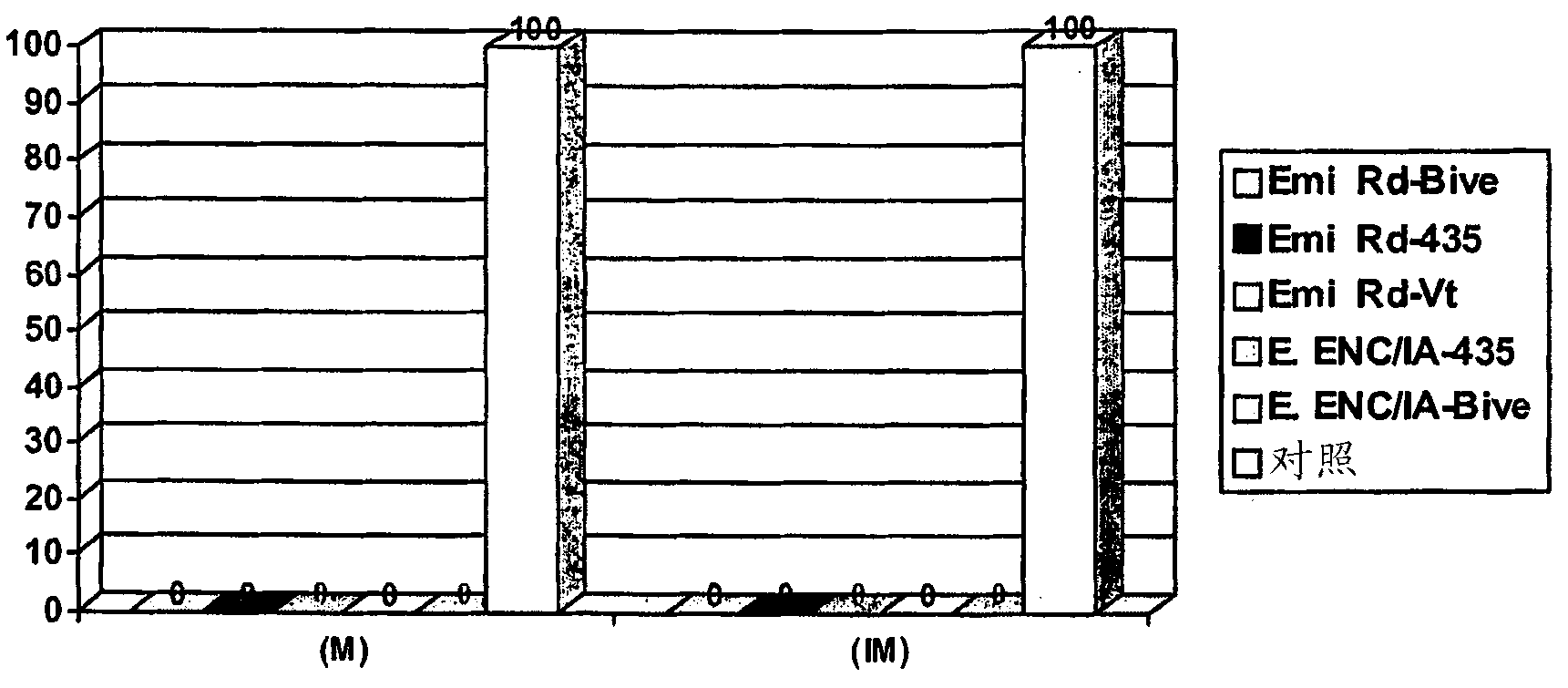
Recombinant Inactivated Virus Vector Vaccine
一种重组疫苗、病毒载体的技术,应用在病毒/噬菌体、疫苗、病毒等方向,能够解决稳定性有限、产业方面复杂、乳液没有优势等问题,达到减少排毒、减少病毒的传播、减少爆发流行的风险的效果
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0076] Generation of Newcastle disease-LaSota vector
[0077] In order to clone the genome of Newcastle disease virus LaSota strain and thus prepare the virus vector, the intermediate vector "pNDV / LS" was first produced. Total viral RNA of Newcastle disease LaSota strain was extracted by triazole method. cDNA (complementary DNA) was synthesized from the purified RNA of the viral genome using the previously purified total RNA as a template. To clone all genes of the Newcastle disease genome (15,183 base pairs (bp)), seven fragments with "overlapping" ends and cohesive restriction sites were amplified by PCR. Fragment 1 (F1) comprises nucleotides (nt) 1-1755, F2 comprises nt 1-3321, F3 comprises nt 1755-6580, F4 comprises nt 6,151-10,210, F5 comprises nt 7,381-11,351 , F6 contains nt 11,351-14,995 and F7 contains nt 14,701-15,186. In the cloning vector pGEM-T, standard ligation techniques were used to assemble the seven fragments to reconstruct the Newcastle disease LaSota ge...
Embodiment 2
[0079] Cloning of HA Gene from VIA Subtype H5N2435 Strain 435
[0080] The total virus RNA was extracted by triazole method in order to clone the HA gene of VIA 435 strain. The purified total RNA was then used to synthesize cDNA (complementary DNA), and the HA gene of the IA virus was amplified with specific oligonucleotides by PCR technique. Then, the HA gene of 435 was inserted into the pGEM-T vector using standard cloning techniques to obtain a plasmid: p-GEMT-435.
Embodiment 3
[0082]Cloning the IA 435HA gene with the SacII site of the pNDV / LS vector to make a plasmid: pNDV / LS-435
[0083] A. Prepare the intermediate vector pSacIIGE / GS:
[0084] The intermediate vector pSacIIGE / GS was constructed to introduce the transcribed sequence GE / GS of Newcastle disease at the 5' end of the HA 435 gene. The method was to perform PCR initial amplification of the GE / GS sequence using the Newcastle disease genome as a template, and then these sequences were Insert into pGEM-T.
[0085] B. Subcloning the HA gene into the pSacIIGE / GS vector:
[0086] Plasmid pGEMT-435 was digested with Hpal-Ndel and cloned into pSacIIGE / GS to obtain plasmid pSacIIGE / GS-HA435.
[0087] C. Subcloning GE / GS-HA435 into pNDV-LS vector
[0088] Two plasmids: pSacIIGE / GS-HA435 and pNDV / LS were digested with SacII, the digested products were purified, the GE / GS-HA435 region was purified and inserted into the SacII site of pNDV / LS, and an infectious clone was obtained: pNDV / LS- 43...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com