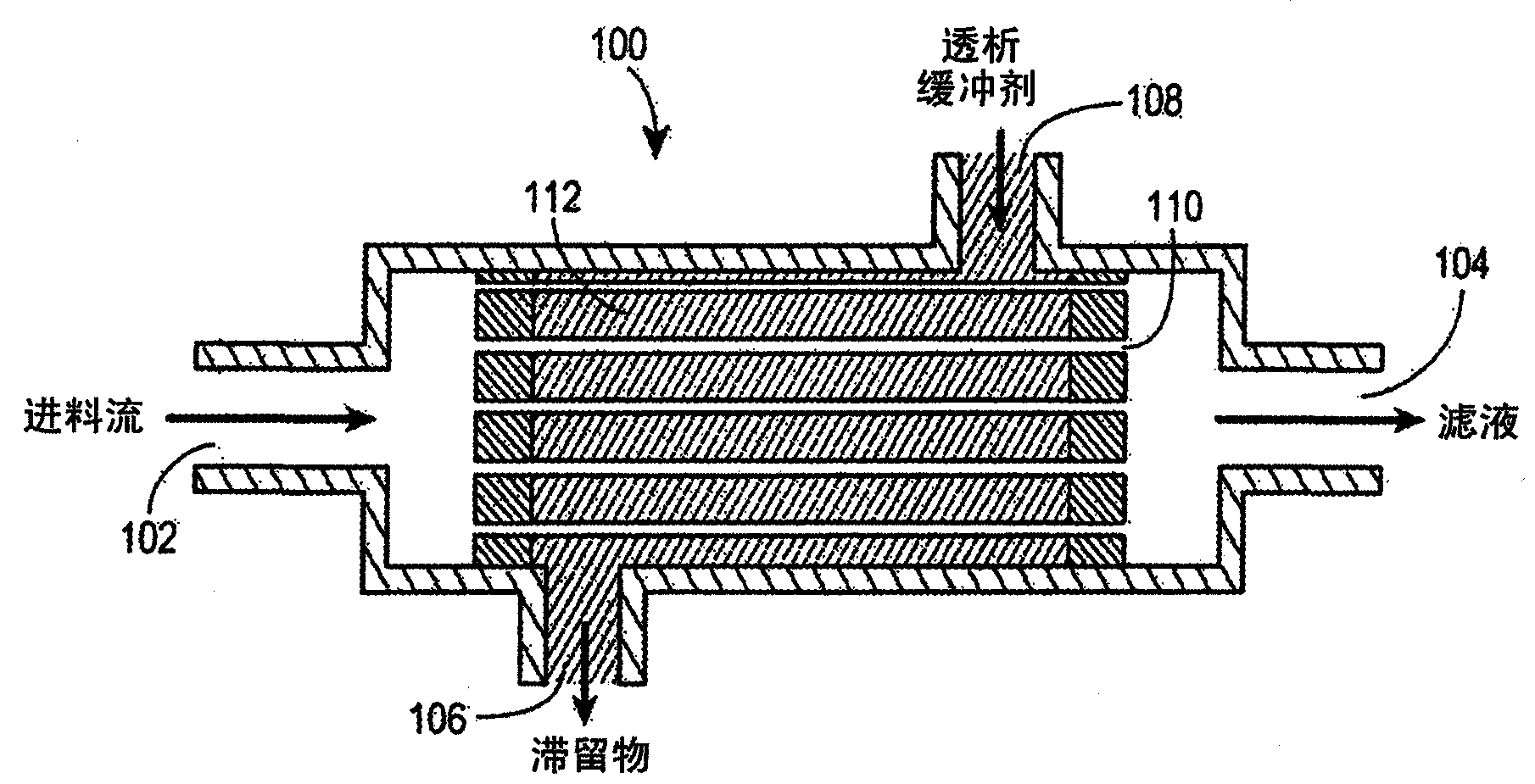
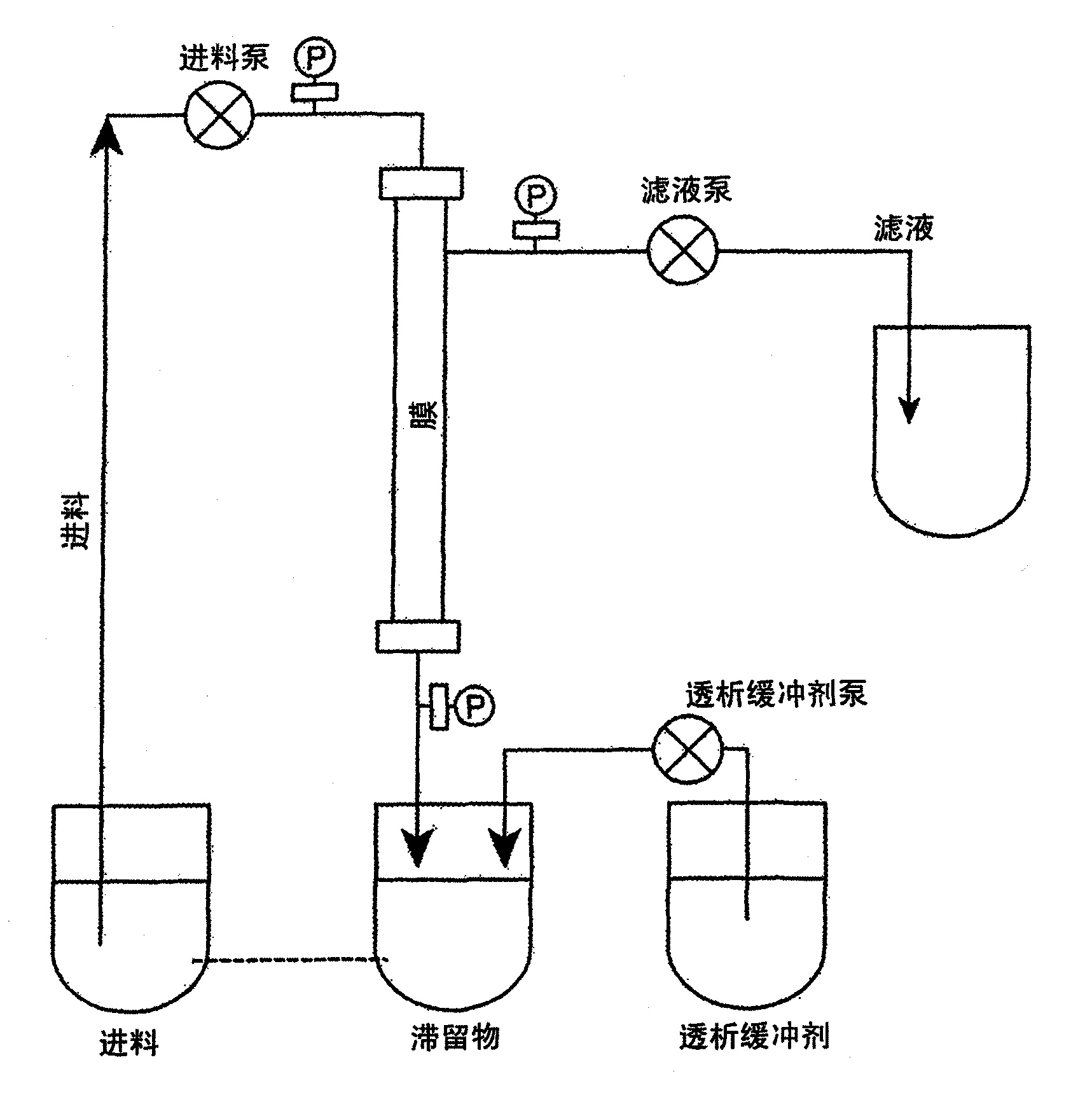
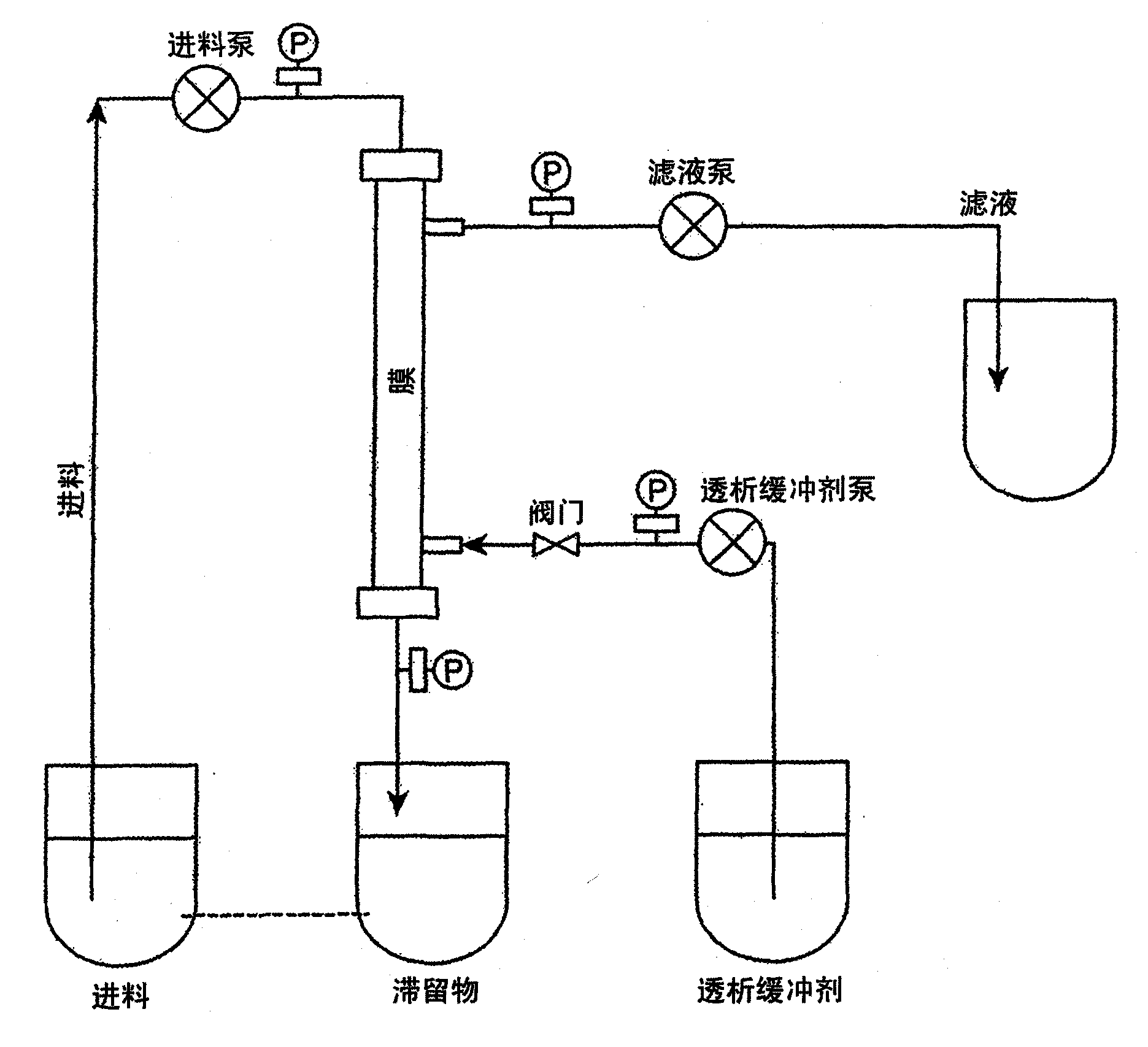
Method of concentrating shear-sensitive biopolymers using hollow fibre membranes
A biopolymer, anti-shear technology, applied in the field of biopolymers, can solve the problems of reducing shear stress, not providing alternative methods, reducing and other problems, and achieving the effect of avoiding protein precipitation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0046] Four experiments were performed using vWF as a shear sensitive biopolymer and hollow fiber dialysis components. The hollow fiber dialysis module has 3000cm 2 Membrane surface area, 30 μm thick membrane, 100 mm fiber length and 200 μm fiber inner diameter. The membrane material is polyethersulfone. The concentrations of the feed streams were 0.7 