Method for structuring quasi-cyclic low-density parity check (QC-LDPC) code based on extrinsic message degree (EMD)
A low-density parity and construction method technology, applied in the field of communication, can solve the problems of large EMD and large stop set, and achieve the effects of reduced impact, effective construction method, and good error correction performance.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
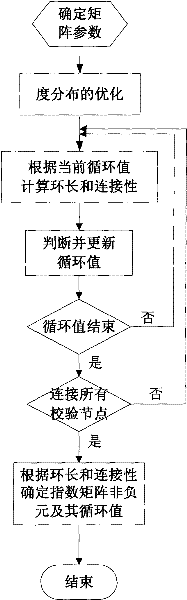
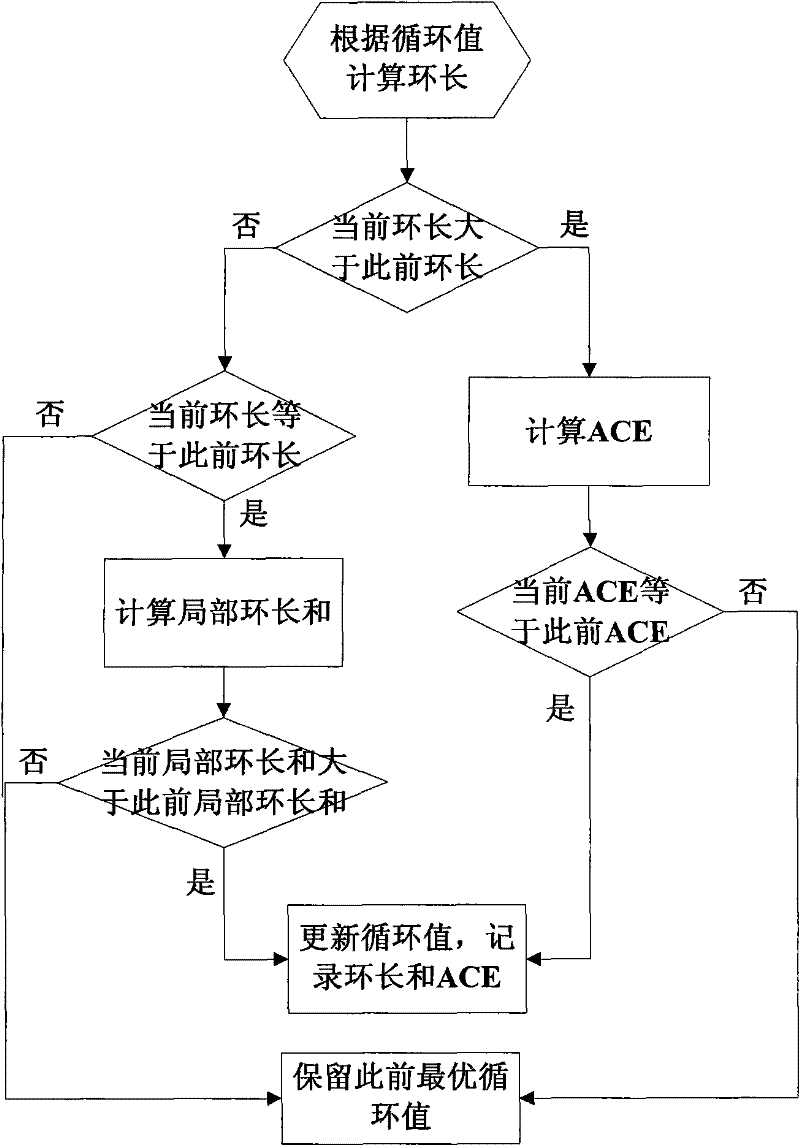
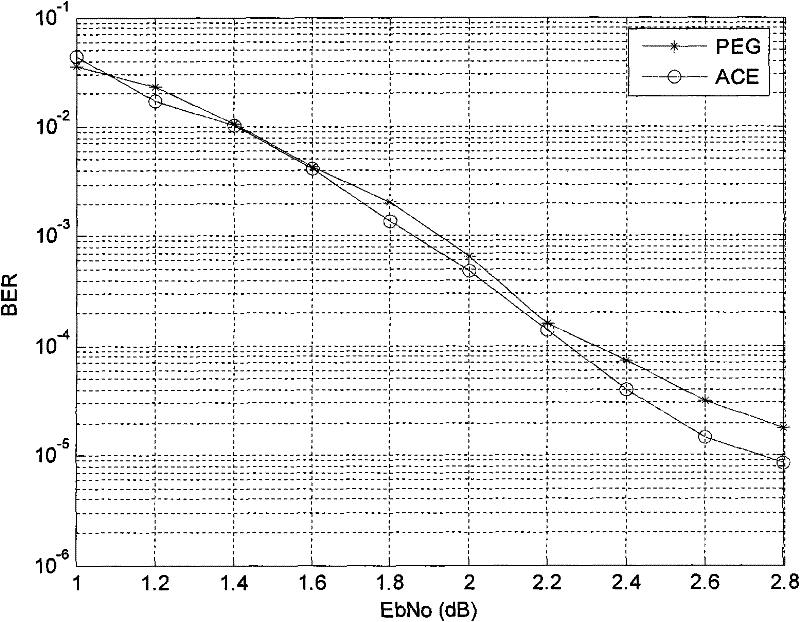
[0042] Below, refer to the attached Figure 1~4 The construction method of the quasi-cyclic low-density parity-check code of the present invention is described in detail.
[0043] like figure 1 Shown, the present invention constructs QC-LDPC code parity check matrix H, comprises the following steps:
[0044] Step 100: Determine the parameters of the coding matrix, such as code length, code rate, degree distribution and other parameters.
[0045] Wherein, in step 100, the parameters of the encoding matrix include the size of the encoding matrix, the size p of each block matrix, and the degree distribution. The code length and specific code rate determine the size of the coding matrix, and the only restriction is that it should be an integer multiple of p.
[0046] In addition, for irregular LDPC codes, a high-quality degree distribution can ensure that the constructed codewords have high anti-noise performance. Therefore, the first step in constructing high-performance LDPC ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com