Method for sending, receiving and transmitting data packets and device therefor
A sending method and data packet technology, applied in the field of communication, can solve problems such as lack of flexibility and scalability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0110] Figure 12 It is a flow chart of Example 1 according to the embodiment of the present invention. Such as Figure 12 As shown, the first example mainly includes the following processing (step S1201-step S1205):
[0111] Step S1201: The MTU (Maximum Transmission Unit) of the IP protocol layer between peer GTP-Us is dwMTU, and wSegMaxSize=(dwMTU-20-byHeaderSize) is preset, wherein wSegMaxSize is the preset threshold configured in the background, and 20 is the IP protocol Header size, byHeaderSize is the above GTP-U data header size;
[0112] Step S1203: Fragmenting the GTP-U data packet by using the data packet fragmentation method;
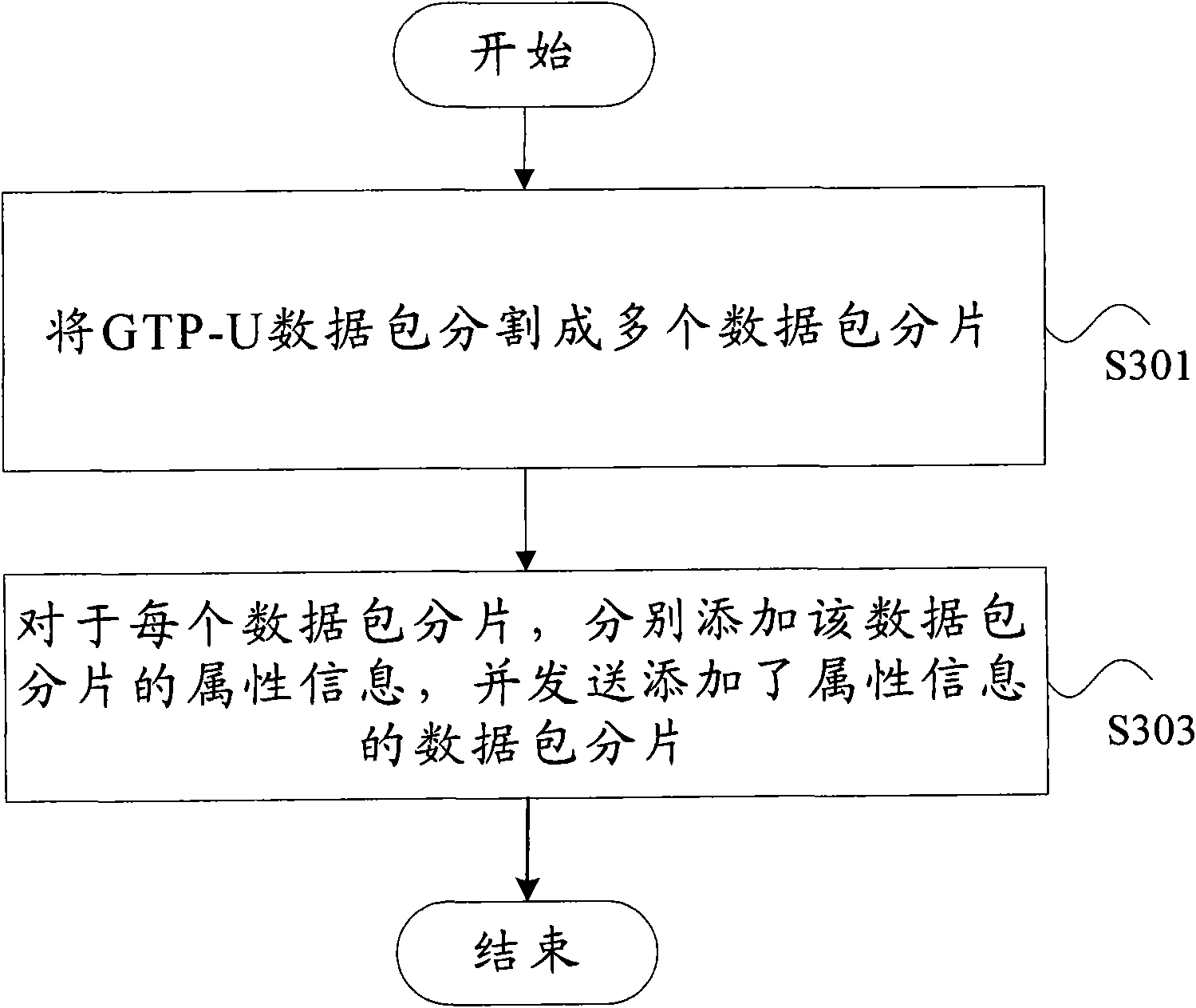
[0113] Among them, the above fragmentation method can be found in image 3 The description in , will not be repeated here.
[0114] Step S1205: After transmitting the fragmented GTP-U data to the IP layer, since each data fragment is within the dwMTU range, the IP protocol layer does not perform fragmentation any more.
[0115] Through ...
example 2
[0117] Figure 13 It is a flow chart of Example 2 according to the embodiment of the present invention. Such as Figure 13As shown, the second example mainly includes the following processing (step S1301-step S1305):
[0118] Step S1301: The size of the data packet delivered by the PDCP or the application layer to the GTP-U is wDataSize, wherein wDataSize is greater than 65535 bytes and less than or equal to 9133025 (65535×15) bytes;
[0119] Step S1303: set wSegMaxSize=65535, and use the packet fragmentation method to fragment the GTP-U data packet. After processing, the payload of each fragment is less than or equal to 65535;
[0120] Among them, the above fragmentation method can be found in image 3 The description in , will not be repeated here.
[0121] Step S1305: After receiving the fragmented data, the peer GTP-U entity reassembles according to the reassembly method, and reassembles each data fragment into a complete data packet, wherein the size of the data packe...
example 3
[0125] Figure 14 It is a flow chart of Example 3 according to the embodiment of the present invention. Such as Figure 14 As shown, the second example mainly includes the following processing (step S1401-step S1405):
[0126] Step S1401: flexibly configure the GTP-U segment length wSegMaxSize through background OAM (Operation And Management);
[0127] Step S1403: Use the fragmentation method to perform GTP-U data fragmentation processing, and each data packet fragmentation after processing is less than or equal to wSegMaxSize;
[0128] Among them, the above fragmentation method can be found in image 3 The description in , will not be repeated here.
[0129] Step S1405: After receiving the fragmented data, the peer GTP-U entity reassembles according to the reassembly method, and reassembles each data fragment into a complete data packet.
[0130] Among them, the above-mentioned recombination method can be found in Figure 4 The description in , will not be repeated here...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com