Sliding time window based WLAN (Wireless Local Area Network) indoor WKNN (Weighted K Nearest Neighbors) tracking method
A sliding time window, indoor positioning technology, applied in the field of pattern recognition, can solve the problems of severe jitter of estimated position coordinates and uneven estimated trajectory.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
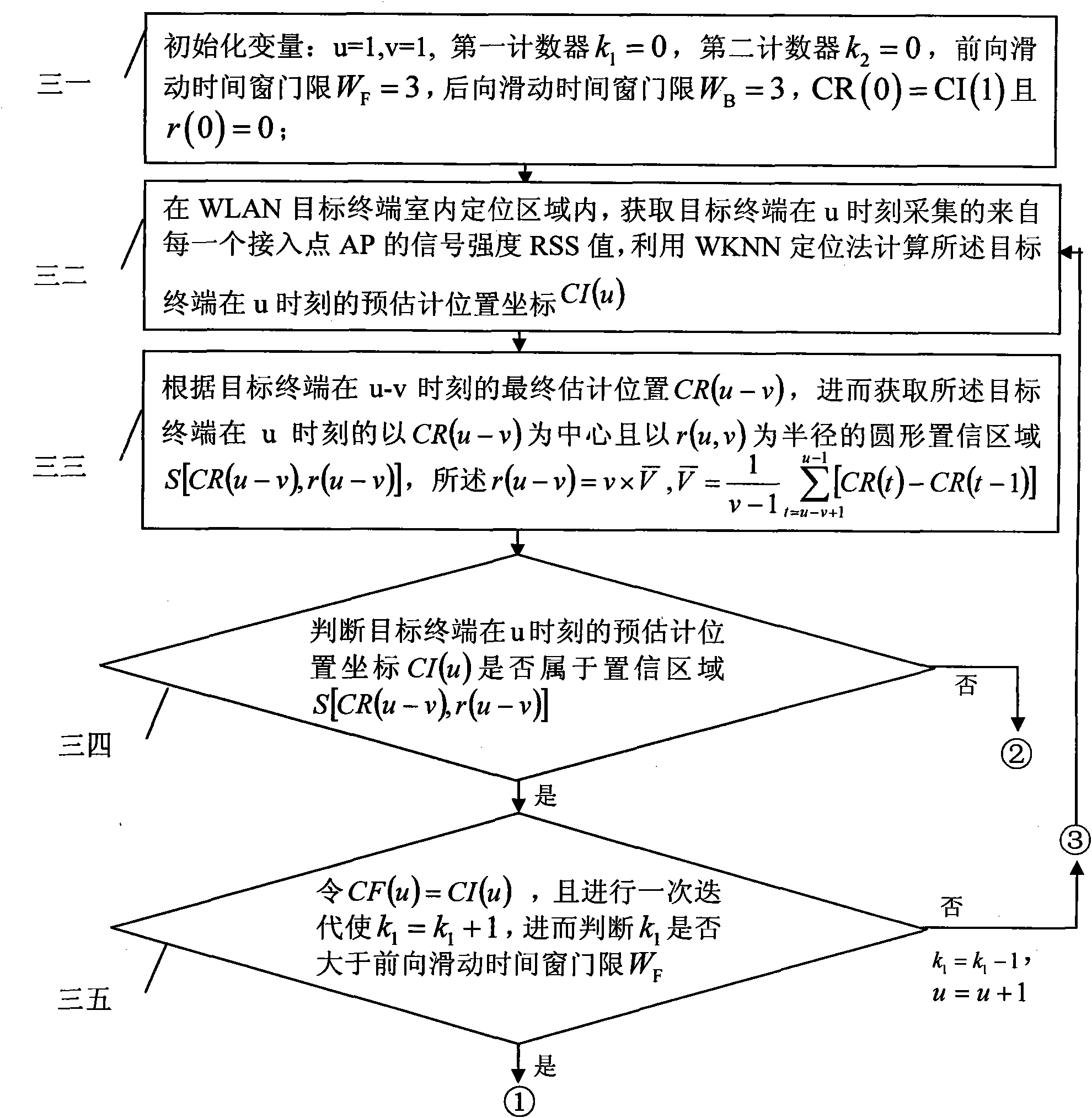
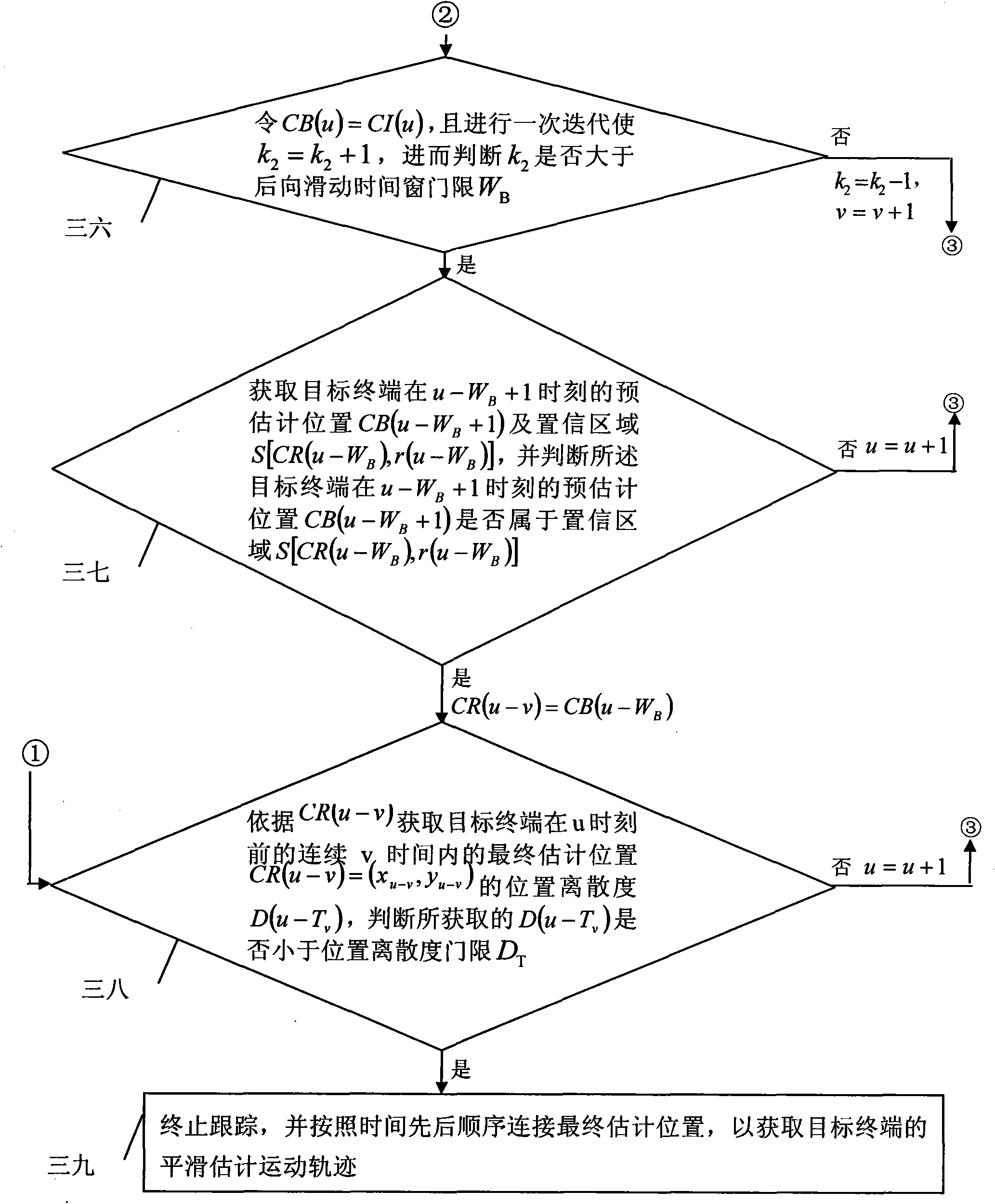
[0024] Specific implementation mode one: according to the instructions attached figure 1 , 2 , 3, 4 and 5 specifically describe the present embodiment, the WLAN indoor WKNN tracking method based on the sliding time window described in the present embodiment, its tracking process is:
[0025] Step 1: Set N evenly in the indoor positioning area of the WLAN target terminal RP reference points, and arrange N in the indoor positioning area c APs, so that each reference point at least collects a signal strength RSS value from one AP;
[0026] Step 2: Select a reference point as the coordinate origin O to establish a two-dimensional rectangular coordinate system, and obtain N RP The coordinate positions of each reference point in the two-dimensional Cartesian coordinate system, and based on the coordinate position of each reference point and the signal strength RSS value from each access point AP collected by each reference point, a location fingerprint database is established ...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0039] Specific embodiment 2: The difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment 1 is that in this embodiment, in step 38, the final estimated position required when obtaining the smooth estimated motion trajectory of the