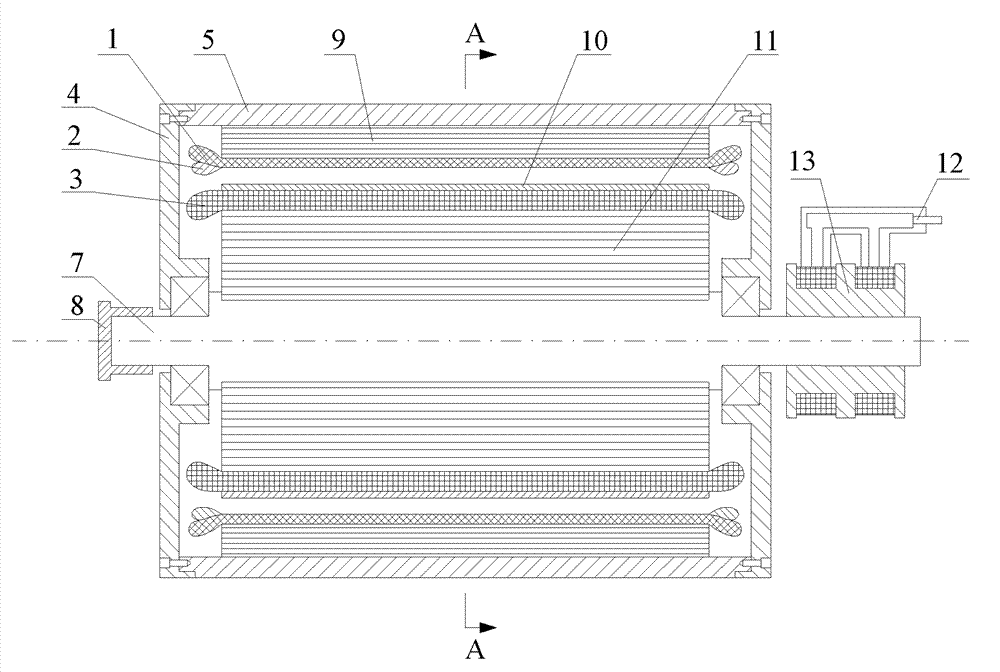
[0022] Specific implementation mode 1: Combination figure 1 with figure 2 To explain this embodiment, the two-phase air-core compensation pulse generator of the present invention includes a stator, a rotor, a clutch 8, a slip ring 12, and a brush 13;
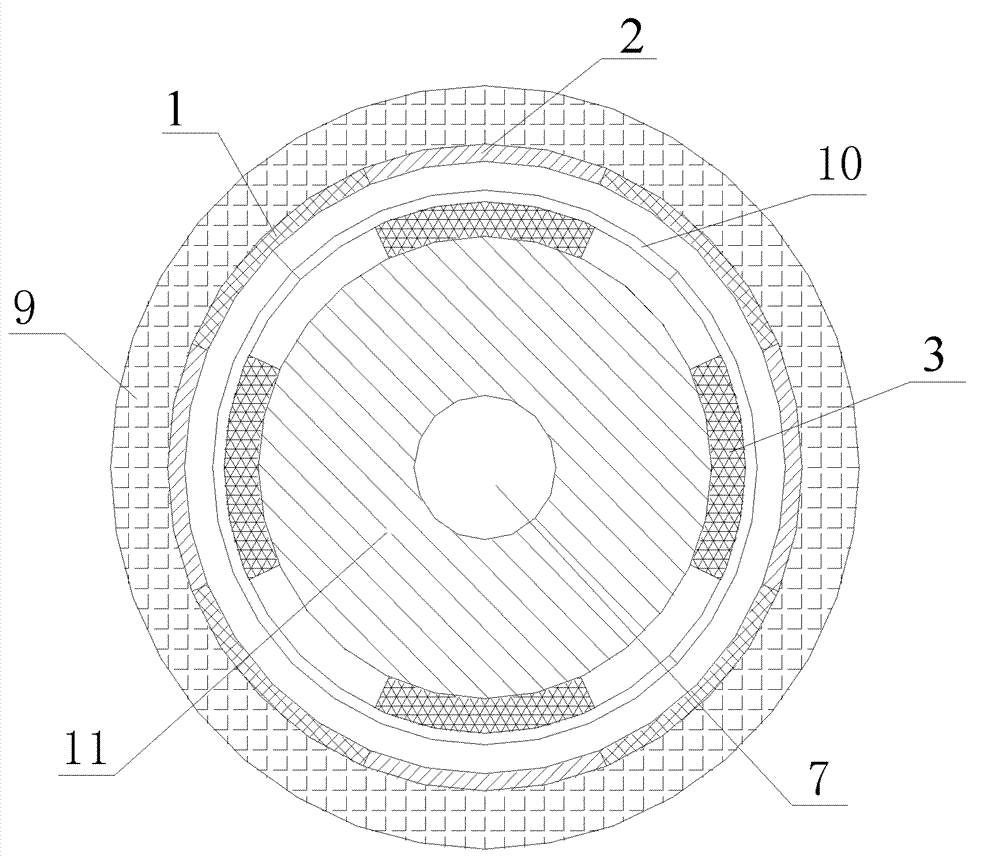
[0023] The stator includes a housing 5, an end cover 4, an air-core stator yoke 9, an A-phase armature winding 1 and a B-phase armature winding 2; the air-core stator yoke 9 is fixed on the inner wall of the housing 5, and the A-phase armature winding The 1 and B phase armature windings 2 are fixed on the inner wall of the hollow-core stator yoke 9, and two end covers 4 are respectively fixed at both ends of the casing 5;
[0024] The rotor includes a main shaft 7, an air-core rotor yoke 11, an excitation winding 3, and a rotor bandage 10. The rotor is arranged in the casing 5 and is concentric with the stator. The air-core rotor yoke 11 is sleeved on the outer surface of the main shaft 7, and the air-core rotor The outer surface of...
