Compositions and methods for treating inflammation and inflammation-related disorders by plectranthus amboinicus extracts
A composition and extract technology, applied in the direction of drug combination, medical raw materials derived from angiosperms, anti-inflammatory agents, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0136] Example 1: Anti-inflammatory activity of PA extract
[0137] The effect of PA on LPS (lipopolysaccharide)-induced expression of 17 cytokines and 5 chemokines is shown in Table 1. Human umbilical vein endothelial (HUVEC) cells were co-incubated with LPS with or without 1 mg / ml PA crude extract. Cytokine expression profiles were determined using Luminex. The results showed that PA crude extract significantly reduced the expression of cytokines IL-6, IL-8, IL-12, MCP-1, and RANTES.
[0138] Table 1. Effect of PA extract on LPS-induced expression
[0139]
[0140]
Embodiment 2
[0141] Example 2: Inhibition of AP-1 binding activity with PA extract
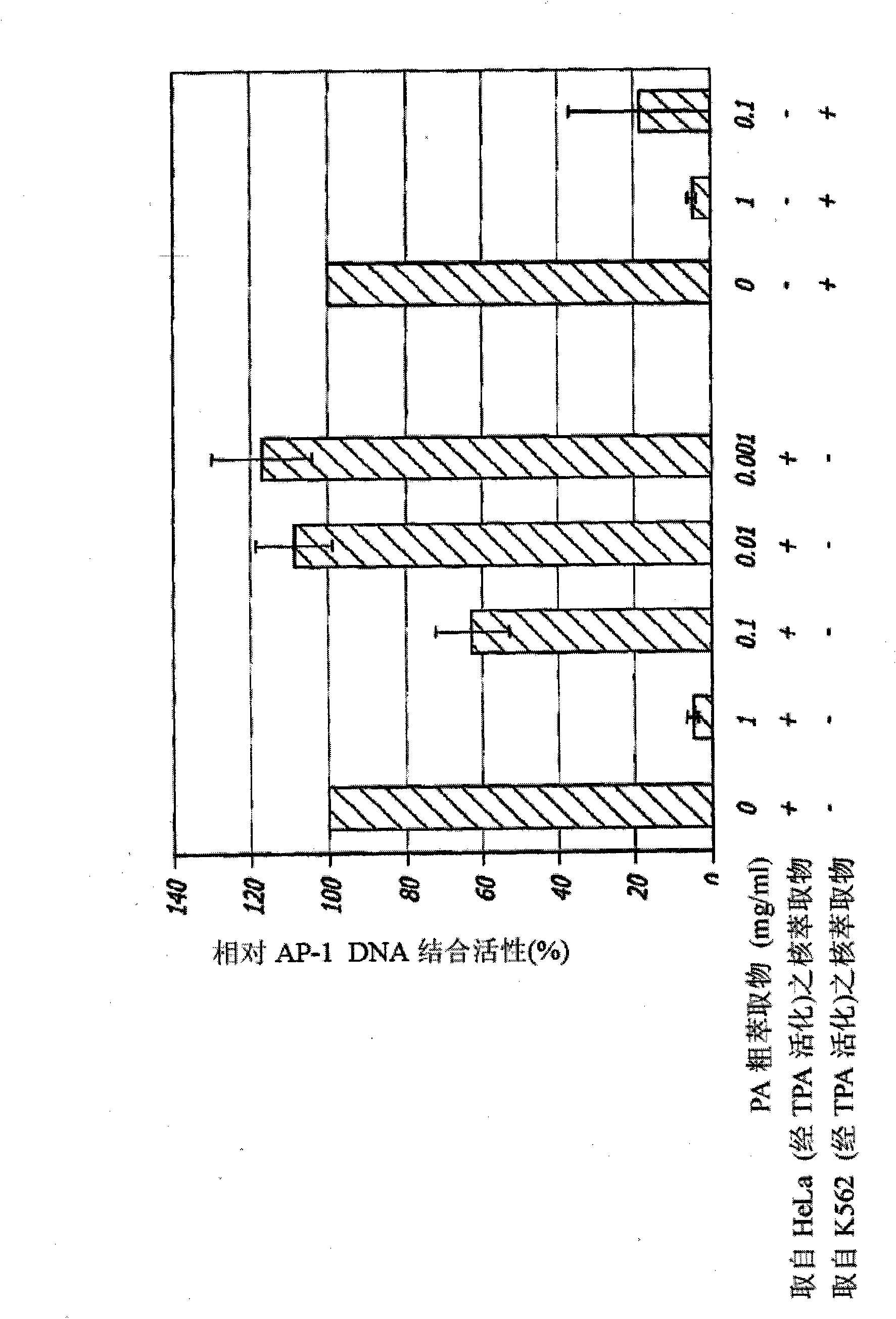
[0142] Since AP-1 activity is involved in inflammatory signaling, the effect of PA crude extract on AP-1 / DNA binding activity was examined. Such as figure 1 As shown, the effect of PA crude extract on the DNA binding activity of the AP-1 transcription factor was determined using an ELISA-based assay. Nuclear extracts prepared from TPA-activated HeLa or K562 cells were used as a source of AP-1 protein. After colocalization with oligonucleotides containing the AP-1 binding site, the AP-1 / DNA complex was detected with an anti-c-Fos antibody complexed with HRP. It was found that the in vitro DNA binding activity of AP-1 was inhibited by PA crude extract, and these effects were dose-dependent.
