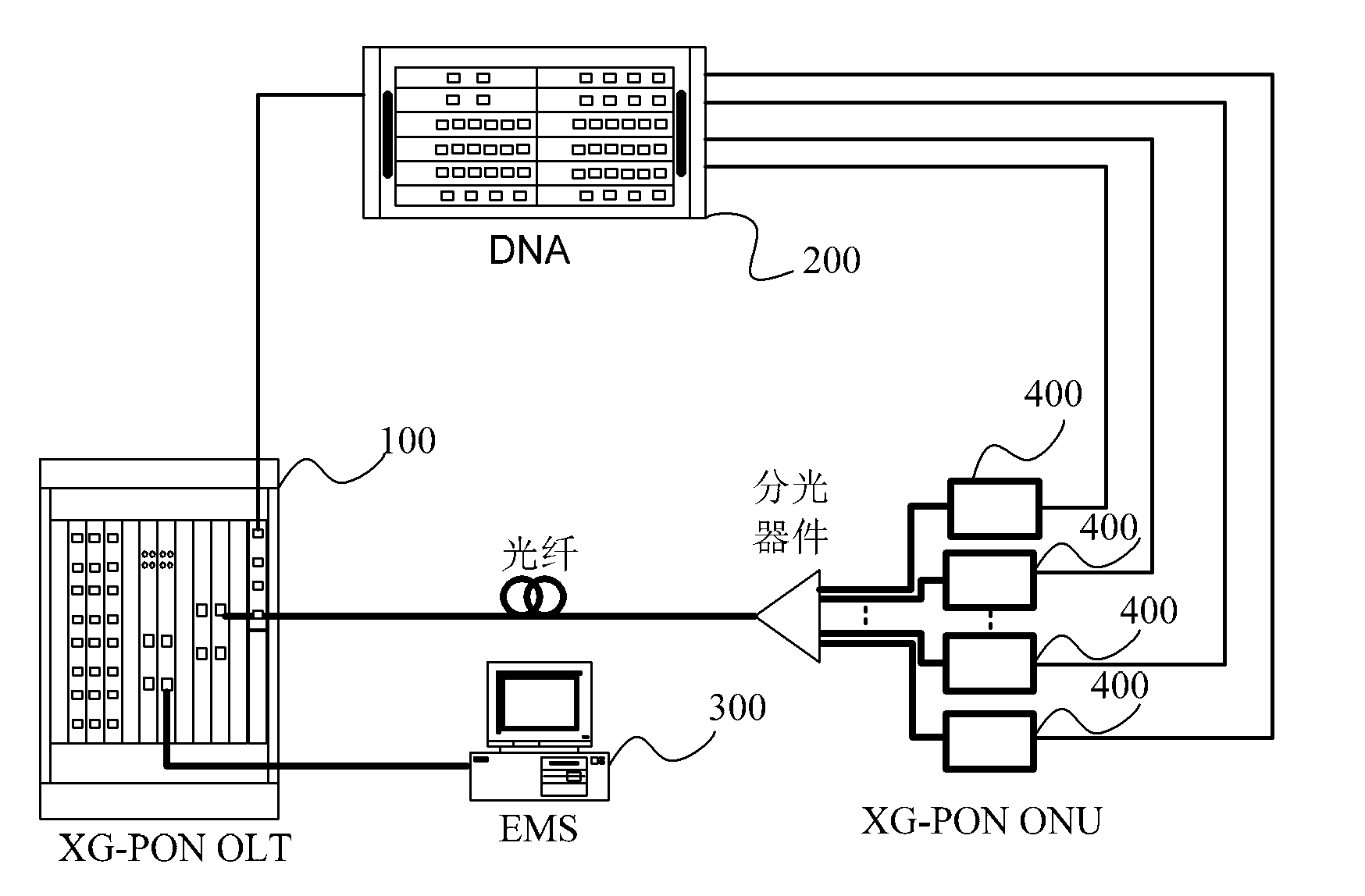
Method and device for distributing dynamic bandwidth of passive optical network
A dynamic bandwidth allocation, passive optical network technology, applied in the field of communication, can solve the problems of inability to achieve rapid dynamic bandwidth adjustment, the inability to achieve optimal bandwidth utilization, and the impact of normal services on the existing network, so as to improve QoS and achieve optimization. , the effect of reducing the probability of packet loss
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
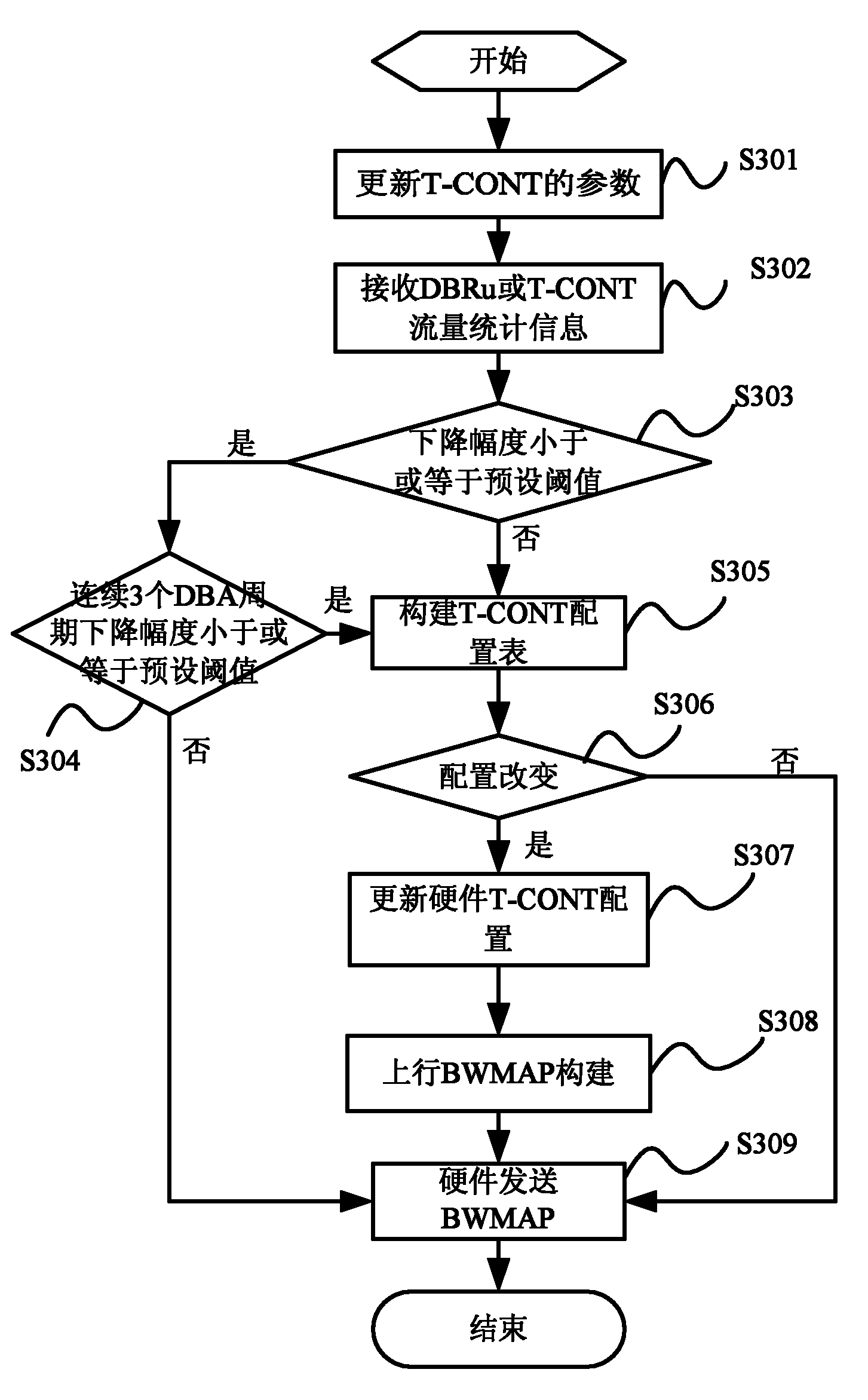
[0042] In the embodiment of the present invention, a DBA cycle is taken as an example to describe the flow of dynamic bandwidth allocation performed by the OLT in the passive optical network.
[0043] image 3 It is a flowchart according to an embodiment of the present invention, such as image 3 As shown, it mainly includes the following steps:
[0044] Step S301: When the current DBA cycle arrives, the OLT updates the parameters of the T-CONT according to the current user's SLA data, including: setting the T-CONT type, configuring the bandwidth value, etc.;
[0045] Step S302: The OLT outputs the bandwidth request of the T-CONT according to the DBRu information input by the ONU or the traffic statistics information of the T-CONT, and the bandwidth request carries the bandwidth required for the next stage of the T-CONT;
[0046] Among them, in the SR-DBA mode, the OLT calculates the bandwidth required for the next stage of the T-CONT according to the DBRu value reported by ...
Embodiment 2
