Method for identifying natural gas hydrate by using incremental ratio between wave impedance of longitudinal and traverse waves
A wave impedance, longitudinal and shear wave technology, applied in the field of geological exploration, can solve the problems such as not very reliable, increased formation compression and shear wave velocity, etc., to achieve the effect of improving exploration accuracy, improving reliability and saving drilling costs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
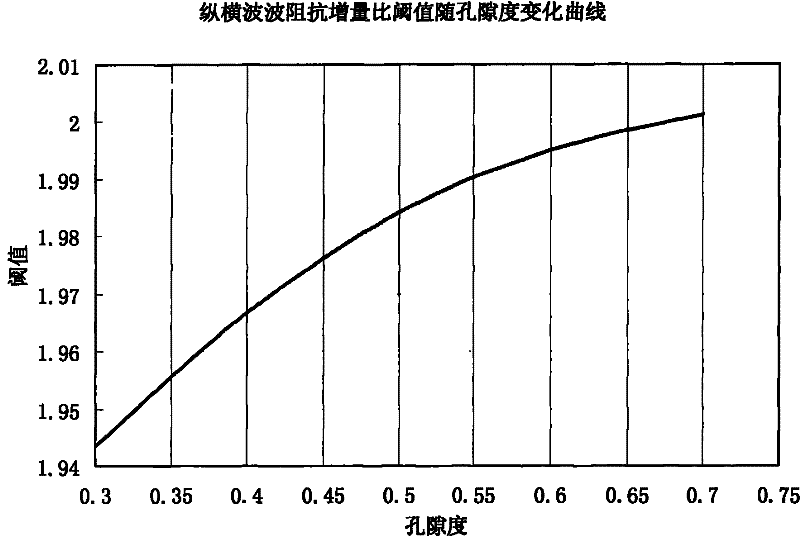
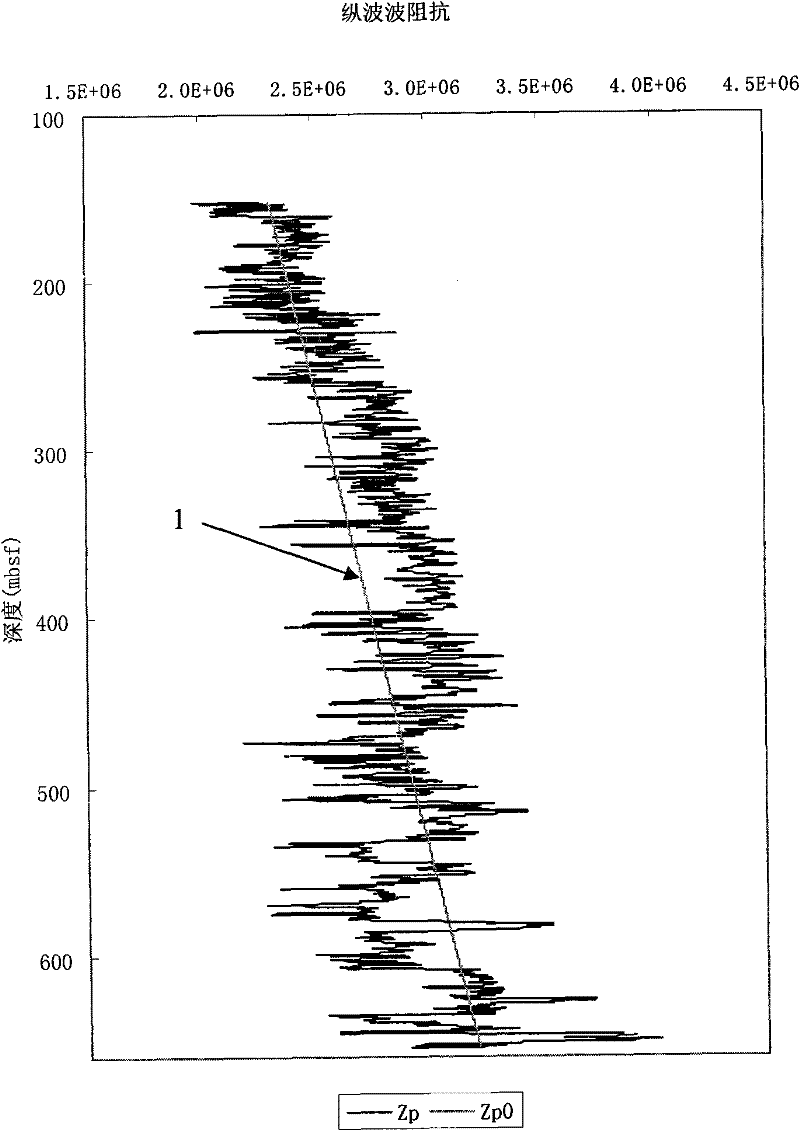
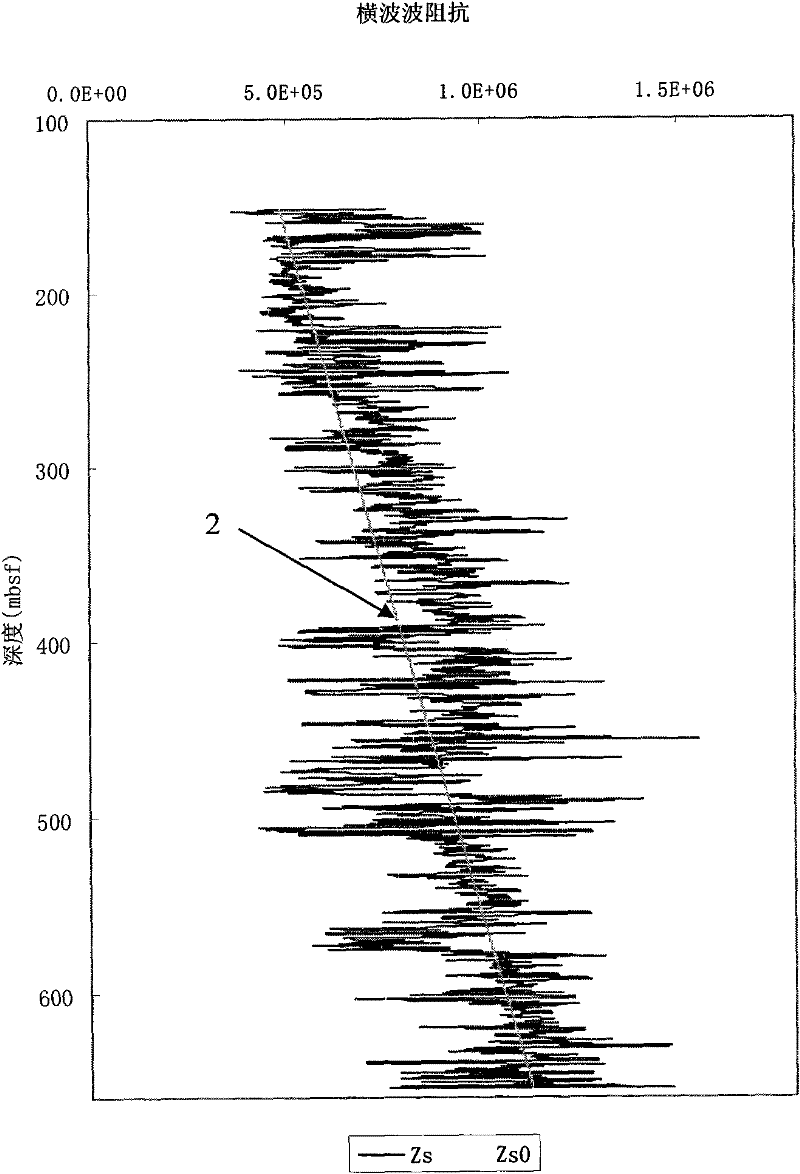
[0050] Ocean Drilling 164 voyage discovered gas hydrates in BlakeRedge wells in the United States, such as Well 995. In this example, using the known P-wave and S-wave velocity curves and density curves in Well 995, the P-S wave impedance increment ratio is calculated. According to the known porosity and the graph of the P-S wave impedance increment ratio threshold relationship curve given in the accompanying drawings, Identify whether the formation contains hydrates. Calculate the depth range of hydrate-bearing formations and compare them with drilling results.
[0051] The method for identifying natural gas hydrates using the ratio of compressional and transverse wave impedance increments of the present invention includes the following steps:
[0052] (1) Multiply the measured formation P-wave velocity and formation S-wave velocity by the actual density of the formation respectively to obtain the compressional wave impedance Z P Curve and shear wave impedance Z S curve. f...
Embodiment 2
