Construction method for controlling rock pillar type rock burst in process of double-head tunneling deep-buried tunnel transfixion
A construction method and tunnel technology, applied in tunnels, earthwork drilling, mining equipment, etc., can solve the problems of potential rockburst risk increase and potential rockburst risk enhancement, so as to improve safety, construction progress is not affected, The effect of eliminating the risk of rockburst of rock pillar type
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0026] Embodiment 1: as figure 1 As shown, this embodiment is mainly aimed at excavating tunnels with a diameter less than 8m, and the rock burst during the penetration process can be effectively controlled by the following measures:
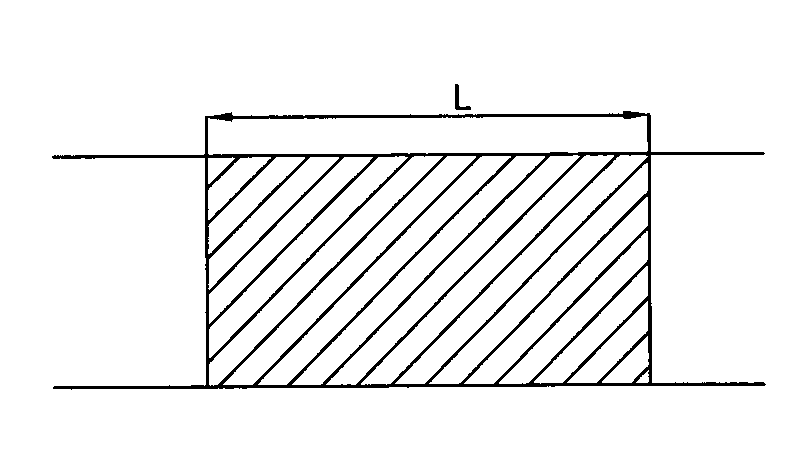
[0027] a. When the distance L between the two tunnel faces is 50m, stop the excavation work on one tunnel face, and change the excavation at both ends to single-head excavation.
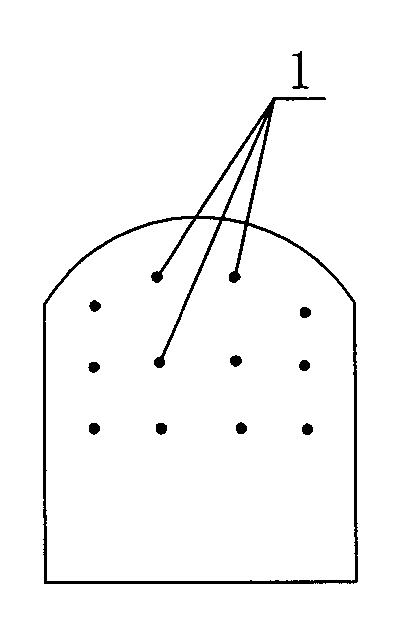
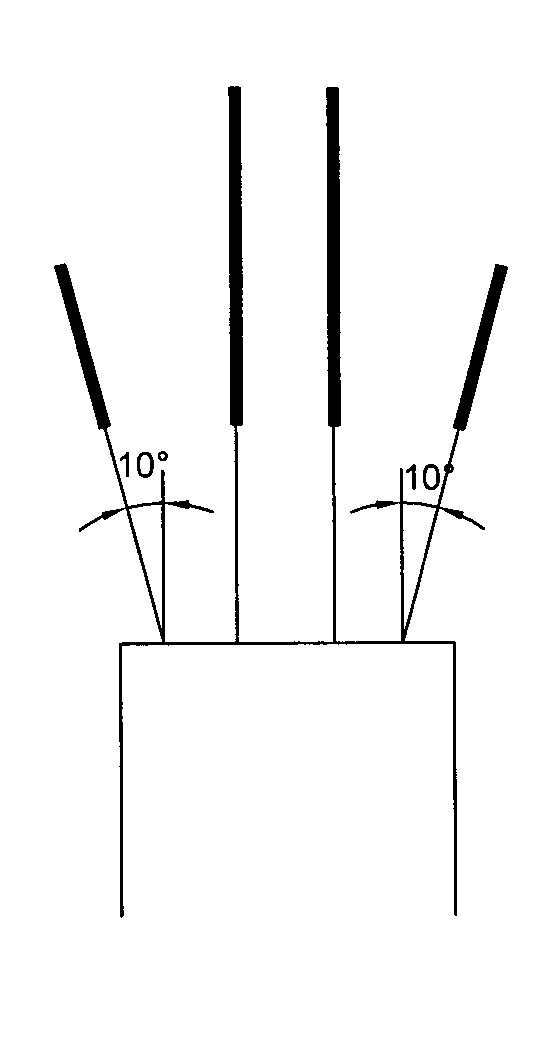
[0028] b. Complete the drilling work of conventional tunneling blasting and stress relief blasting in sequence, and complete the charging and sealing of each blasting hole after drilling; the hole diameter, hole depth and charge of conventional tunneling blasting holes should meet the requirements of tunneling. The blasting footage is 1.8m-2m / blasting cycle requirements, that is, the footage of one blasting cycle is 1.8-2m (the same below); the layout of stress relief blasting hole 1 is as follows: Figure 2-Figure 4 As shown, there are three rows of upper, middle and...
Embodiment 2
[0032] Embodiment 2: as Figure 5 As shown, this embodiment is mainly aimed at excavating tunnels with a diameter greater than 8m. The difference between it and Embodiment 1 is that the pilot tunnel 2 is used and the layout of the stress relief blast hole 1 is adjusted. The specific measures are as follows:
[0033] a. When the distance L between the two tunnel faces is 80m, stop the excavation work on one tunnel face, change the excavation at both ends to single-head tunneling, and excavate a pilot hole on the upper face of the single-head tunneling 2 , in order to facilitate the control of rockbursts, the cross-section of the pilot tunnel 2 in this example is arranged in the shape of a city gate with a diameter of 5m*5m.
[0034] b. Complete the drilling work of the conventional excavation blasting and stress relief blasting of the pilot tunnel 2 in sequence, and complete the charging and sealing work of each blasting hole after the drilling is completed; the aperture, hole ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com