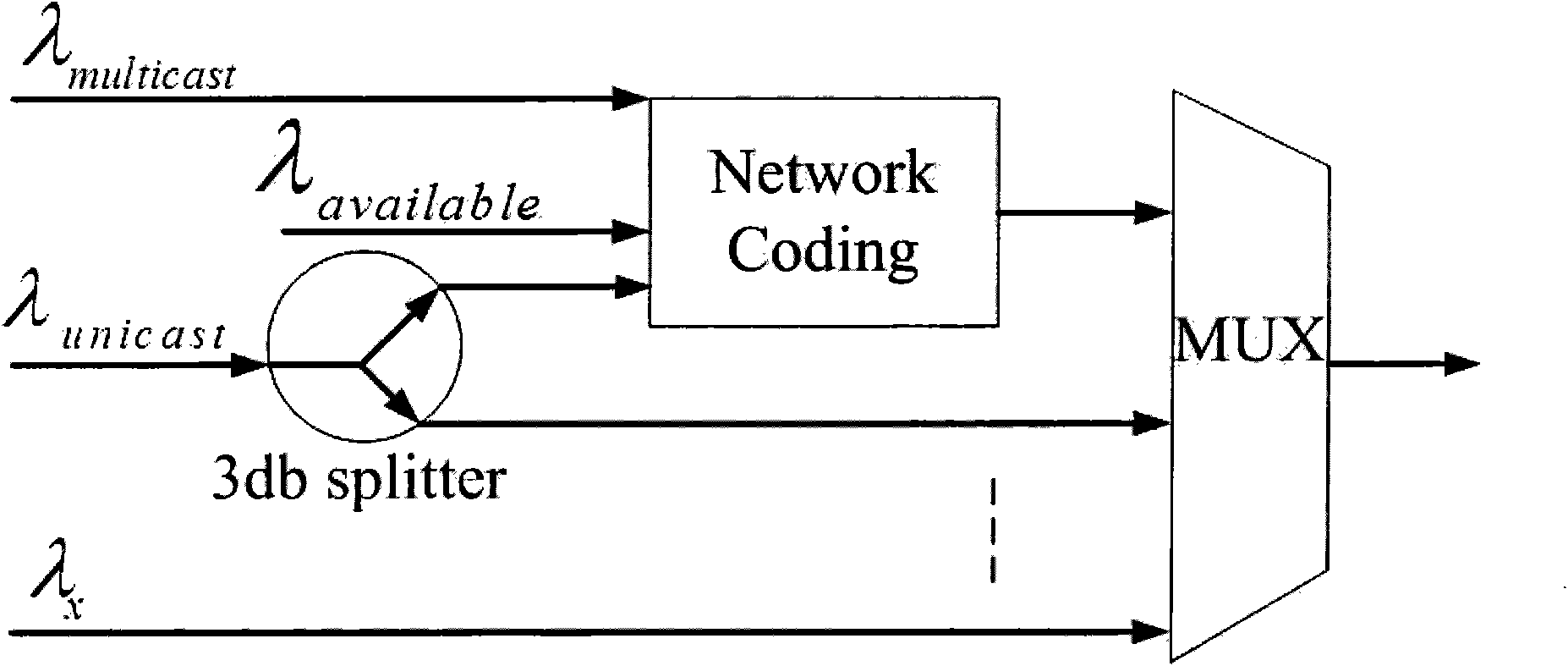
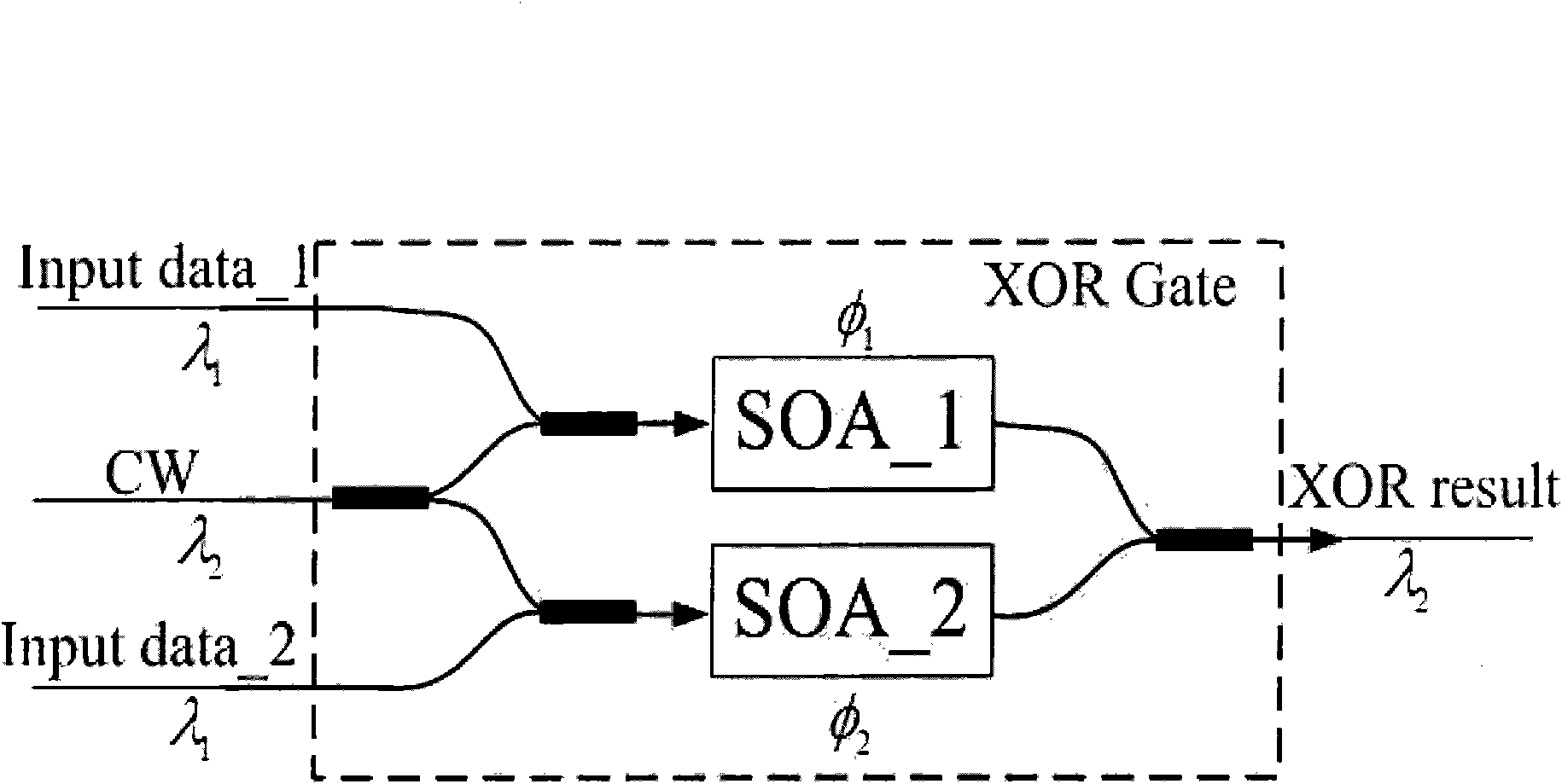
Network coding based wavelength conflict solution in WDM (Wavelength Division Multiplex) multicast network
A network coding and wavelength technology, applied in the field of optical switching network, can solve the problems of high cost of full-wavelength converters and unsatisfactory wavelength conflicts
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
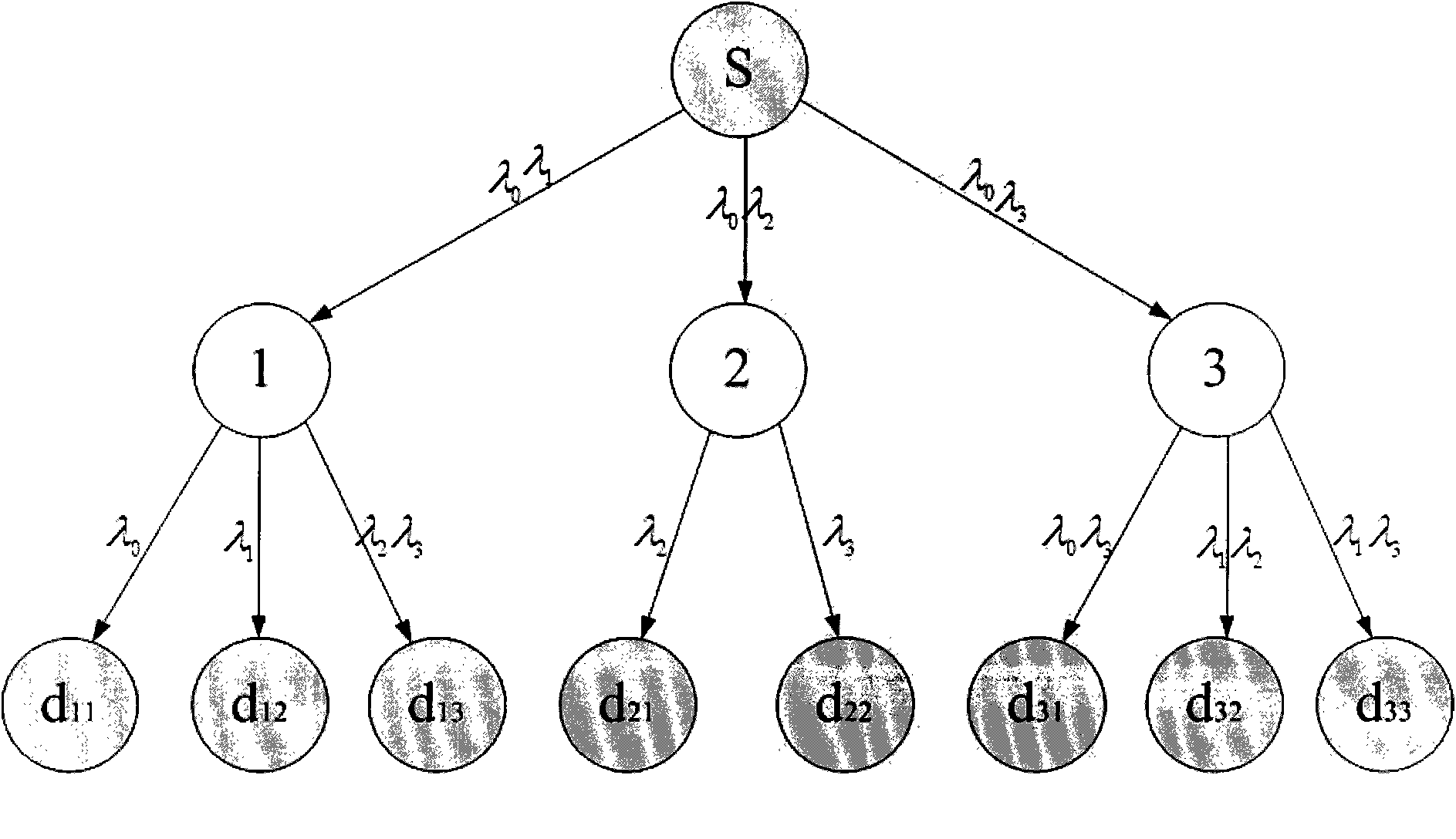
[0025] Such as figure 1 In the shown multicast tree, node S is a multicast source node, which is used to send multicast signals to the destination node; node d 11 -d 33 It is a multicast destination node for receiving multicast signals; the wavelength marked on each link in the figure is the available wavelength on the link. Suppose the source node S adopts λ 0 When sending a multicast signal to the downstream link, if the path between the source node and the destination node λ 0 When both are available, the multicast signal can be normally transmitted to the destination node. For example figure 1 Middle path S->1->d 11 and path S->3->d 31 , the λ in these two paths 0 are available, so the multicast signal can be transmitted from the source node S to the destination node d without blocking 11 and d 31 .
[0026] However, at link 1->d 12 , 1->d 13 , 2->d 21 , 2->d 22 ,3->d 32 ,3->d 33 on, λ 0 Occupied by unicast signals to the same destination as multicast sign...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com