target terminal also includes Final estimated position at non time Among them, CR(a) x Represents the acquired x-direction coordinates of the final estimated position CR(a) of the target terminal at time a, CR(a) y Indicates the y-direction coordinates of the acquired final estimated position CR(a) of the target terminal at time a, CR(b) x Indicates the acquired x-direction coordinates of the final estimated position CR(b) of the target terminal at time b, CR(b) y Indicates the acquired y-direction coordinates of the final estimated position CR(b) of the target terminal at time b, the time non is adjacent to time a and time b respectively, and b
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0040] Specific implementation mode three: according to the instructions attached Figure 6 and 7 Describe this implementation mode in detail. This implementation mode is a further description of the specific implementation mode 1 or 2. In the specific implementation mode 1 or 2, in step 38, the position dispersion threshold where x g,p and y g,p Respectively represent the x-direction coordinates and y-direction coordinates of the position of the target terminal in the indoor positioning area of the WLAN target terminal in the two-dimensional square area Γ when it jumps randomly for the pth time when the final estimated position of the target terminal is tested for the gth time, The indoor positioning area of the WLAN target terminal is a square area Γ=χ×χ, where, N mobile Indicates the number of final estimated position coordinates of the target terminal, N rand Indicates the number of random jumps of the target terminal in the square area Γ, N text Indicates the ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com