[0056] The embodiment of the present invention explains the flow of the OLT constructing the T-CONT configuration table in Embodiment 1. In the embodiment of the present invention, the OLT needs to judge the type of the T-CONT during the process of constructing the T-CONT configuration table, such as TYPE 1 / 2, directly construct the T-CONT table and enter the hardware T-CONT configuration process; if it is TYPE3 / 4 / 5, further configuration of T-CONT is required, including priority (CLASS) and weight (WEIGHT ) configuration to further subdivide the bandwidth and further improve the bandwidth scheduling performance in the above-mentioned type of T-CONT.
[0057] Such as Figure 4 As shown, in Embodiment 2 of the present invention, the OLT constructs the T-CONT configuration table according to the following steps:
[0058] Step S401: The T-CONT configuration module of the OLT receives the uplink bandwidth request output by step S301 of Embodiment 1, and parses parameters such as ...
Embodiment 3
[0065] In the embodiment of the present invention, the DBA is in SR-DBA mode, and the bandwidth required by the OLT to obtain the next stage of the T-CONT is less than the bandwidth allocated in the previous DBA cycle, and the difference between the two is greater than the above-mentioned preset threshold, and the bandwidth of the T-CONT The type is Type1, combined with image 3 and Figure 4 , OLT realizes dynamic bandwidth allocation in the present embodiment and comprises the following steps:
[0066] Step S501: When the current DBA cycle arrives, the OLT updates the parameters of the T-CONT according to the current user's SLA data, including: setting the T-CONT type, configuring the bandwidth value, etc.;
[0067] Step S502: The OLT receives the DBRu information reported by the ONU, and outputs the bandwidth request of the T-CONT according to the DBRu information, and the bandwidth request carries the bandwidth required for the next stage of the T-CONT;
[0068] Step S50...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com