[0062] In 2007, my country's first drill in the Shenhu area of the South China Sea successfully obtained hydrate samples. Prior to drilling, hydrate identification was performed prior to drilling using seismic data and the method of the present invention. The identification result shows the presence of hydrates, which provides a basis for determining the well location. Subsequent drilling results confirmed the correctness of the identification results. This embodiment presents the identification process.
[0063] The method for identifying gas hydrates by using the ratio of compressional and shear wave impedance increments includes the following steps:
[0064] (1) Using AVO inversion technology to invert the actual compressional wave impedance Z of the formation from the seismic data P and shear wave impedance Z S Variation curves with depth, respectively, as Figure 5 and Figure 6 As shown, the depth is expressed in two-way travel time, and the unit is milliseconds;...
Embodiment 3
[0074] Both of the above two examples only show the variation curve of the P-to-S wave impedance incremental ratio with depth at the drilling position and the hydrate identification results. We can also perform the same processing on the seismic section to obtain the hydrate identification section, that is, the P-wave and S-wave impedance increment ratio section. This example shows the BlakeRedge hydrate identification section in the United States, which passes through Well 995.
[0075] The method for identifying gas hydrates by using the ratio of compressional and shear wave impedance increments includes the following steps:
[0076] (1) Using AVO inversion technology to invert the actual compressional wave impedance Z of the formation from the seismic data P Profile and shear wave impedance Z S profile, such as Figure 8 and Figure 9 shown;
[0077] (2) For each track on the section, estimate the compressional wave impedance Z of the water-saturated formation accordin...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com