Method for suppressing side lobes of sum beams and difference beams of planar phased array only by utilizing one kind of analogue weighting
A technology of sidelobe suppression and plane phase, which is applied in directions such as direction finders using radio waves, components of radio wave directors, space launch diversity, etc., and can solve problems such as unsatisfactory sidelobe suppression effects and unsuitable planar arrays
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
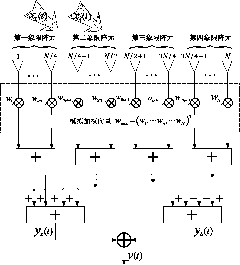
[0045] Specific implementation mode one: the following combination figure 1 with figure 2 Describe this embodiment, the planar phased array and beam and difference beam sidelobe suppression method using only one analog weighting described in this embodiment:
[0046] For a planar phased array composed of N array elements, each array element is set on a rectangular grid on the xoy plane, including Nx×Ny=N array elements, and they are equally spaced in the x direction and the y direction. Indicates the elevation angle and azimuth angle, and the array beam points to The first array element is located at the origin of the coordinates as the reference array element, and the coordinates of the nth array element are (x n ,y n ), wherein n=1,..., N, said N is a multiple of 4;
[0047] The planar phased array is equally divided into four quadrants, and the serial numbers of each array element in the first quadrant are set as The serial numbers of each array element in the seco...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0056] Specific implementation mode two: this implementation mode further describes specific implementation mode one, w ana The function of is to simultaneously suppress the sidelobe of the sum beam and the difference beam, and its value should have the best sidelobe suppression effect on the sum beam and the difference beam. To this end, to determine the simulated weight w ana , assuming that there is interference located in the entire sidelobe area of the sum beam and the difference beam, the optimal adaptive filtering is performed on the interference, and the adaptive weight is taken as w ana . However, the sidelobe suppression effect of this analog weighting is not particularly ideal, so digital weighting is further used at the sub-array level to improve the sidelobe suppression effect.
[0057] Let the hypothetical interference x ∑ (t) and x Δ (t) The side lobe regions of the sum beam and the difference beam are incident on the array respectively, and their powers a...
specific Embodiment approach 3
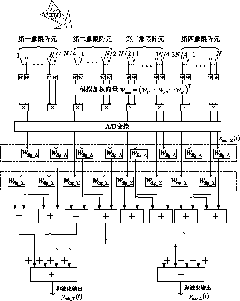
[0107] Specific implementation mode three: the following combination image 3 Describe this embodiment. This embodiment will further explain Embodiment 1. The analog weighting method given in Embodiment 1 can suppress the side lobes of the sum beam and the difference beam at the same time, but the effect is not very ideal. Therefore, it is necessary to The sub-array stage further uses digital weighting to improve sidelobe suppression. The starting point for determining digital weighting is to make it the closest to Taylor or Bayliss weighting in the mean square sense.
[0108] Therefore, the method of the present invention further increases sub-array level digital weighting processing, see image 3 The specific process is described as:
[0109] For a planar phased array composed of N array elements, each array element is set on a rectangular grid on the xoy plane, including Nx×Ny=N array elements, and they are equally spaced in the x direction and the y direction. Indicate...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com