Systems and methods for link processing with ultrafast and nanosecond laser pulses
A laser pulse and laser system technology, applied in the field of laser processing, can solve the problems of small processing critical difference and failure to reach the processing window
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
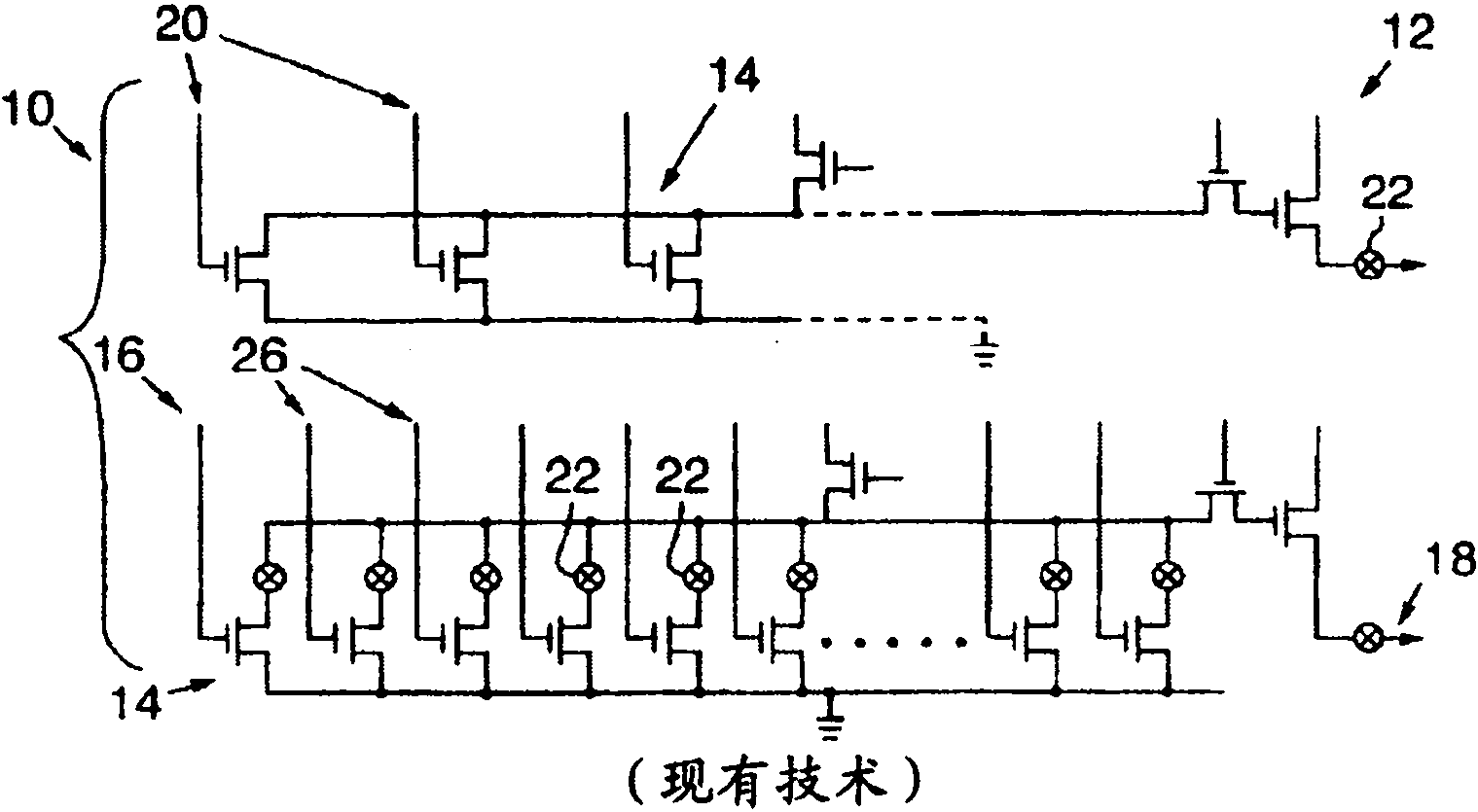
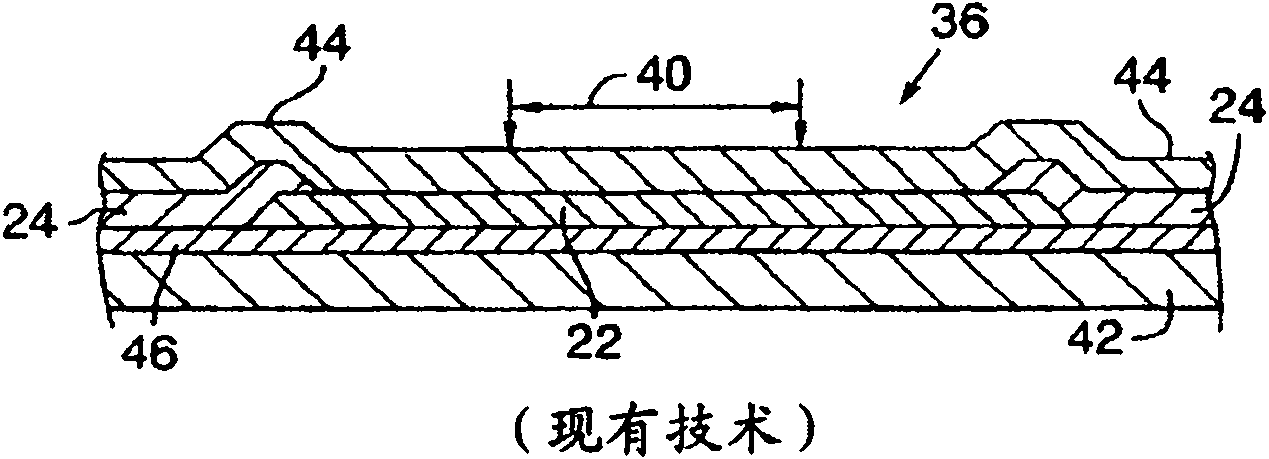
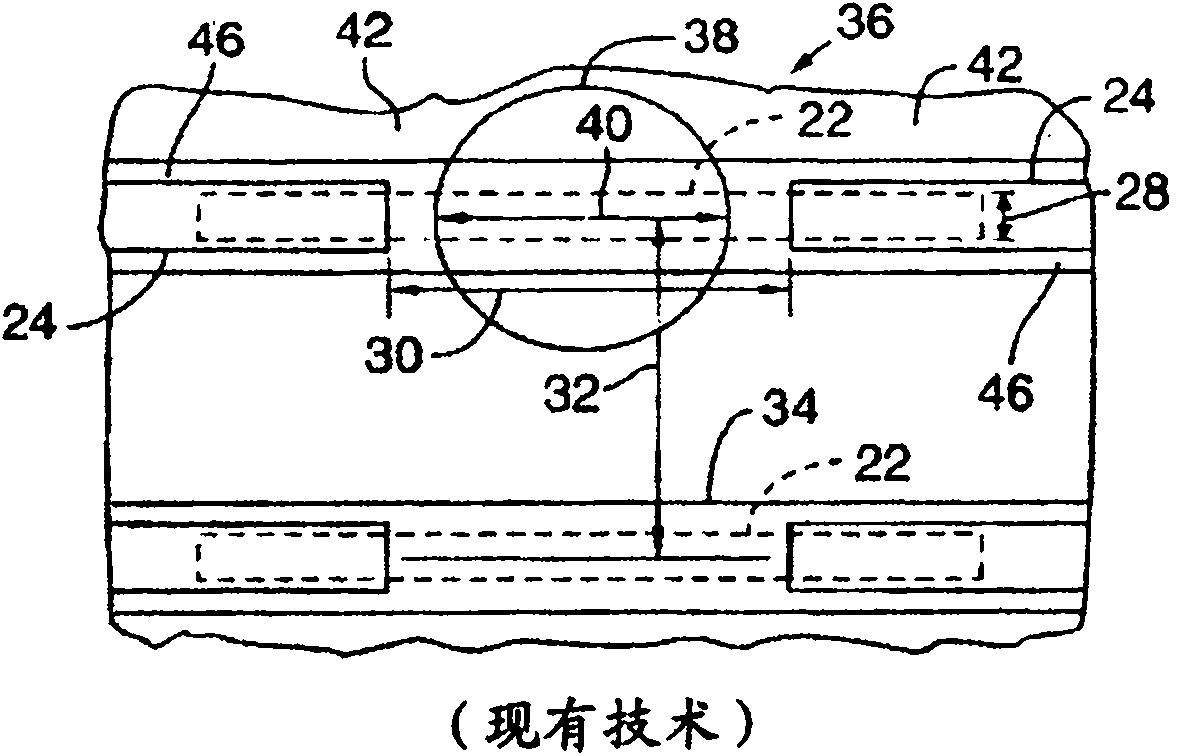
[0020] The present invention describes the use of an ultrafast laser pulse, or a cluster of ultrafast laser pulses, followed by one or more nanosecond laser pulses to process conductive connections in integrated circuits (ICs), which laser pulses have the conventional temporal pulse shape or custom-made time pulse shape.
[0021] The ultrafast laser pulse or pulses process a passivation material overlying the link and a portion of the link material. In one such embodiment, the ultrafast laser pulse or pulses treat the overlying passivation layer based at least in part on laser intensity induced collapse. In an embodiment, the ultrafast laser pulse or pulses treat a substantial portion of the link.
[0022] Next, a nanosecond laser pulse completes the removal of the remaining bonding material. Since the treatment provided by the nanosecond laser pulse is primarily based on heat generated by laser absorption of the target material and the underlying passivation material is a n...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| wavelength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| wavelength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| wavelength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com