Embodiment 3
[0143] Example 3: Inhibition of AP-1 Binding Activity with Fraction 10, CHM9102, and Rosmarinic Acid
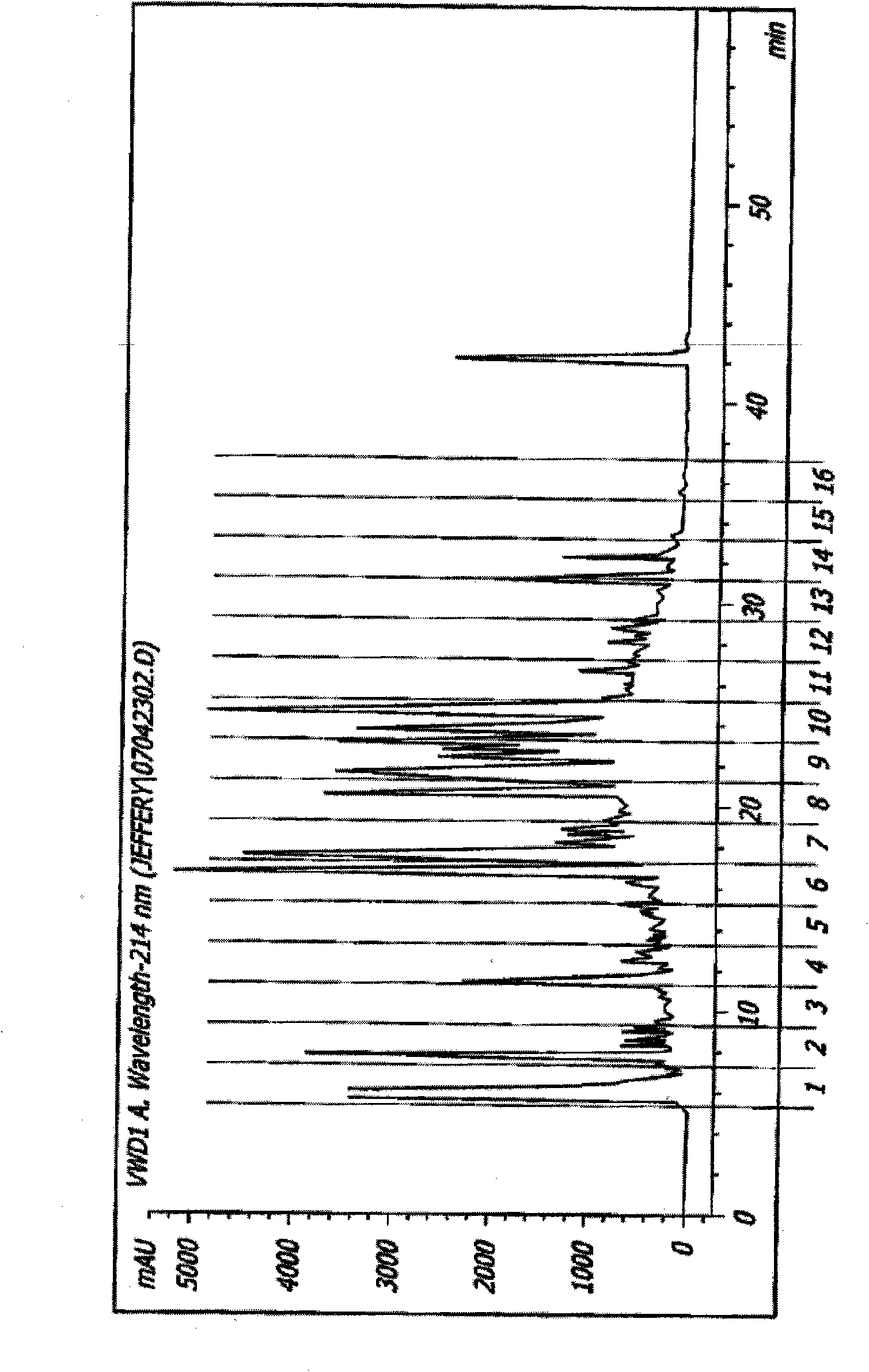
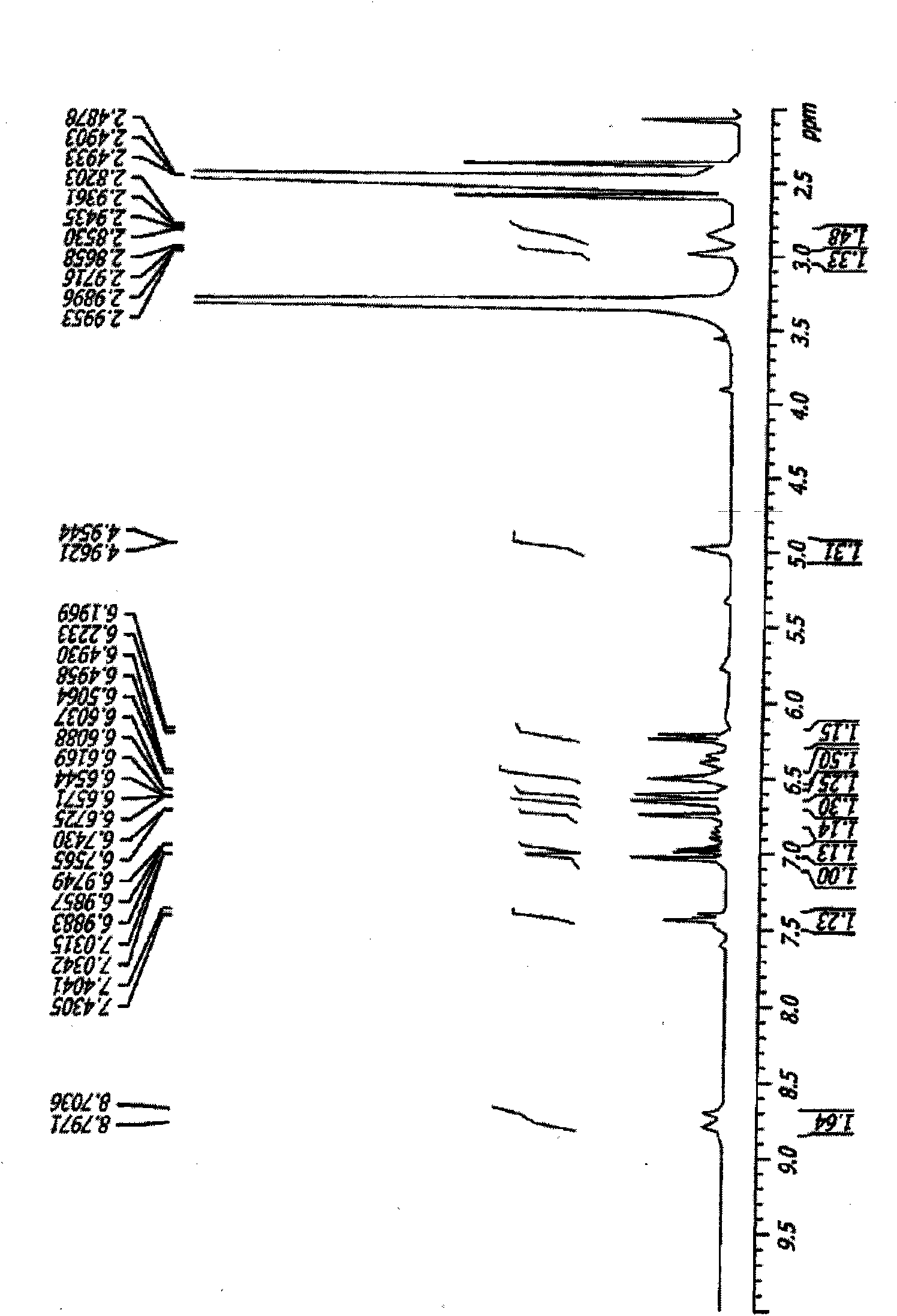
[0144] The PA crude extract was further fractionated by preparative HPLC using a C18 column. Such as figure 2 As shown, it separates the crude extract of P. chinensis into 16 fractions. Fraction 10 showed an inhibitory effect against AP-1 binding. This fraction was further purified on another C18 column using a solvent gradient from 2% acetonitrile to 90% acetonitrile containing 0.1% trifluoroacetic acid. The main peak is collected, and then its structure is determined by MASS and NMR analysis, such as image 3 shown. These studies lead to structural deduction for the active component CHM9102. Rosmarinic acid (an analog of CHM9102) was also tested for AP-1 inhibitory activity.
[0145] Although the methods and reagents have been described in terms of what are presently considered to be the most practical and preferred implementations, it should be understood that the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com