Three-level inverter circuit
A technology of three-level inverter and inverter circuit, which is applied to electrical components, irreversible DC power input to AC power output, and AC power input to DC power output. It can solve the problem that conduction and cut-off are not instantaneous Completion, system efficiency drop, electromagnetic interference, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
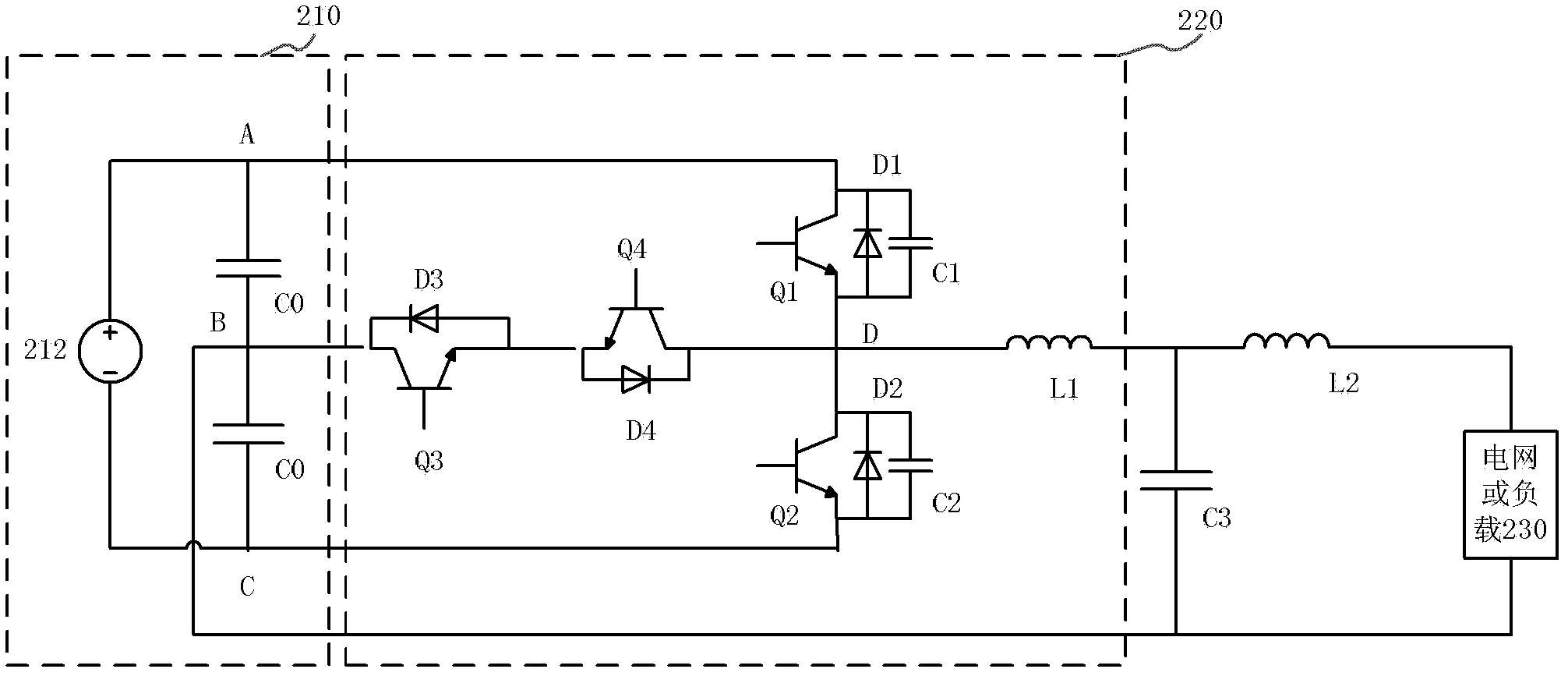
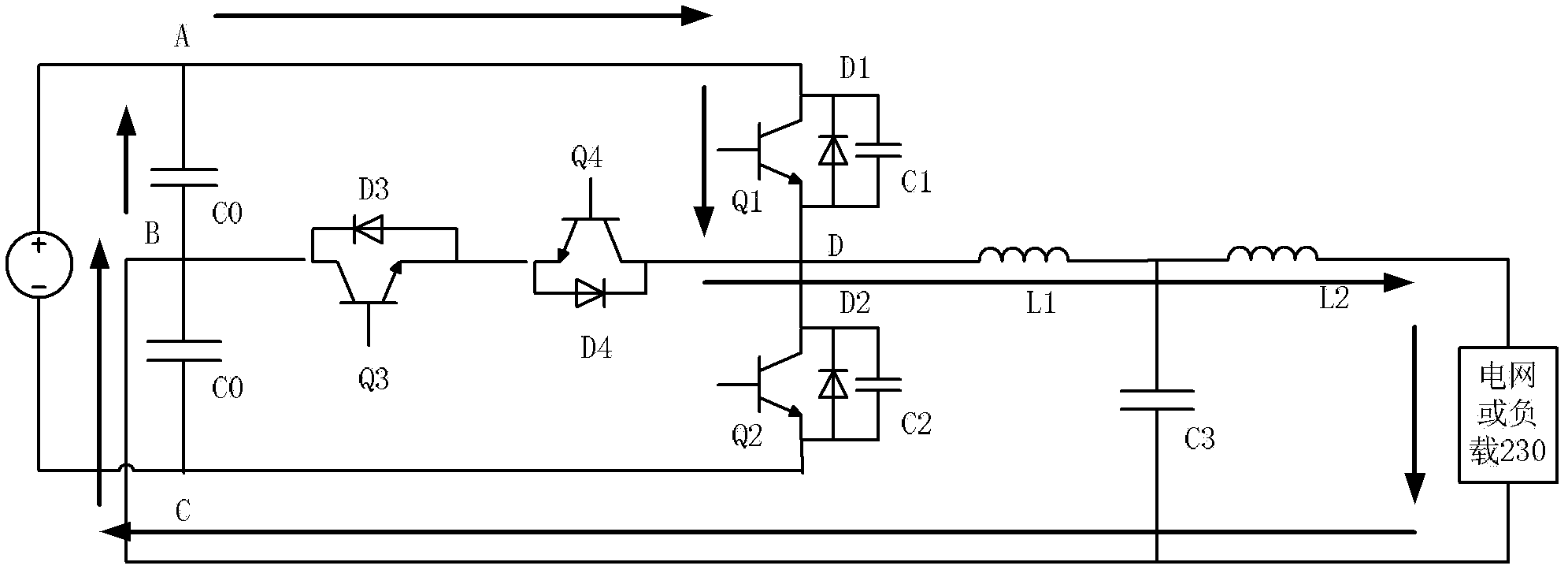
[0031] Please refer to figure 2 , which shows a schematic circuit diagram of the inverter circuit provided by Embodiment 1 of the present invention. The inverter circuit adopts a single-phase three-level T-type inverter circuit topology, and the inverter circuit includes a voltage supply circuit 210 and a single-phase inverter circuit 220 .
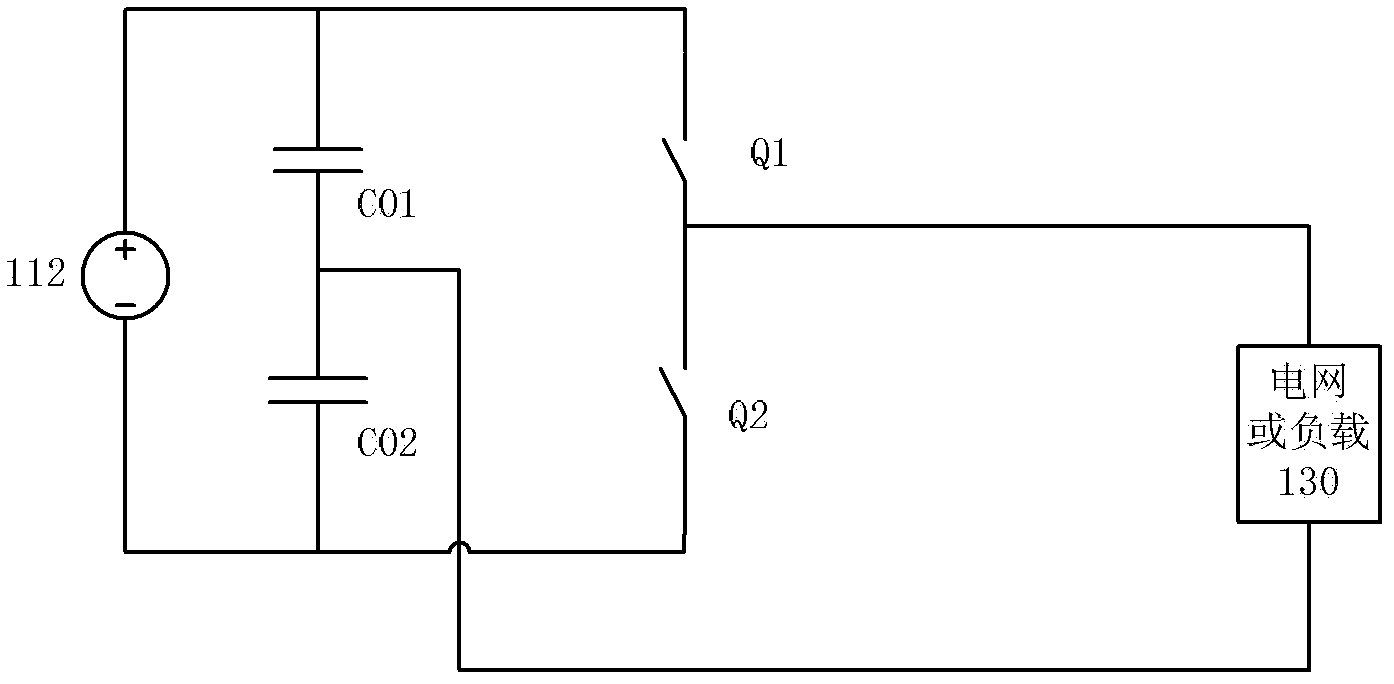
[0032] The voltage supply circuit 210 includes a positive voltage terminal A, an intermediate voltage terminal B and a negative voltage terminal C. Normally, the voltage difference between the positive voltage terminal A and the intermediate voltage terminal B is equal to the voltage difference between the intermediate