Flow control switch
A flow control and switch technology, applied in the direction of valve lift, valve details, engine components, etc., can solve the problems of high price of solenoid valve, large volume of float valve, low reliability, etc., and achieve low cost, small size and reliable operation Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
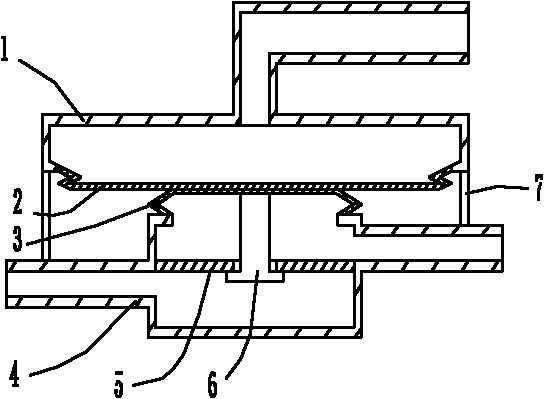
[0027] Such as figure 1 As shown, the flow control switch of this embodiment has a bellows 1 , a valve body 4 and a bracket 7 . The valve seat 5 is located in the valve body 4; the valve body 4 is formed with two interfaces for communicating with the fluid pipeline, the valve seat 5 is fixed in the valve body 4 and is located between the two interfaces in the valve body 4, and the valve The seat 5 is formed with a fluid passage hole. There is an interface on the bellows 1 to connect with the pressure source, as well as the elastic element I2; the valve body 4 has the elastic element II3, the valve seat 5 and the valve core 6, and two interfaces connecting the fluid pipeline; the bracket 7 Connect bellows 1 and valve body 4 together. When the pressure source pressure rises, the elastic element I2 protrudes through the elastic element II3 to push the valve core 6 away from the valve seat, and the valve opens; when the pressure source pressure drops, the elastic element I2 is d...
Embodiment 2
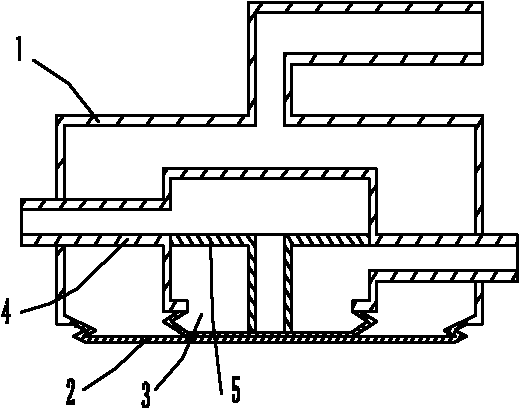
[0029] Such as figure 2 As shown, the flow control switch of this embodiment has a bellows 1 , a valve body 4 and a valve seat 5 . There is an interface on the bellows 1 to connect with the pressure source, and there are elastic elements I2 and elastic elements II3; there are elastic elements II3 and valve seat 5 in the valve body 4, and there are two interfaces connected to the fluid pipeline; the valve body 4 Placed in capsule 1. The fluid valve in this embodiment does not need a valve core, and the valve seat can be directly closed by a diaphragm (elastic element). The fluid passage hole on the valve seat 5 is connected with an extension tube, and the extension tube is pushed against the elastic element II3 and closed or opened by the fluctuation of the elastic element II3 to realize the closing or opening of the fluid valve. When the pressure source pressure rises, the elastic element I2 protrudes and moves up through the elastic element II3 to close the opening of the ...
Embodiment 3
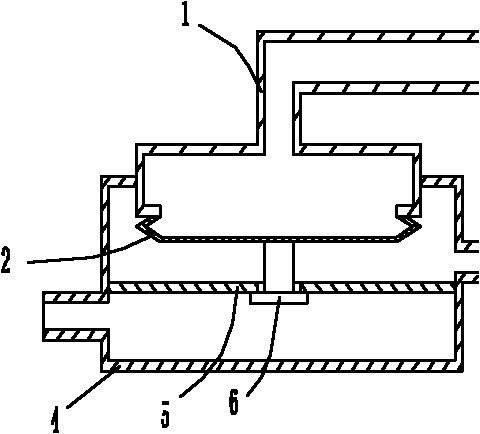
[0031] Such as image 3 As shown, the flow control switch of this embodiment has a bellows 1 and a valve body 4 . The valve seat 5 is located in the valve body 4; the valve body 4 is formed with two interfaces for communicating with the fluid pipeline, the valve seat 5 is fixed in the valve body 4 and is located between the two interfaces in the valve body 4, and the valve The seat 5 is formed with a fluid passage hole. There is an interface on the bellows 1 to connect with the pressure source, and an elastic element I2; the bellows 1 is placed in the valve body 4 . When the pressure source pressure rises, the elastic element I2 protrudes to push the valve core 6 away from the valve seat, and the valve opens; when the pressure source pressure drops, the elastic element I2 sinks to drive the valve core 6 to press the valve seat, and the valve closes.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com