Motion compensated image averaging
A moving and averaging technology, applied in the field of image averaging, can solve problems such as low SNR and difficult to analyze images
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example
[0142] Using the computer 200, an exemplary image frame is processed according to process S100.
[0143] The processing used to process these image frames includes algorithms utilizing the following pseudocode example:
[0144] =======================================
[0145] %% Begin Pseudocode
[0146] Loop from i=1 to N
[0147] {execute subprocess S102 to generate filtered frame I f i from raw frame I i
[0148] execute subprocess S104 to generate deconvolved frame J i from filtered
[0149] frame I i
[0150] execute subprocess S160 to identify landmark points in J i
[0151] If i > 1
[0152] {execute S162 to correlate landmark points in J i and J i-1
[0153] execute S108 to align I f i with I a i-1 , generating aligned frame I a i
[0154] execute S110 to correct alignment of I a i to I ref i-1 , generating
[0155] corrected frame I n i and reference frame I i ref
[...
example I
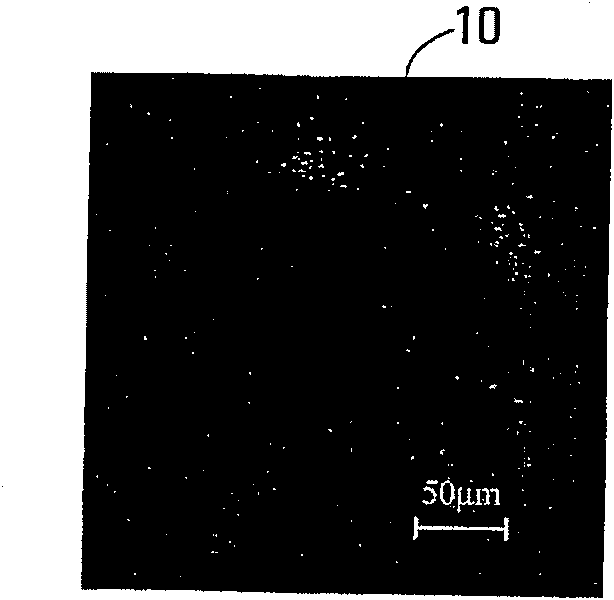
[0164] Figure 3A A sample original frame of a GFAP-GFP image of a mouse retina taken in vivo and processed in this example is shown in .
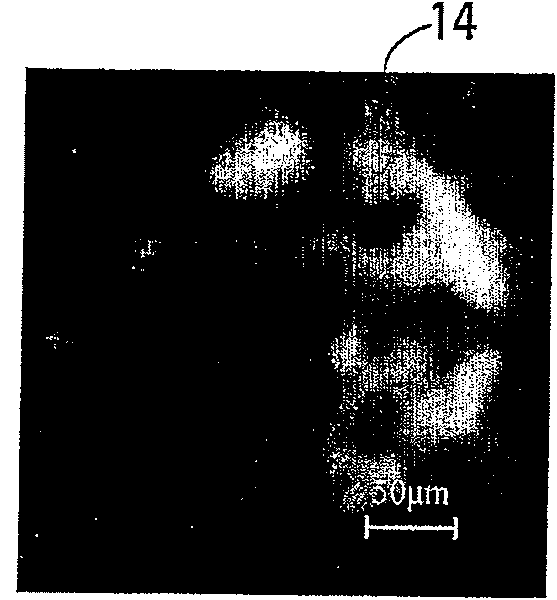
[0165] Figure 3B shows the deconvolved frame resulting from the filtered frame, itself obtained from Figure 3A generated by the original frame. It can be seen that in Figure 3B In , the base features in the image are enhanced without significant distortion. This result demonstrates that, in this case, deconvolution of the filtered frames facilitates accurate assessment of the basal fluorescence signal in the filtered frames.
[0166] Figure 3C shows just by applying a 9×9 median filter from Figure 3B The control frame generated by the filtered frame of . and Figure 3B In contrast, the basal signal was less enhanced. Figure 3C Image artifacts are visible in , but in Figure 3B There is no such image artifact in .
[0167] Figure 3D Control frames generated by simple averaging are shown.
[0168] Figure 4A , 4B , 4C a...
example II
[0170] Raw image frames were acquired from the retinas of two different mice with FVB / N lesions using the Heidelberg Retina Angiograph (HRA2) system. A blue laser (488nm) was used to excite the transgenic GFAP-GFP expression and the blocking filter was set at 500nm. The field of view was initially set to 30°, but the image shown here is of a more localized area around the optic nerve head, as this is the area of interest. All retinal images have a lateral resolution of 10 μm. Raw retinal images were collected over two weeks at specific times (different days). At the beginning of the experiment, ie, on day 0 immediately after retinal imaging, control mice were injected with saline and treated mice received intraperitoneal injection of kainic acid. A sequence of raw images is taken each day, and as detailed in the example above, the sequence of raw images is averaged according to process S100 to obtain the final image for that day. The parameters used for this averaging pro...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com