Risk evaluation method and system based on security dependence relation
A dependency and risk assessment technology, applied in the field of security risk assessment of computer network information systems, can solve security threats, ignore risk propagation, spread to other hosts or even the entire network, and achieve accurate risk assessment
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
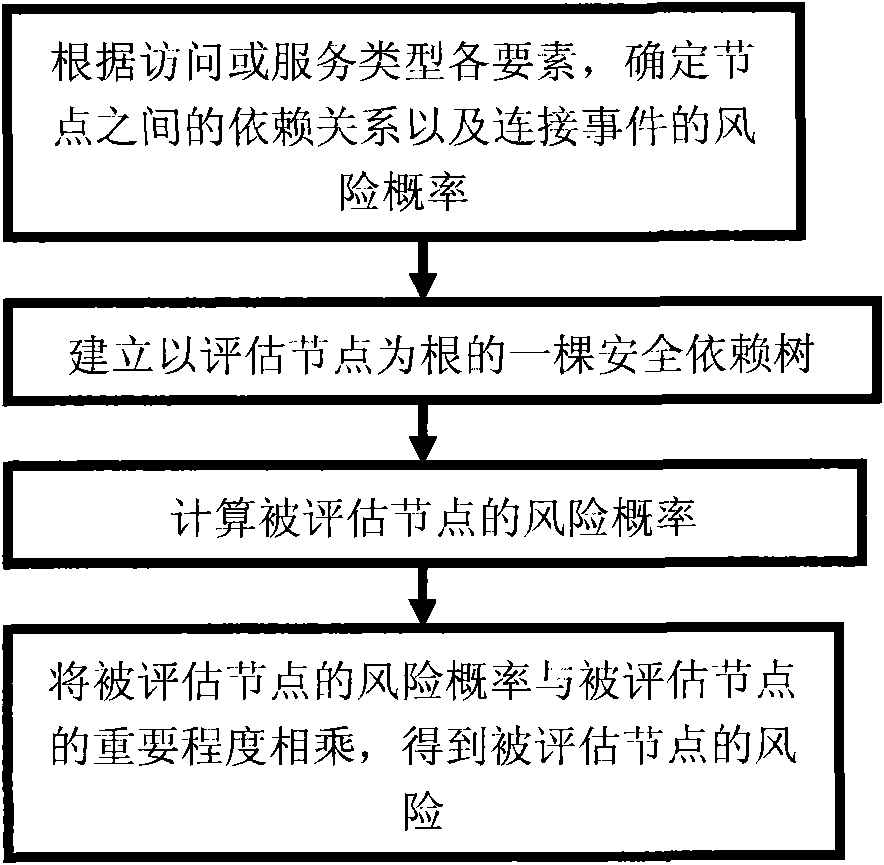
[0019] This embodiment is a risk assessment method based on security dependencies, the hardware used by the method includes: the Internet, and the steps of the method are as follows:
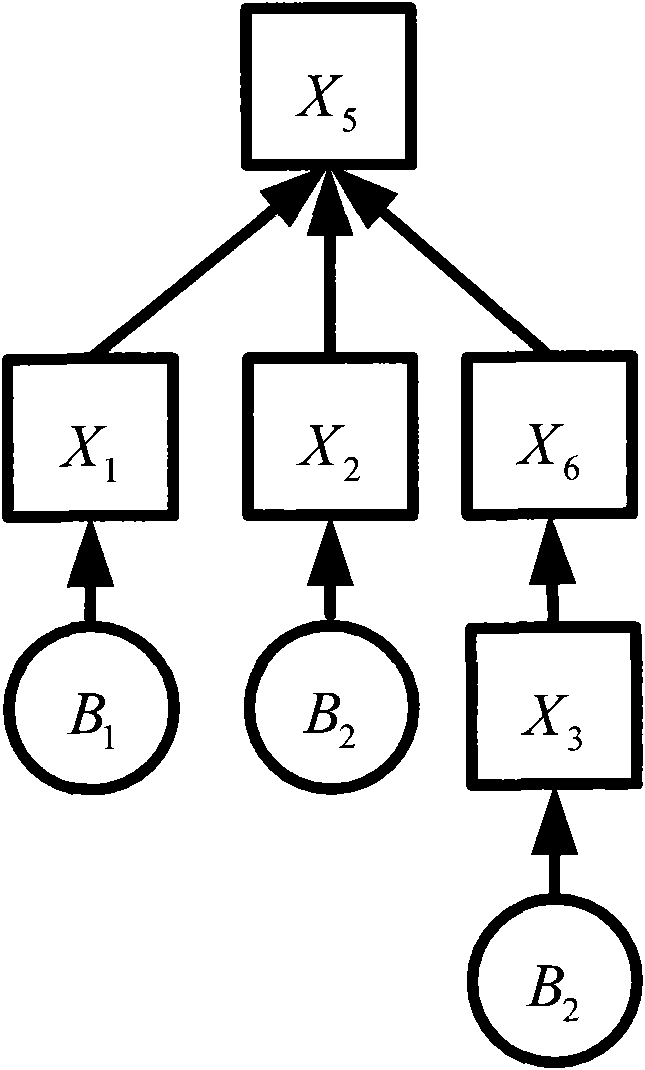
[0020] Step 1: According to the elements of access or service type, determine the risk probability of connection events between dependent nodes. Establish a dependency network between nodes and evaluate the probability of each connection event. If node X i and x j There is a security dependency between Then establish the risk probability of its connection event with express.
