Permanent magnet rotating motor and compressor using the same
A rotating motor and permanent magnet technology, applied in the field of compressors, to achieve the effects of suppressing eddy current loss, alleviating stress concentration, high efficiency and performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
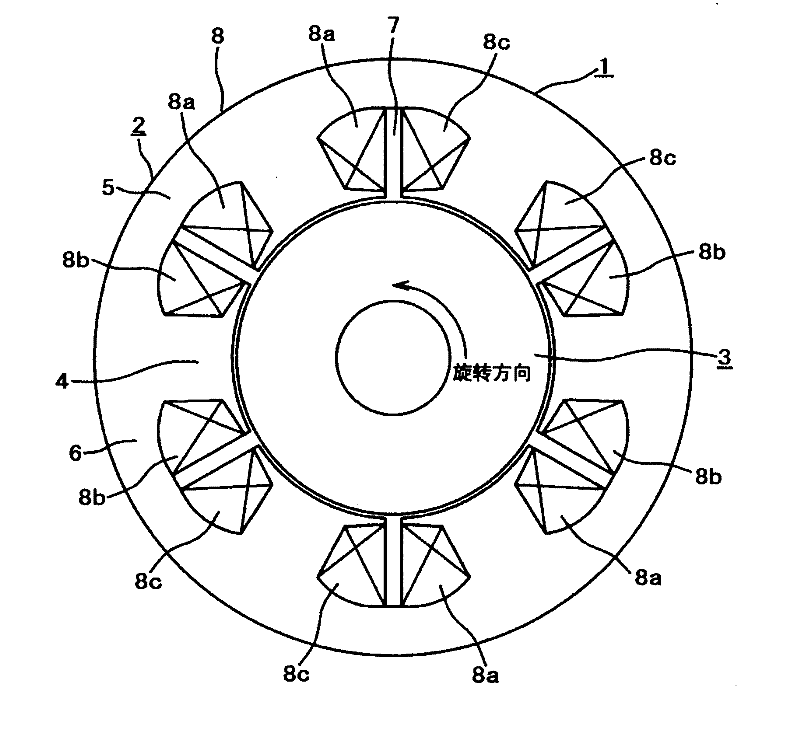
[0059] First, in order to explain the principle of operation of the present invention, a permanent magnet rotating electrical machine according to a first embodiment (Embodiment 1) of the present invention will be described. It should be noted that the attached figure 1 is a cross-sectional view of the permanent magnet rotating electrical machine of Embodiment 1, figure 2 This is a cross-sectional view of, in particular, the rotor in the permanent magnet rotating electrical machine of the first embodiment.
[0060] in the figure 1 Among them, a permanent magnet rotating electrical machine 1 includes a cylindrical stator 2 and a rotor 3 rotatably mounted inside the cylindrical stator. The stator 2 includes: a stator core 6 composed of a plurality of teeth 4 and a core support 5; and an armature winding 8 ( U-phase winding 8a, V-phase winding 8b, and W-phase winding 8c) of the three-phase windings. Here, since the permanent magnet rotating electrical machine 1 has four po...
Embodiment 2
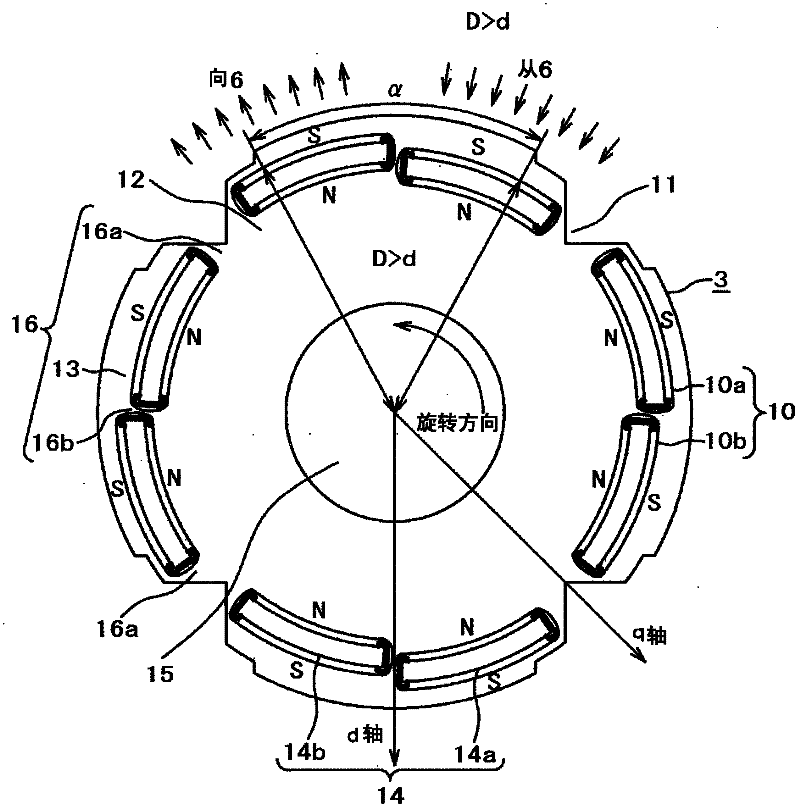
[0072] image 3 is a cross-sectional view showing details of a rotor of a permanent magnet rotating electric machine according to Embodiment 2 of the present invention, wherein figure 2 The same constituent elements are labeled with the same symbol to avoid repeated descriptions.
