Methods for forming multiple-layer electrode structures for silicon photovoltaic cells
A technology of electrode structure and photovoltaic cells, applied in photovoltaic power generation, circuits, electrical components, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
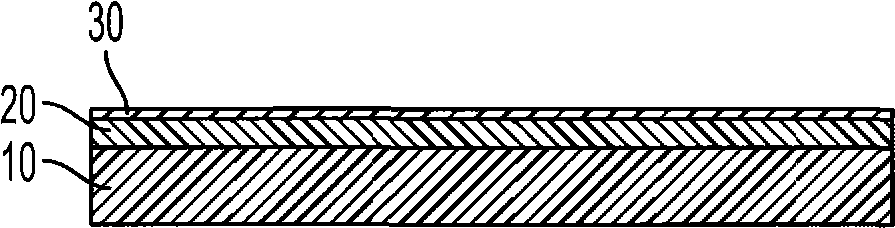
[0078] A nitride passivation layer is formed on the top surface of the silicon semiconductor substrate. Holes are formed in the nitride passivation layer using laser direct writing. Each of the plurality of holes has a diameter of about 20 μm and a pitch of about 0.25 mm. A Ni conductive contact layer is deposited on the nitride passivation layer and within the plurality of holes formed in the nitride passivation layer. The thickness of the Ni contact layer is about 100 nm.
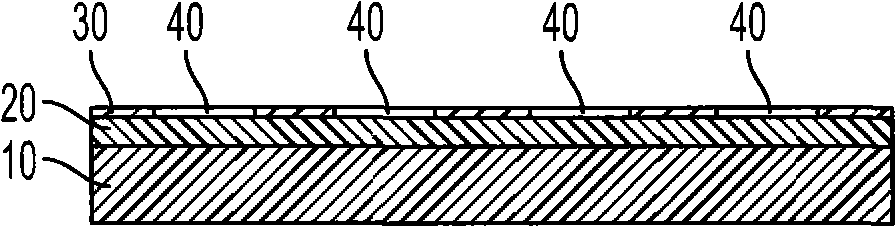
[0079] An Ag paste is deposited via screen printing on the Ni conductive contact layer in alignment or registration with the plurality of holes formed in the nitride passivation layer. Next, the silicon substrate was fired at about 500° C. to form an Ag / Ni multilayer electrode structure with sintered current-carrying Ag gridlines.
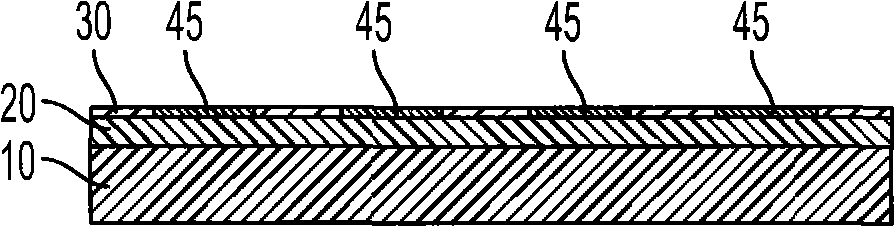
[0080] The contact resistance of the Ag / Ni multilayer electrode was about less than 0.03 ohms for a wire about 25.4 mm long. In addition, the contact resistance of the Ag / ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com