grams of vWF protein per liter (gvWF / L), 0.56 gvWF / L, 0.39 g vWF / L, 0.27 g vWF / L. The concentrations of the retentate after concentration were 2.52 g vWF / L, 4.59 g vWF / L, 2.23 g vWF / L and 1.26 g vWF / L, respectively. The experiment took approximately 2 to 4 hours to complete.
[0047] The solution buffer in the feed stream was 20 mM (millimolar) HEPES and 150 mM NaCl buffer, pH 7.4 at room temperature. The dialysis buffer was 20 mM citrate and 15 mM glycine buffer, pH 7.3 at room temperature. The HEPES concentration shrunk from greater than 15 mM in the feed to less than 1 mM in the retentate.
[0048] Table 2: Data for Tria...
Embodiment 2
[0051] Two experiments were performed using vWF as a shear sensitive biopolymer and a hollow fiber dialysis module. The hollow fiber dialysis module has 7000cm 2 Membrane surface area, 30 μm thick membrane, 100 mm fiber length and 200 μm fiber inner diameter. The membrane material is polyethersulfone. Experiments were performed at a feed flow rate of 300 ml / min, an initial volume reduction rate of 2 L / hr and a dialysis rate of 5 L / hr. The shear rate applied by the feed flow rate is approximately 571 seconds -1. Feedstream concentrations were about 0.18 g vWF / L and about 0.22 g vWF / L. The retentate concentrations were about 0.88 g vWF / L and about 0.95 g vWF / L, respectively.
[0052] The solution buffer in the feed stream was 20 mM (millimolar) HEPES and 150 mM NaCl buffer, pH 7.4 at room temperature. The dialysis buffer was a salt-free, 20 mM citrate and 15 mM glycine buffer, pH 7.3 at room temperature. The HEPES concentration shrunk from greater than 15 mM in the feed t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com