Systems for clinical trials
A system, action technique, applied in the field of physiologic and psychological test results for presumptive disease-modifying treatments
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0201] Example 1 - Disease Severity and Rate of Disease Progression at Baseline
[0202] It has been generally recognized in the literature that disease severity or stage is an important predictor of disease progression (recently reviewed in Schaufele, M., Bickel, H., Weyerer, S. (2002) Which factors influence cognitive decline in older adults suffering from dementing disorders? International Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry, 17: 1055-1063).
[0203] However, the rember TMThe study is the first to prespecify CDR severity at baseline as a stratification covariate in the primary outcome analysis. Subjects were divided into two groups: subjects with mild CDR at baseline (including 3 [1% of randomized total] subjects who were CDR-questionable at baseline) and subjects with moderate CDR at baseline of subjects. Although CDR has been previously advocated as a means of classification (Berg, L., Danziger, W.L., Storandt, M., Coben, L.A., Gado, M., Hughes, C.P., Knesevich, J.W., Bo...
Embodiment 2
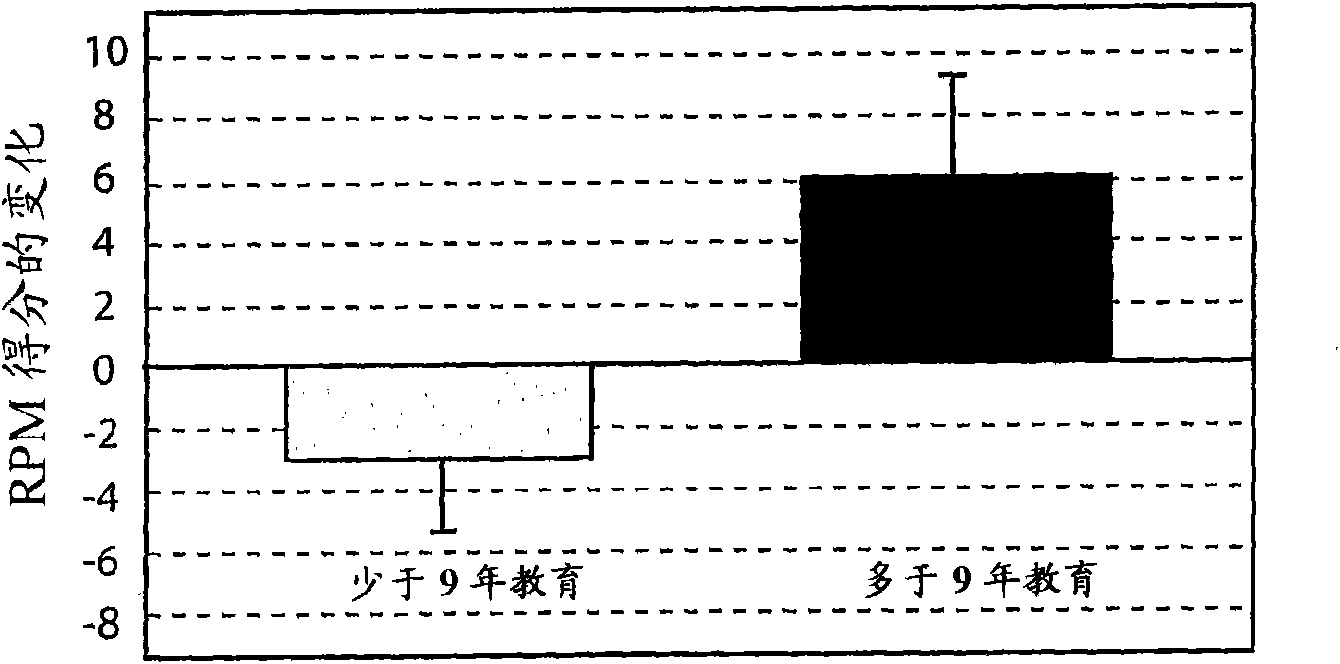
[0224] Example 2 - Cognitive Reserve
[0225] Although there was a general association between increased brain pathology burden and cognitive decline, this association did not explain all the variance in the data. Attempts to explain the variability have been stated in terms of the concepts of "brain reserve" or "cognitive reserve", which involve two different theoretical formulations (Stern, Y. (2002) What is cognitive reserve? Theory and research application of the reserve concept. Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society, 8:448-460). The first is the passive brain reserve model, where reserve is defined by brain size or neuronal count. It is described as passive because it is defined in terms of the amount of damage or burden an individual can withstand before clinical symptoms manifest. The second, or active cognitive reserve model, states that the brain is capable of compensating for pathological load by recruiting other processes to perform disease-com...
Embodiment 3
[0232] Example 3 - Psychometric testing failed to demonstrate in CDR mild AD over 24 weeks of study clear therapeutic efficacy
[0233] Analytical method
[0234] Two methods of analysis were provided for each OC and LOCF analysis: linear least squares and linear mixed-effects models for change in ADAS-cog score from baseline over 24 weeks. After the baseline severity term was found to be highly significant in all initial analyses, further analyzes were performed that included a treatment:severity:interaction term. Severity (defined by CDR) was used as a baseline grouping variable. A further ANCOVA analysis of the 24-week LOCF data was performed using only the analysis of ADAS-cog score change at the 24-week evaluation point (using both non-interaction and interaction models).
[0235] ITT / OC Analysis
[0236] non-interaction model
[0237] Treatment Effects in Linear Least Squares and Linear Mixed Effects Non-Interaction Models Applied to the Whole ITT / OC Population D...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com