Selenium-containing unicellular microalgae for animal plankton feeds and method of culturing selenium-containing animal planktons using the same
A zooplankton, single-cell technology, applied in the field of preventing selenium deficiency in larvae and juveniles during post-hatch cultivation during the production of fish seedlings, and can solve the problems of rotifers and unknown effects of hatching larvae and juveniles.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
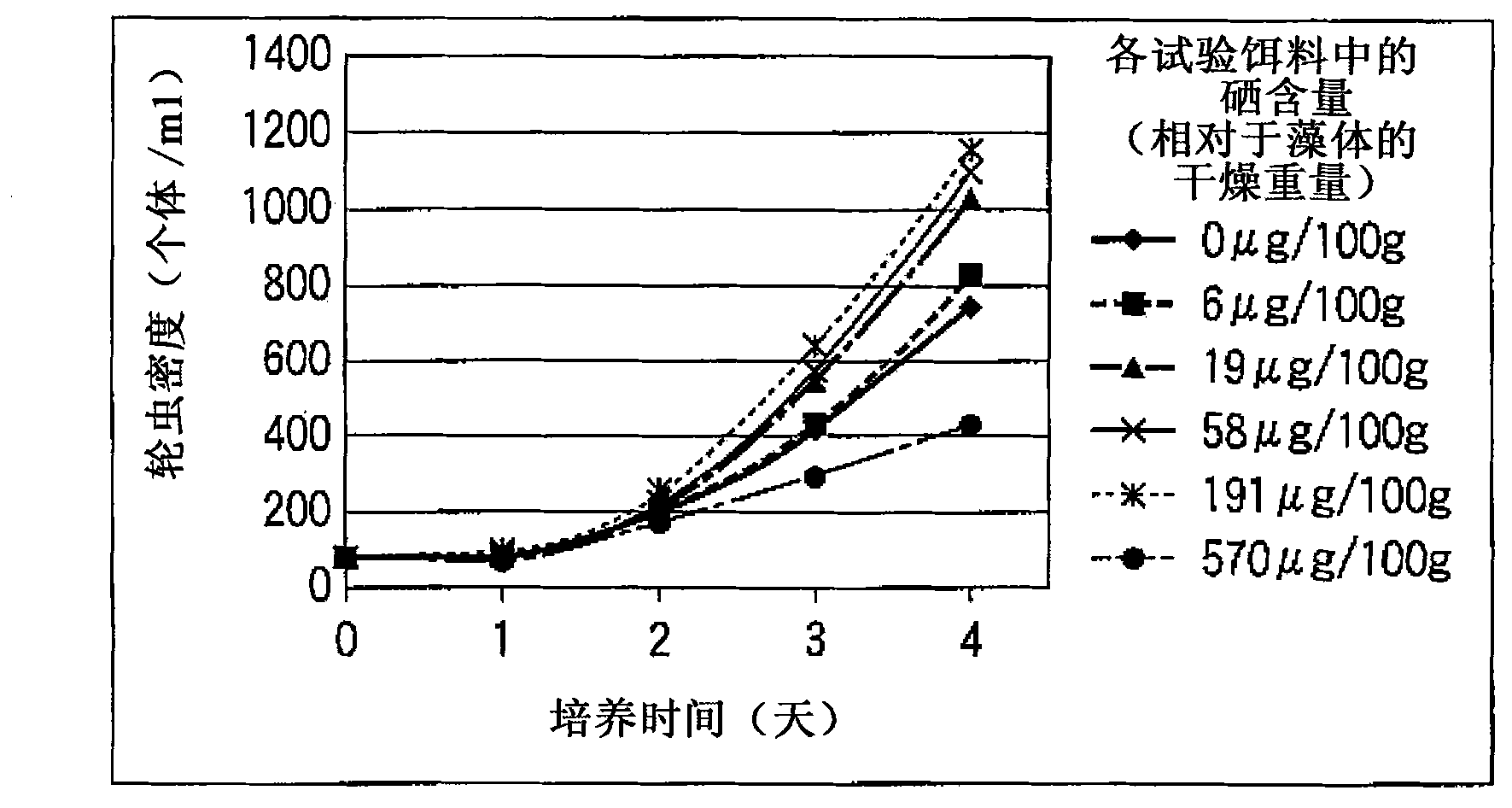
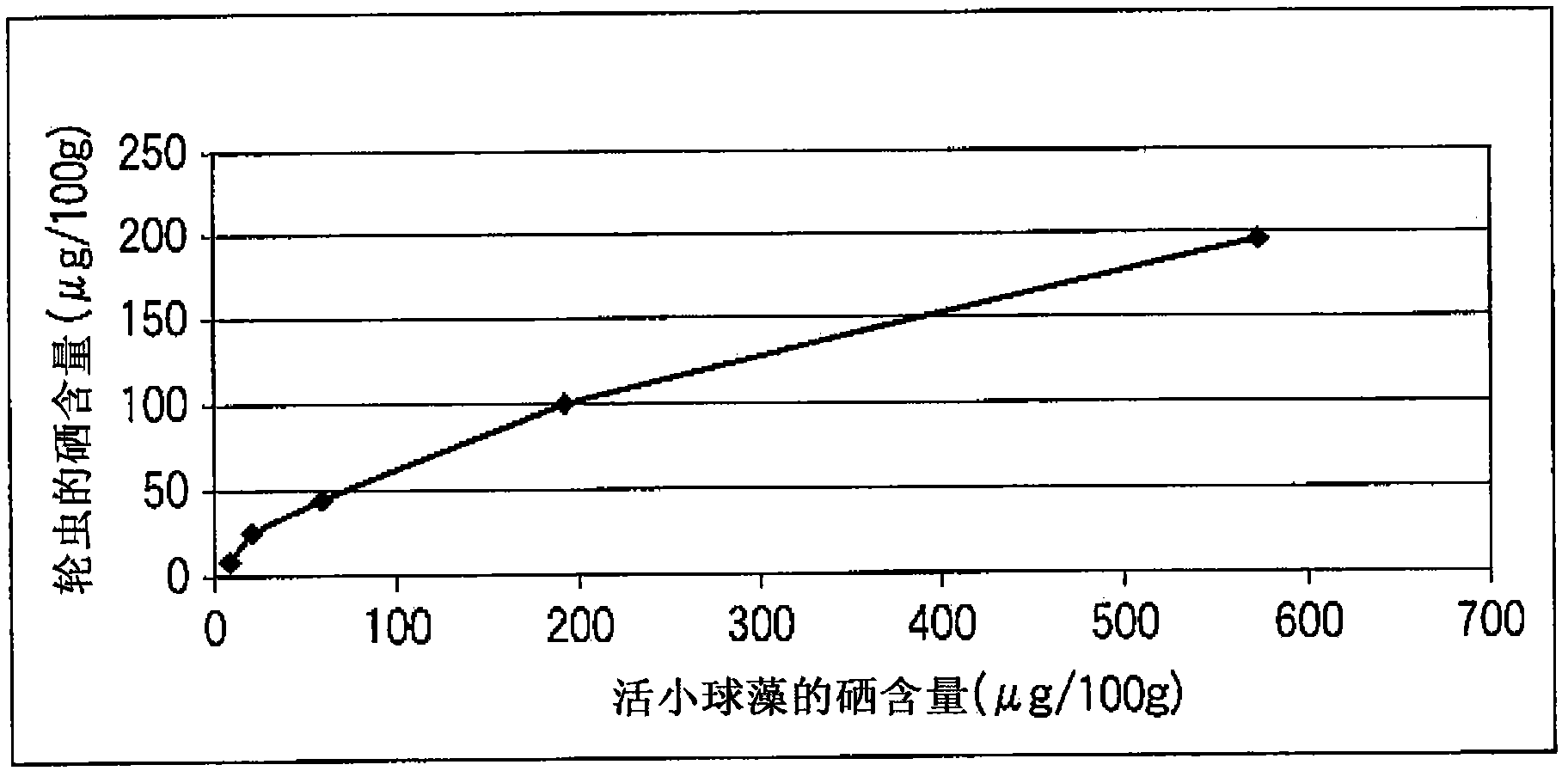
[0045] Production of selenium-containing rotifers using selenium-containing live chlorella as bait
[0046] A 10L fermenter was used for the cultivation of selenium-containing live Chlorella. A slant of a Chlorella vulgaris strain owned by our company was aseptically inoculated into a Sakaguchi flask of a dark culture basal medium, and preculture was performed at 28°C. After the assimilation of glucose was completed, the inoculation was continued in the 10L culture tank, and the aseptic culture of selenium-fortified Chlorella was carried out. The culture conditions are as follows: culture medium volume 6L, temperature 36°C, ventilation 3L / min, pH 7.0, stirring speed 300rpm / min. The composition of the medium used is glucose 80g / L, potassium phosphate 2.0g / L, magnesium sulfate 2.0g / L, Fe·EDTA 4.8mg / L, trace mineral A 5 (×10)1.08ml / L, Vitamin B 12 Add 5.4μg / L, 18μg / L, 54μg / L, 180μg / L and 540μg / L sodium selenite to the basal medium of 2.4mg / L and urea 6.0g / L respectively, and ...
Embodiment 2
[0054] Production of selenium-containing Daphnia using live selenium-containing Nannochloropsis as bait