specific Embodiment approach 2
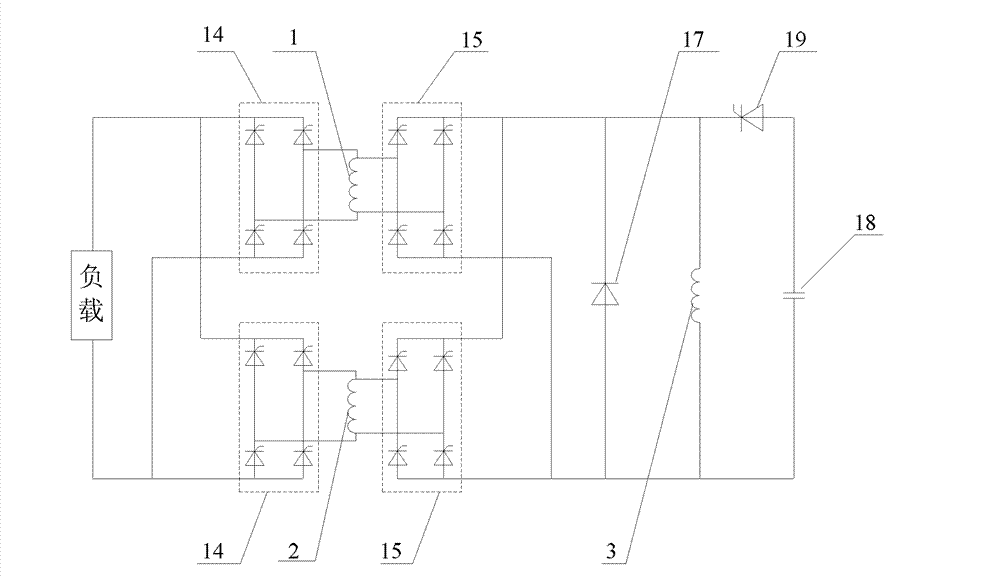
[0027] Embodiment 2: This embodiment further defines the two-phase air-core compensation pulse generator described in Embodiment 1. The A-phase armature winding 1 and the B-phase armature winding 2 are arranged alternately along the circumference. The phase A armature winding 1 and the phase B armature winding have an electrical angle difference of 90°.
[0028] The electrical angles of the two-phase armature windings of the motor are arranged orthogonally, and there is no magnetic field coupling. Therefore, the two-phase windings will not induce currents to each other during discharge, and the output current of each phase is relatively independent, which is more conducive to pulse shaping, thereby achieving output Ideal trapezoidal pulse current required by railguns.
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0029] Embodiment 3: This embodiment further defines the two-phase air-core compensated pulse generator described in Embodiment 1. The A-phase armature winding 1 and the B-phase armature winding 2 adopt slotless concentric windings , The coil that composes the winding is composed of multiple strands of Litz wire, which are connected in parallel to form the winding.
[0030] The A-phase armature winding 1 and the B-phase armature winding 2 are wound in parallel with Litz wire, which can effectively reduce the skin effect during discharge, reduce the internal resistance of the motor, and improve the efficiency of the motor; the armature winding coil uses the mold and the ring Oxygen resin molding, epoxy resin plays the role of shaping and strengthening; for windings with no slot structure, it is easier to wind and arrange with concentric winding.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com