Production method of Japanese pepper sprouts
A production method and technology for sansho sprouts, applied in the application, cultivation, agriculture and other directions, can solve the problems of less market sales, short supply time, unable to meet the living needs of the masses, etc., and achieve the effect of satisfying living needs and long supply period
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0027] Embodiment 1 Natural low temperature breaks dormancy, moves into greenhouse to produce pepper buds
[0028] When cultivated in the open field, thornless sansho and Asakura sansho lose their leaves in mid-November and enter a dormancy period of about 70 days. After the dormancy period expires, after the Sansho pepper is moved into the greenhouse, the temperature is controlled at 20-25°C during the day, 13-18°C at night, and the air humidity is 60%-80%. Generally, germination begins in about 10 days, and the length of the pepper buds can reach 100% after 15 days of growth. 7 ~ 10cm for harvesting. Due to the different temperature changes in winter every year, the time required for sansho to break dormancy varies, and the time for greenhouse cultivation is not easy to determine, and the time for picking pepper buds is also uncertain. In the present embodiment, it takes about 80 days in total from the leaves falling in mid-November to the germination of pepper buds in the ...
Embodiment 2
[0029] Embodiment 2 Artificial low temperature treatment breaks dormancy and carries out greenhouse pepper bud production technology
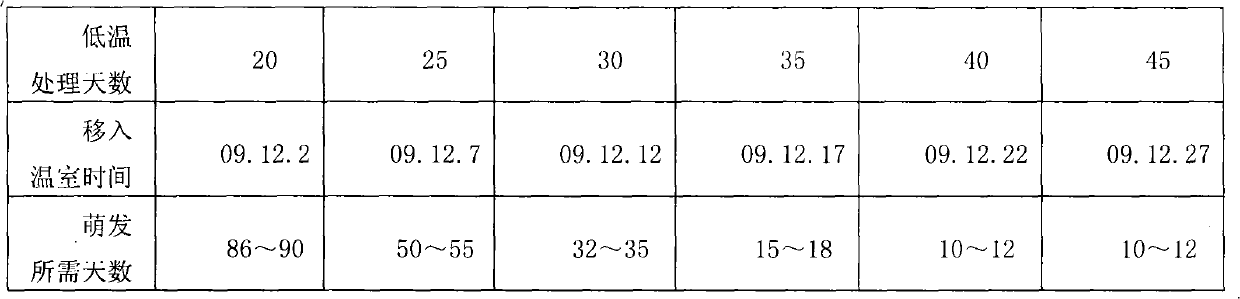
[0030] In November 2009, one-year-old Sansho grafted seedlings were planted in pots, among which, Sansho Asakura and Sansho Hana were half and half. The potting soil is 3 parts of pastoral soil and 1 part of cow dung, and it should be watered thoroughly after planting. Moved into the cold storage on November 12, the temperature of the cold storage is 1-6°C, the humidity is 50%-60%, the light time is 8-10 hours, and the dark time is 14-16 hours. Starting from December 2, 60 pots were moved to the greenhouse every 5 days, including half of Asakura Sansho and half of Sansho without thorns. The temperature in the greenhouse is 20-25°C during the day, 13-18°C at night, and the air humidity is 60%-80%. Observe the germination of pepper buds daily. The germination standard is that the scales at the top of the leaf buds are cracked and green. Table...
Embodiment 3
[0034] Embodiment 3 Artificial low temperature and hormone treatment break dormancy and carry out greenhouse pepper bud production technology
[0035] In November 2009, one-year-old sansho grafted seedlings were planted in flower pots, of which half of Asakura sansho and half of thornless sansho were used. The potting soil is 3 parts of pastoral soil and 1 part of cow dung, and it should be watered thoroughly after planting. Moved into the cold storage on November 12, the temperature of the cold storage is 1-6°C, the humidity is 50%-60%, the light time is 8-10 hours, and the dark time is 14-16 hours. From December 2nd, 30 pots were moved into the greenhouse every 5 days, of which half of Asakura Sansho and half of Sansho without thorns. The temperature in the greenhouse is 20-25°C during the day, 13-18°C at night, and the air humidity is 60%-80%. After Sansho pepper was moved into the greenhouse, 50mg / L gibberellin was sprayed, 100ml per plant. Observe the germination of pe...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com