[0073] Should image 3 The rotor of the permanent magnet rotating electrical machine shown is the same as the above figure 2 The difference is that, instead of the above-mentioned curved (arc-shaped cross-sectional shape) permanent magnets 14a, 14b, flat-shaped permanent magnets with a rectangular cross-section are used, and accordingly, the cross-sections of the insertion holes 10a, 10b are also formed in a rectangular shape. . It should be noted that the above-mentioned two pieces of permanent magnets 14a, 14b are arranged in a so-called inverted "V" shape in such a manner that their opposing parts protrude relative to the outer peripheral surface of the rotor 3, and are arranged in a directi...
Embodiment 3
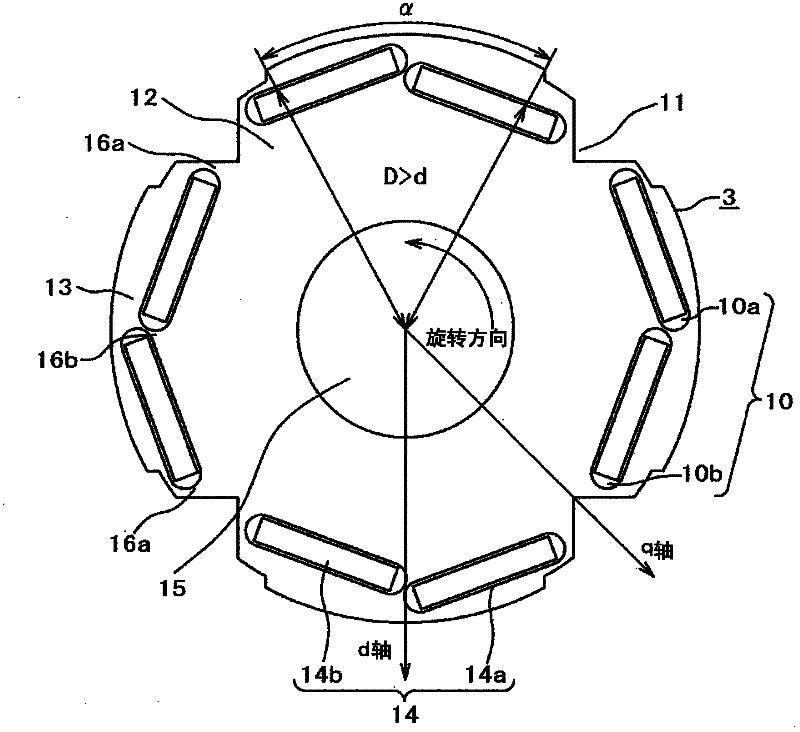
[0076] Next, attach Figure 4 It is a cross-sectional view showing the details of the rotor of the permanent magnet rotating electric machine according to the third embodiment of the present invention, and here, the above-mentioned figure 2 The same constituent elements are labeled with the same symbol to avoid repeated descriptions.
[0077] in the Figure 4 In the rotor of the permanent magnet rotating electrical machine shown, the difference from the above-mentioned embodiment is that, as can be clearly seen from the figure, the above-mentioned permanent magnets divided into two are permanent magnets 14a and 14b with a rectangular cross section, and the permanent magnets are The magnet insertion holes 10a, 10b are not along the outer peripheral surface of the pole core 13, but are arranged linearly and obliquely to a perpendicular line to the center line of each pole (the line passing through the center of the opening α of the pole core 13). into a straight line. In add...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com