Network bandwidth-adaptive video stream transmission control method
An adaptive network, streaming control technology, applied in image communication, selective content distribution, electrical components, etc., can solve the same video bit rate, delay and other problems
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
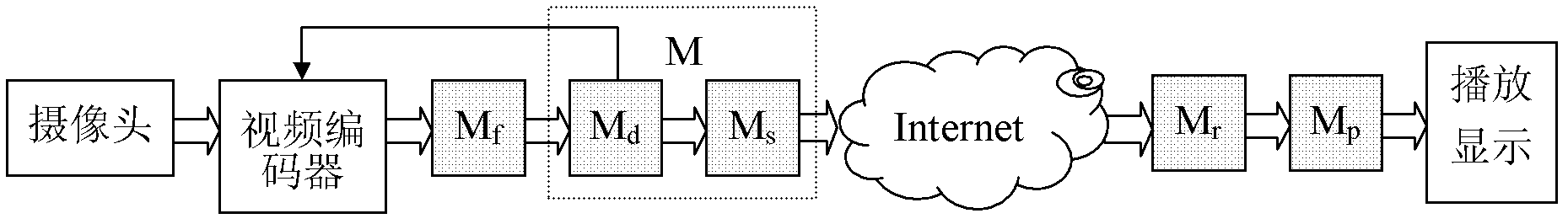
[0051] The present invention provides an adaptive network bandwidth video stream transmission control method, which divides the cache M of the sender into two: one is the video data cache, denoted as M d , used to store the video frame data from the video encoder, and the other is the video sending buffer, denoted as M s , used to temporarily store a frame of video data from the video data cache, waiting for the transmission link to send; if M d , M s The total byte length is denoted as L d , L s , then the length of the buffer M of the sender is L d +L s . figure 1 is a schematic diagram of the data transfer relationship between caches during video transmission, where M d For first-in-first-out stream buffering, M f A frame of video data buffer output by the video encoder, M r Buffer for data reception, M p Cache for video playback, the double-line arrow in the figure indicates the direction of data flow transmission, and the single-line arrow indicates the direction...
Embodiment 2
[0064] The difference from Example 1 is:
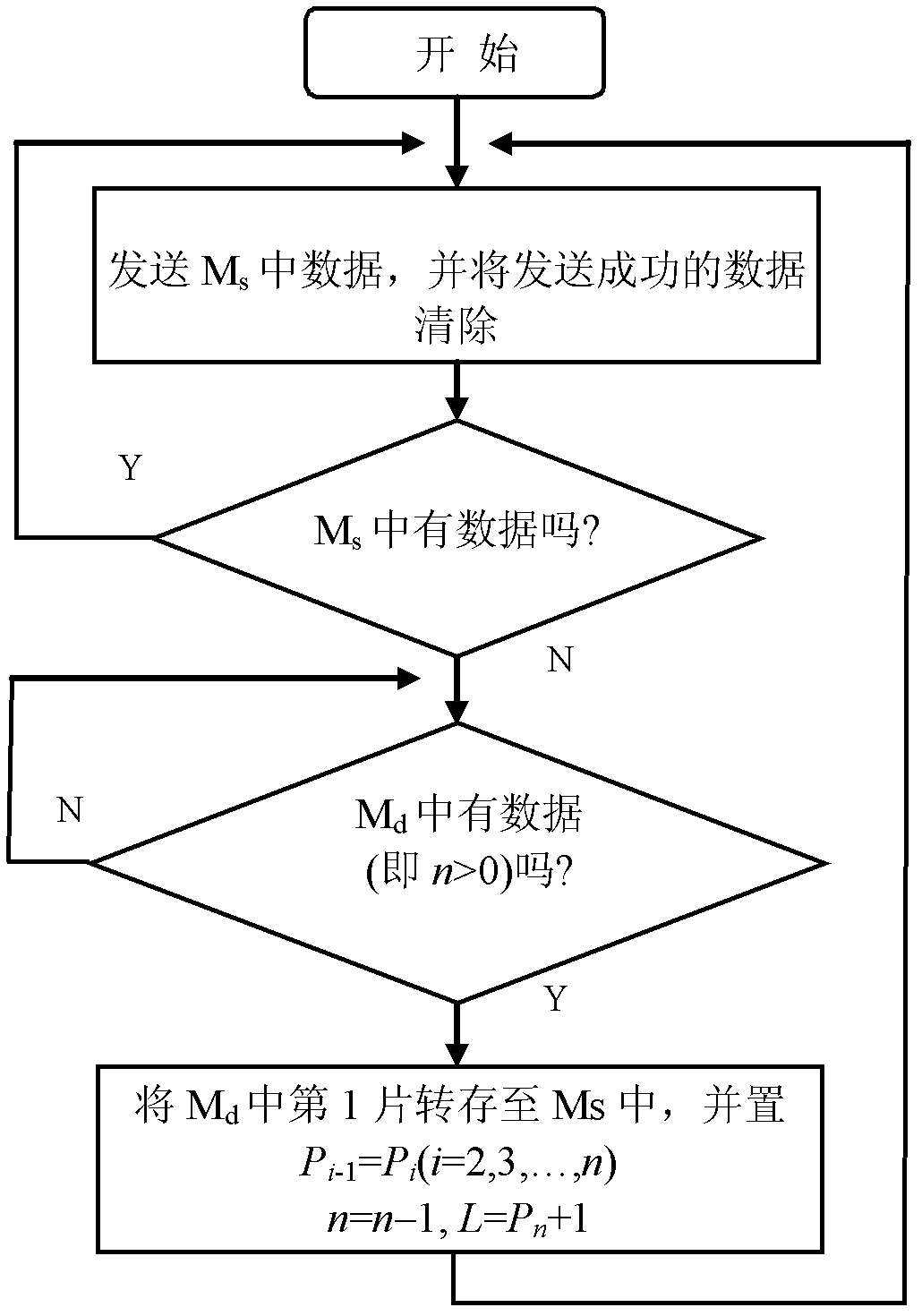
[0065] Set the video code rate output by the video encoder to multiple levels, when the video encoder has video data M f Input to video data buffer M d , detect the video data cache M d The length L of the existing data in, if when L+L f > L H , immediately notify the encoder to lower the video bit rate by one level; but within a period of time after that, when the video data cache receives the video data M f , L+L will still be detected f > L H , which may be caused by the following two reasons: ① Due to the delay in the video code rate reduction, it will take a while for L+L f will not exceed L H ;②The network bandwidth is too small, and the video bit rate must be lowered by 2 levels or above. If it is only the first case, there is no need to lower the bit rate of the video encoding, but for the second case, the video encoder must be notified to continue lowering the video bit rate.
[0066] After notifying the video encode...
Embodiment 3
[0077] Different from Example 2,
[0078] When the network bandwidth becomes larger or the video scene changes tend to be stable in the variable bit rate mode, the video bit rate will become smaller than the network bandwidth, M f Dump data to M d Send out immediately after, M d There is no accumulation of video data. Since the higher the video bit rate, the better the overall picture quality of the video stream, therefore, the control method will increase the video bit rate within the range allowed by the network bandwidth.
[0079] In Example 2, once L+L appears f > L H , the video bit rate will be lowered immediately, and if M d If there is no data in (i.e. L=0), the video code rate will be increased immediately, which may make M d The amount of accumulated data has increased dramatically. Because before M d The lack of data in the middle may be caused by the short-term bandwidth of the unstable network or the short-term stability of the video scene. When the bandwi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com