[0055] The culture of Nannochloropsis containing selenium was carried out using a plate culture tank with a volume of 30 L. From the Nannochloropsis slant held by our company, carry out aseptic inoculation in a 100ml volume small flat bottle containing the bright culture basal medium, in 80ml of the bright culture basal medium, 5% (v / v) CO 2 Two weeks of pre-cultivation were carried out under the conditions of ventilation and stirring, illuminance of 2000 lux, and water temperature of 20°C. When the concentration of algae reached 2g / L (relative to the dry matter), inoculation was continued in the 30L plate culture tank to carry out selenium-enhanced cultivation. The culture conditions are as follows: medium volume 25L, 5% CO 2 Ventilation and stirring 3L / min, illumination 2500 lux, water temperature 20°C. The composition of the medium is potassium nitrate 0.5g / L, sodiu...
Embodiment 3
[0058] Feeding experiment of flounder larvae using selenium-containing rotifers
[0059] A rearing experiment of flounder (Paralichthys olivacens) larvae was carried out using selenium-containing rotifers produced with selenium-containing live chlorella as bait. The breeding conditions are as follows: put 500L of filtered seawater into each 600L circular polycarbonate water tank, the water exchange rate is 100% / day, the water temperature is 17-20°C, the ventilation is 500ml / min, and it accommodates 1.1×10 4 Tail hatching larvae (body length 2.1±0.05mm *1 ). As the test bait, use selenium-containing rotifers (the selenium content is 100 μg / 100g dry weight) to start raising, feed twice a day so that the rotifers density in the breeding water is 6-12 individuals / ml, in a total of 2 water tanks (a In , b), a 17-day feeding test was carried out. As a result, it was observed that the flounder larvae were fed vigorously and grew smoothly during the test period.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com