Method for realizing endoscopic minimal invasive surgery simulated training 3D platform system
A technology of minimally invasive surgery and simulation training, which is applied in the field of computer simulation, can solve the problems of single modeling method, large difference between simulation effect and actual situation, and insufficient support of 3D control terminal, etc., and achieves convenient use, wide application range, and simulation effect precise effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
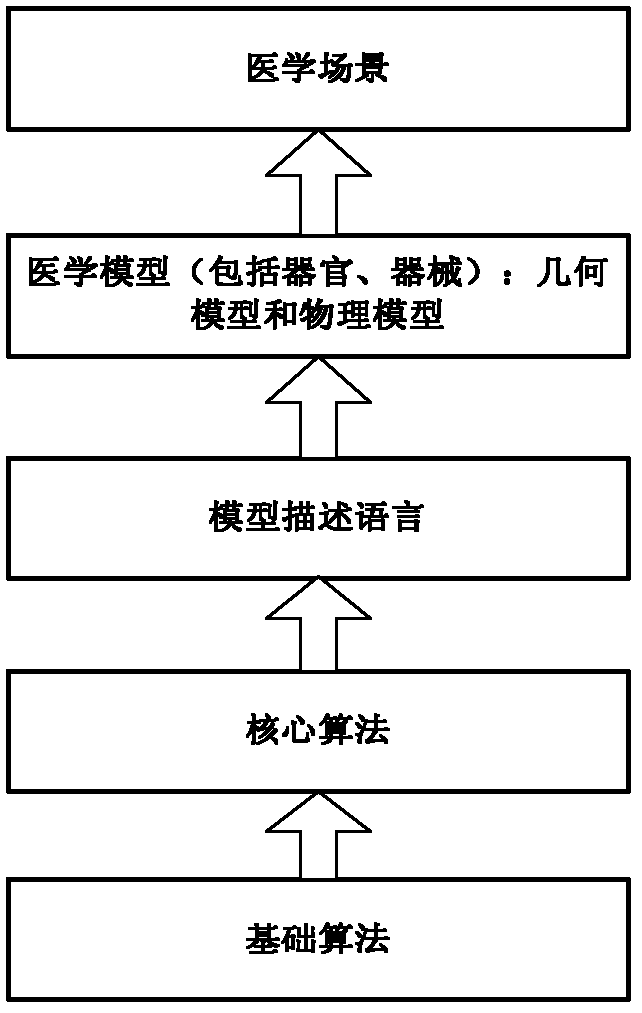
[0033] The realization method of the 3D platform system for endoscopic minimally invasive surgery simulation training includes the following contents:
[0034] Step 1: Build the basic system component library: use euler, euler_ordered, runge, runge_4thorder algorithms to build a 3D model component library, use quasi, quasi_ordered, bogus, FSA, FSAF to build a model computing component library, and use perlin noise to build a simulation map component library.
[0035] In this embodiment, euler and euler_ordered algorithms are used to build point, line and surface component libraries, and quasi and quasi_ordered algorithms are used to build calculation methods for models (such as soft bodies, rigid bodies, etc.) under different behaviors.
[0036] Use the perlin noise method to build a simulation map library. The method is to first fix the color of some points, smooth the color in the middle of these fixed points, generate several smooth noises of different frequencies, and then ...
Embodiment 2
[0060] The realization method of the 3D platform system for endoscopic minimally invasive surgery simulation training includes the following contents:
[0061] The first step: building the system basic component library: In this embodiment, use runge, runge_4thorder algorithm to build point, line, surface component library, use bogus, FSA, FSAF algorithm to build model (such as soft tissue, rigid body, etc.) under different behaviors The calculation method used.
[0062] The second step: use the system basic component library to build the core algorithm to realize the core functions of the 3D platform. In this embodiment, the collision detection adopts the AABB bounding box (Axis Aligned Bounding Box) algorithm, mainly through the point, line, and surface component library to build a binary tree algorithm. accomplish.
[0063] Step 3: The medical model description language is a script language, and this step is the same as that in Embodiment 1.
[0064] Step 4: Call various ...
Embodiment 3
[0076] The implementation method of the 3D platform system for endoscopic minimally invasive surgery simulation training includes the following contents: the first step: building the system basic component library: in this embodiment, the point, line and surface component library are constructed with euler, euler_ordered, runge, runge_4thorder algorithms , using quasi, quasi_ordered, bogus, FSA, FSAF algorithms to construct the calculation methods adopted by the model (such as soft tissue, rigid body, etc.) under different behaviors.
[0077] Use the perlin noise method to build a simulation map library. The method is to first fix the color of some points, smooth the color in the middle of these fixed points, generate several smooth noises of different frequencies, and then add them together. In order to ensure the frequency of noise generation, generally through Change the number of fixed points. If there are more fixed points, the noise will be relatively messy and the freque...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com