[0021] Step 2: Establish a security dependency tree rooted at the evaluated node;
[0022] Step 3: Calculate the risk probability of the evaluated node;
[0023] Step 4: Multiply the risk probability of the evaluated node by the importance of the evaluated node to obtain the risk of the evaluated node. It can be expressed with a simple formula: R=V×P to calculate its risk. Where R represents the risk of the evalu...
Embodiment 2
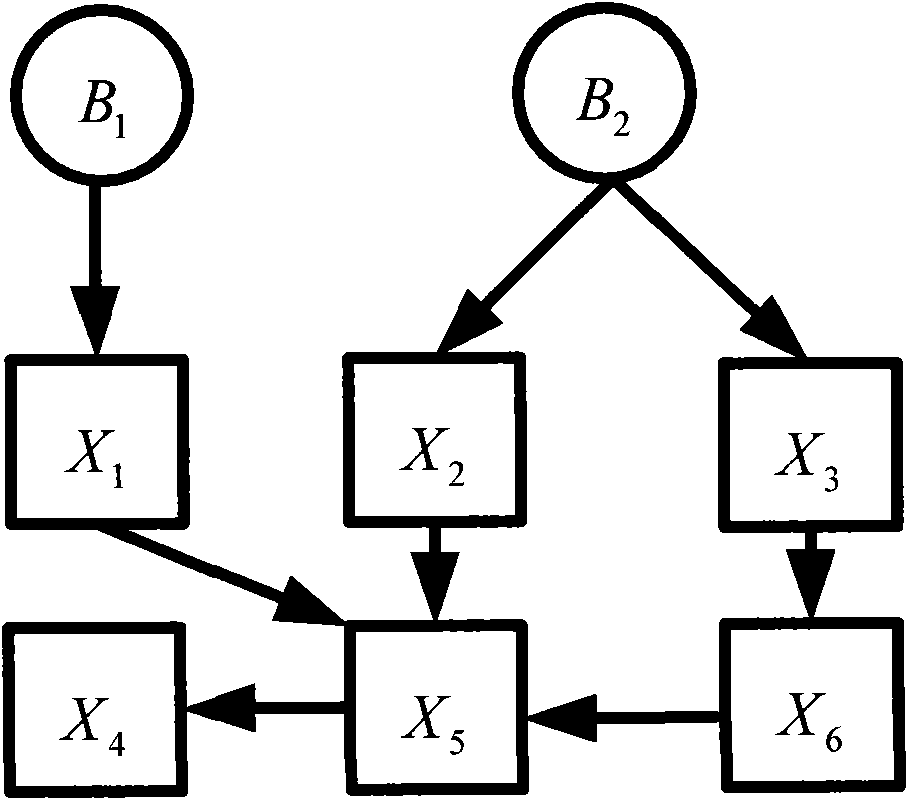
[0041] This embodiment is the preferred solution of Embodiment 1, which is a refinement of the step of establishing a security dependency tree rooted at the evaluated node in Embodiment 1, and the step of establishing a security dependency tree rooted at the evaluated node Substeps include:
[0042] (1). Take the target node to be evaluated as the starting root node of the security dependency tree, and add it to the security dependency tree;
[0043] (2). For each newly added node of the security dependency tree, add all its directly dependent nodes as its direct child nodes to the security dependency tree;
[0044] (3). If the newly-added node in the substep (2) is already the root node of a certain subtree that includes the node, then delete the branch of the root node that includes the newly-added node;
[0045] (4). Repeat steps (2) to (3) above until the dependency tree no longer grows, and finally form a safe dependency tree without loops.
Embodiment 3
[0047] This embodiment is a preferred solution of Embodiment 1. In Embodiment 1, the step of calculating the risk probability of the evaluated node is refined, and the sub-steps include:
[0048] (1). Take the node to be evaluated as the starting root node, stratify according to the distance between each node and the starting root node, and according to the formula
[0049] P ( Y ) = P ( U i = 1 n X i E X i , Y ) = 1 - Π i = 1 n ( 1 ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com