Method for collecting and routing data in wireless sensor network and device thereof
A wireless sensor and network data technology, applied in network topology, wireless communication, error prevention/detection using the return channel, etc., can solve the problems of nodes not considering resource constraints, blind resource utilization, and long cluster head generation time
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach 1
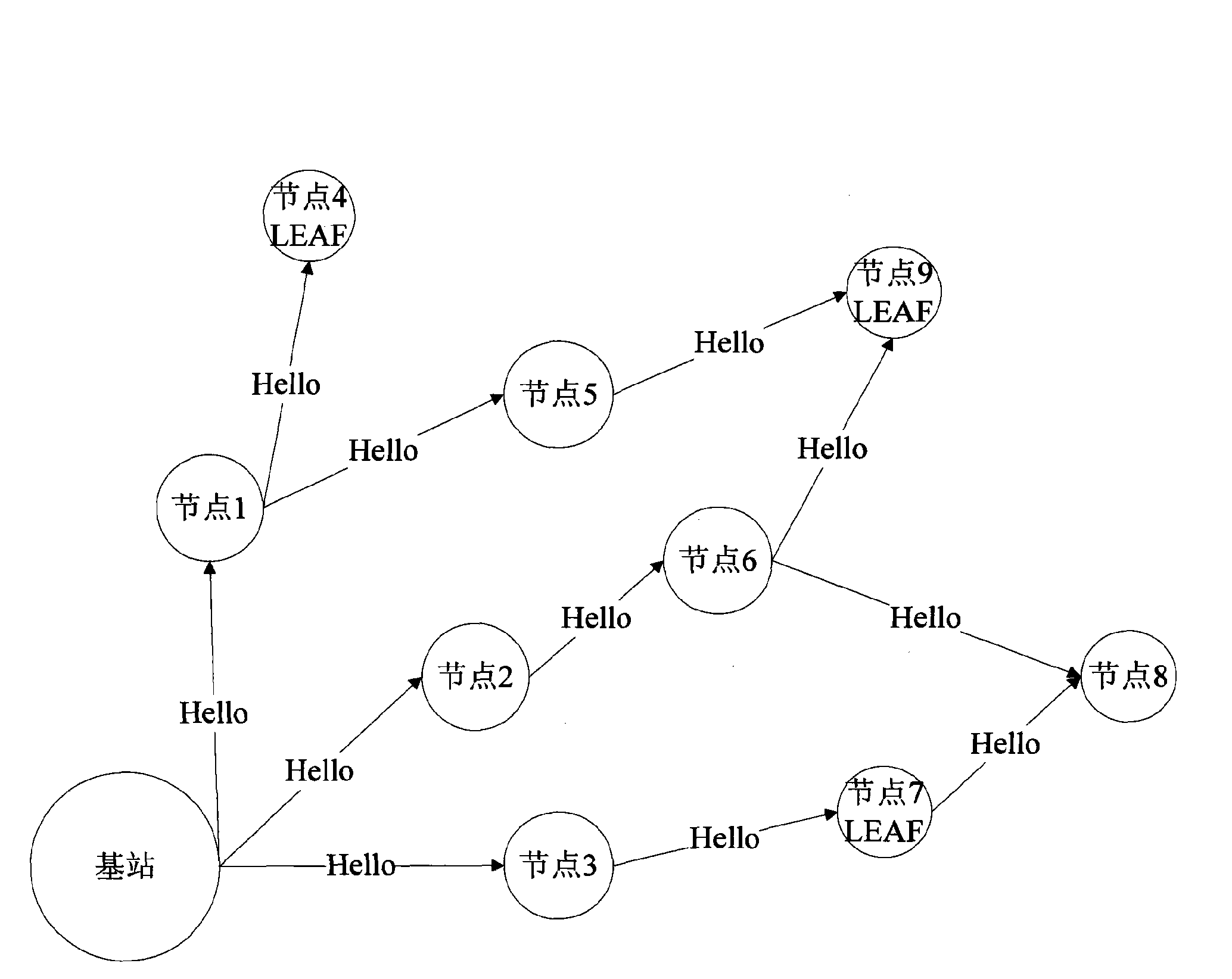
[0150] Route establishment phase:
[0151] Step 1: The base station sends a hello packet. The content of the packet is the node number of the node, the number of hops from itself to the base station, the remaining energy, and the LEAF identifier; among them, the number of hops from the base station to itself is 0, and the number of hops from other nodes to the base station initialized to infinity;
[0152]Step 2: The node receives the hello packet and establishes a neighbor table. The content of the neighbor table includes the node number of the neighbor node, the number of hops from the neighbor node to the base station, the remaining energy of the neighbor node, and the link quality indication to the neighbor node;
[0153] Step 3: If the number of hops to the base station decreases, broadcast your own hello packet;
[0154] Generate the hibernate scheduling stage:
[0155] Step 4-1: The node starts its own Tw after waiting for a random time, and broadcasts the hello packe...
Embodiment approach 2
[0166] Embodiment 2: The difference between this embodiment and the routing method described in Embodiment 1 is that if the node does not receive a hello packet during Ttopo, step 4-2 is performed;
[0167] Step 4-2: The node waits for the random time Trandom, starts to monitor the time Tw, and broadcasts the route repair package with T1 as the period. The content of the route repair package includes the time difference Δt between the current time of the node and the start time of the latest Tw, and the hop from itself to the base station. The number of steps, the remaining energy and the node number of the node, where T1<Tw; stop sending when the data collection phase begins, and execute step 11;
[0168] Step 11: Update the number of hops from the node itself to the base station, the number of hops is the smallest hop number in the neighbor table plus 1; if the number of hops is smaller than the number of hops that have not been updated before, wait for the neighbor nodes to ...
Embodiment approach 3
[0170] Embodiment 3: The difference between this embodiment and the routing method described in Embodiment 1 is that in step 6-1, when a routing repair package is received, step 12 is performed;
[0171] Step 12: Update the neighbor table information, where the calculation formula of the time difference t between the neighbor node and the local node is Δt1-Δt2, where Δt1 is the time difference contained in the routing repair packet sent by the sending node, and Δt2 is the current time distance of the current node from the latest Tw The time difference of the start time; if the number of hops in the received routing repair packet is infinite, reply a routing repair packet;
[0172] In Embodiment 3, when a node receives a routing repair packet during the data collection phase, it judges that a new node has joined, and replies with a routing repair packet, which includes the time difference Δt between the current time of the node and the start time of the latest Tw, and the time d...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com