voltage terminal B and the negative voltage terminal C. For example, the voltage of the positive voltage terminal A is 2Vd, the voltage of the intermediate voltage terminal B is Vd, and the negative The voltage of the voltage terminal C is 0; for another example, the voltage of the positive voltage terminal A is Vd, the v...
Embodiment 2
[0053] Please refer to Figure 4 , which shows a schematic circuit diagram of a three-level inverter circuit provided in Embodiment 2 of the present invention. The three-level inverter circuit adopts a three-phase three-level T-type inverter circuit topology, and the three-level inverter circuit includes a voltage supply circuit 410, a first phase inverter circuit 420, a second phase inverter circuit and a third phase inverter circuit. phase inverter circuit.
[0054] Obviously, the voltage supply circuit 410 in the three-level inverter circuit provided in the second embodiment may be the same as or similar to the voltage supply circuit 210 in the three-level inverter circuit provided in the first embodiment. The difference is that the three-level inverter circuit provided by Embodiment 1 only includes a single-phase inverter circuit, while the three-level inverter circuit provided by Embodiment 2 includes a three-phase inverter circuit whose input ends are connected in paral...
Embodiment 3
[0060] Please refer to Figure 5 , which shows a schematic circuit diagram of a three-level inverter circuit provided by Embodiment 3 of the present invention. The three-level inverter circuit adopts a single-phase three-level T-shaped inverter circuit topology, and the three-level inverter circuit includes a voltage supply circuit 510 , a single-phase inverter circuit 520 and a single-phase auxiliary inverter circuit 530 .
[0061]Apparently, the voltage supply circuit 510 in the three-level inverter circuit provided in the third embodiment may be the same as or similar to the voltage supply circuit 210 in the three-level inverter circuit provided in the first embodiment. The difference is that the three-level inverter circuit provided in Embodiment 1 only includes a single-phase inverter circuit, while the three-level inverter circuit provided in Embodiment 3 also includes a single-phase inverter circuit in which the input and output terminals are connected in parallel 520 ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com