Variable-rigidity flexible joint design of humanoid robot
A humanoid robot and flexible joint technology, applied in the field of humanoid robots, can solve the problems of high energy consumption and environmental adaptability of robots, and achieve the effects of diversified walking functions, no return error, and small friction.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0027] The present invention will be further described below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and specific embodiments, but not as a limitation of the present invention.
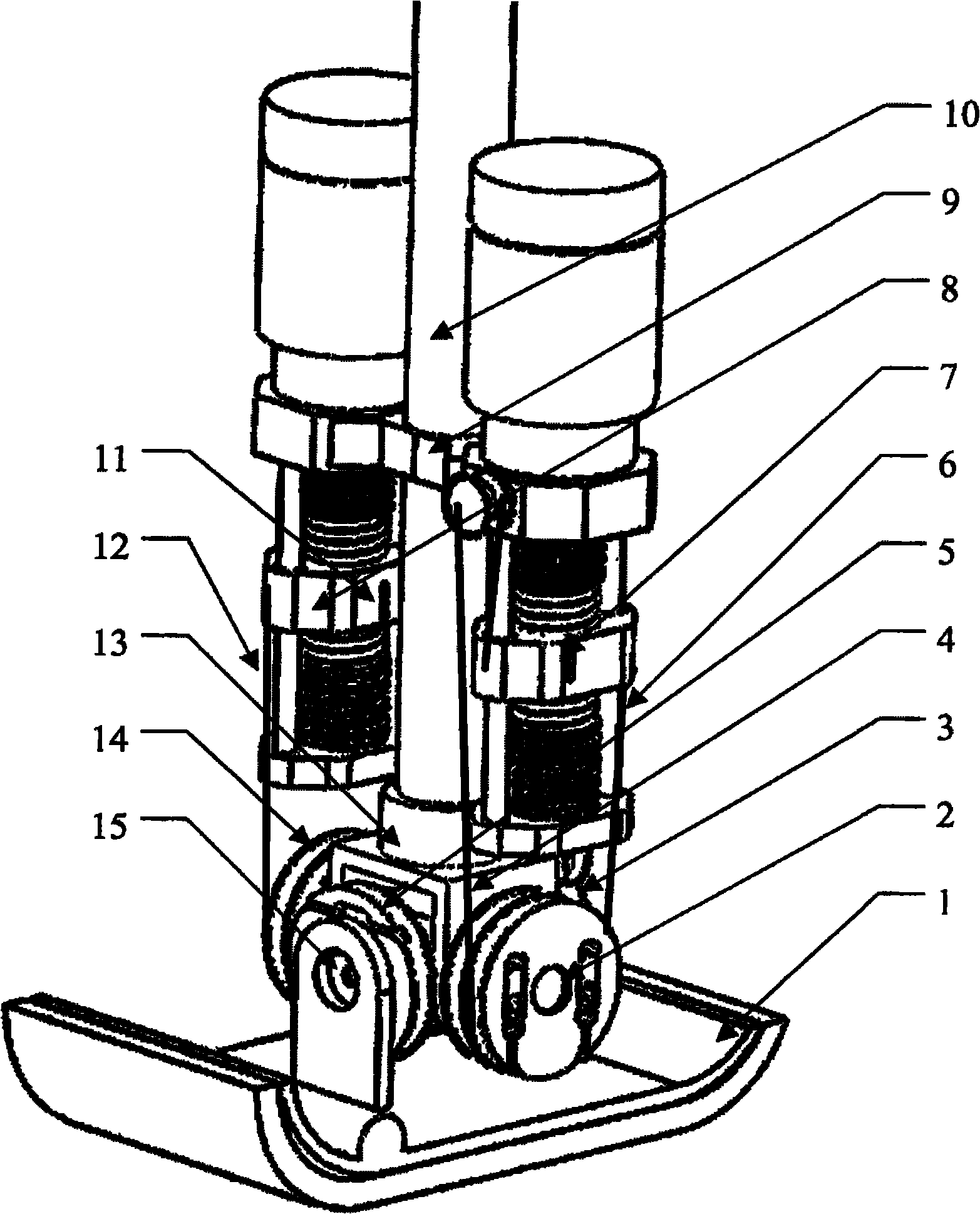
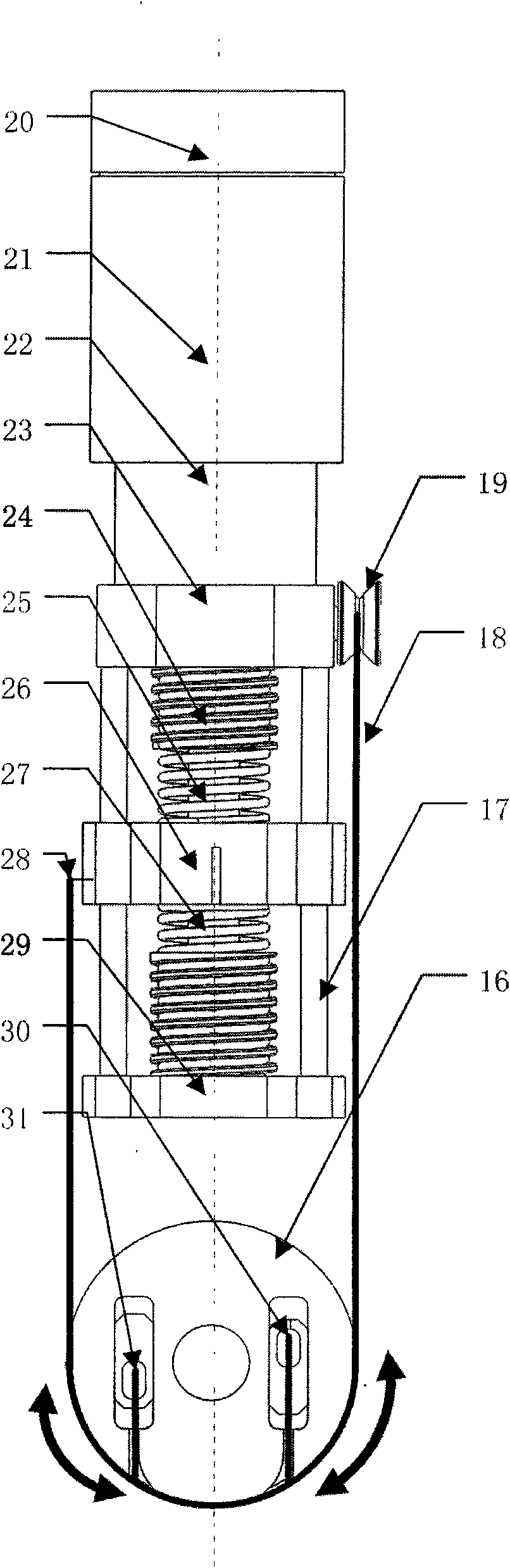
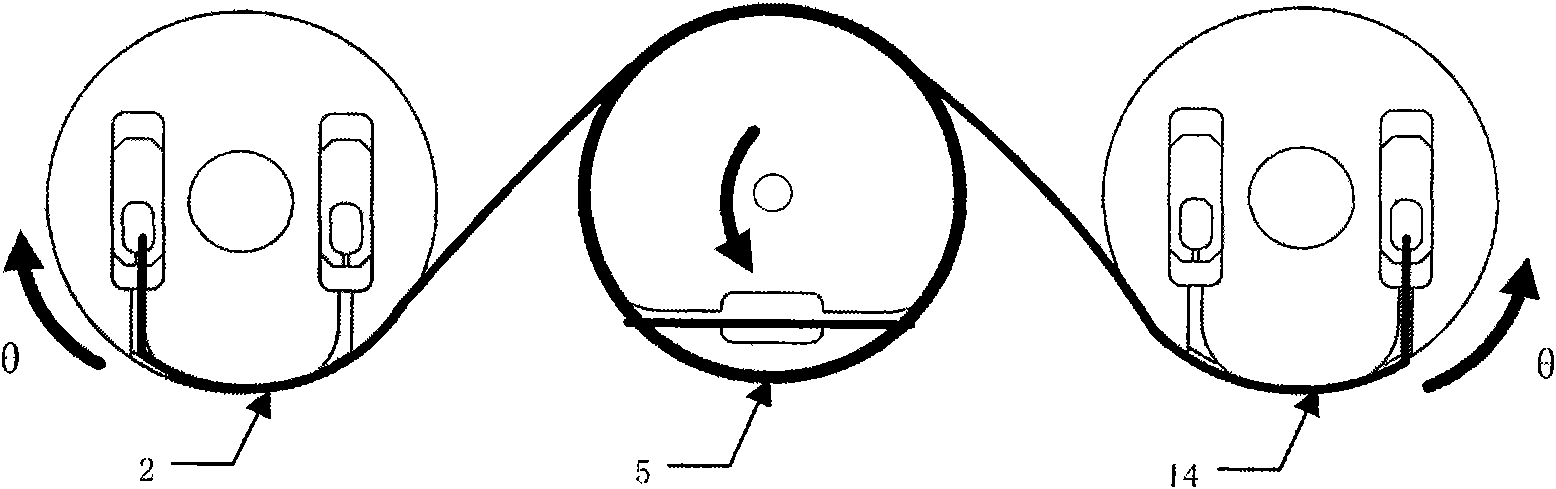
[0028] see figure 1 , a variable flexible joint structure of a humanoid robot, mainly including a 2-DOF differential drive ankle joint 12, variable stiffness flexible drives 7, 8, flexible cables 4, 6, 11, 12. The flexible cables 4, 6, 11, 12 pass through the variable stiffness flexible drivers 7, 8 respectively, and one end bypasses the fixed pulley, and is fixed to the flexible cable consolidation blocks 5, 20 of the differential 2-DOF differentially driven ankle joint 12. The specific implementation method is: through the flexible cables 4, 6, 11, 12, the flexible cable input wheel A 2, the flexible cable input wheel B 14 are connected to the output end C 5, the output end D 3, and the input wheel A 2, the input wheel B 14 The two parallel rotations are converted into two orthogonal directio...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com