Control channel transmission method and device
A technology for a control channel and a transmission method, applied in the field of transmission methods and devices for control channels, can solve problems such as power reduction, interference reduction, and limited coverage, and achieve the effects of improving resource utilization efficiency, improving coverage distance, and improving receiving performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
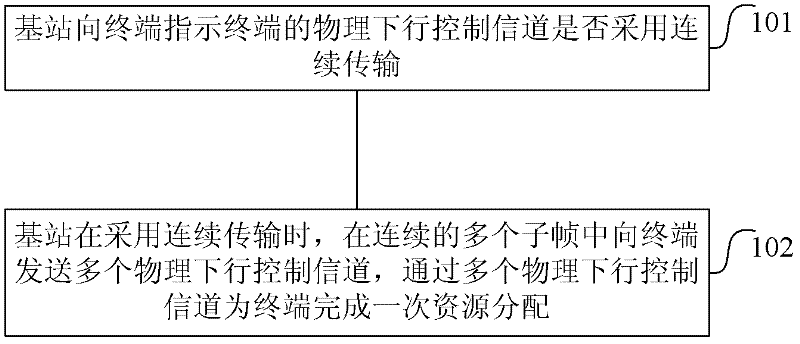
[0070] figure 2 Shown is the common transmission method of PDCCH in the mobile communication network, that is: each PDSCH is indicated by a PDCCH in the same subframe, the terminal first detects the PDCCH, and determines the relevant information of receiving the PDSCH according to the control information in the PDCCH. figure 2 Shown in , the aggregation level of the PDSCH is 4, that is, 4 CCEs are occupied.
[0071] In the above existing method, for some terminals with poor channel quality, the solution adopted by the base station can only be to use a larger aggregation level, for example, use 8 CCEs to improve the detection success rate.
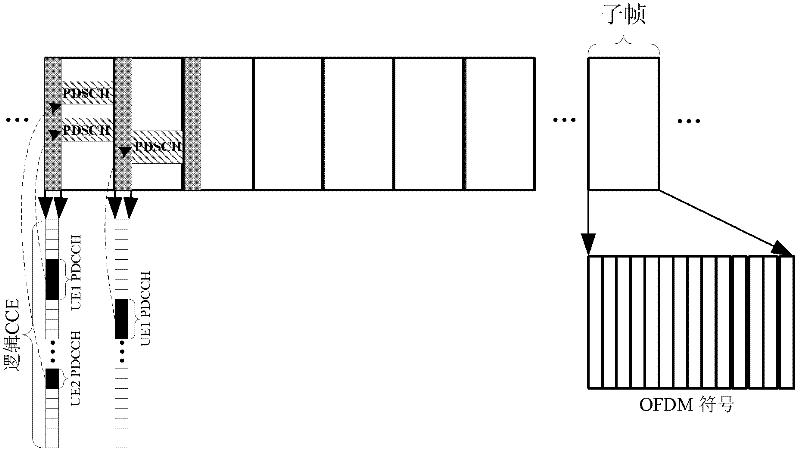
[0072] image 3 It is a schematic diagram of continuous transmission of PDCCH in this embodiment, image 3 In order to implement a PDSCH transmission for a terminal with poor channel quality, the base station sends three PDCCHs in three consecutive subframes. These three PDCCHs can be different HARQ versions of the same information. Aft...
example 2
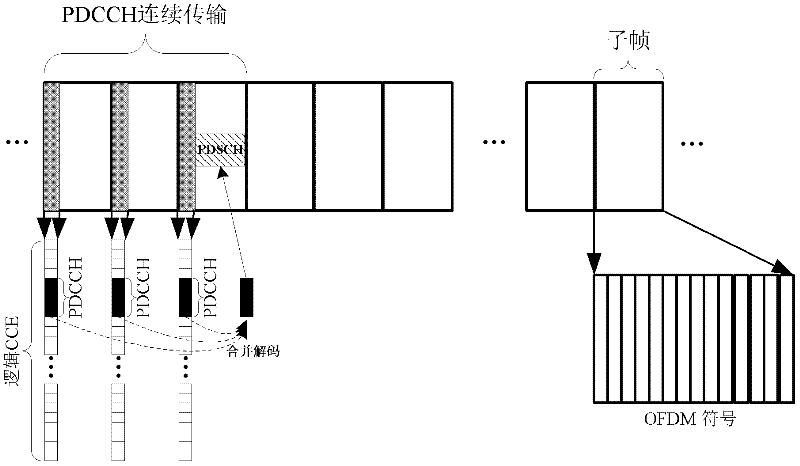
[0077] Figure 4 Example 2 of continuous transmission of PDCCH in this embodiment;
[0078] In the scheme of PDCCH continuous transmission, the number or times of PDCCH continuous transmission needs to be determined, including the following schemes:
[0079] (1) It can be a certain number, for example, preferably 3 times, as long as the base station uses the PDCCH continuous transmission scheme for a certain terminal, it will transmit continuously 3 times fixedly. image 3 Shown in is a fixed continuous transfer of 3 times.
[0080] (2) It can be configured by the base station, for example, configured with 1-2 bits. Taking 2 bits as an example, it corresponds to four consecutive transmission times 1, 2, 3 and 4.
[0081] Figure 4 In order to implement a PDSCH transmission for a terminal with poor channel quality, the base station sends 4 PDCCHs in 4 consecutive subframes. These 4 PDCCHs can be different HARQ versions of the same information, and the terminal receives 4 PD...
Embodiment 3
[0085] Figure 5 Example 3 of continuous transmission of PDCCH in this embodiment;
[0086] In this example, with image 3 and Figure 4 The difference between the continuous transmissions is that the base station can set different consecutive transmission times for different terminals.
[0087] Both terminal 1 and terminal 2 are located at the edge of the network, and the channel quality is not good, but the channel quality of terminal 1 is better than that of terminal 2, so terminal 1 does not need to use an excessively high aggregation level, for example, aggregation level 4 Instead of using 8, on the other hand, there is no need for too many consecutive transmission times, for example, 3 consecutive transmissions instead of 4; on the one hand, terminal 2 needs to use the highest aggregation level, for example, using aggregation level 8, and on the other hand, perform The maximum number of consecutive transmissions, for example, 4 consecutive transmissions.
[0088] It ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com