Method for preparing ZSM-5 zeolite by in situ crystallization
A ZSM-5, in-situ crystallization technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, crystalline aluminosilicate zeolite, borocarbonane silicone crystalline aluminosilicate zeolite, etc. The pore area and micropore volume are small, and the method is complicated to achieve the effect of high zeolite content, abundant mesopores, and increased micropore volume.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
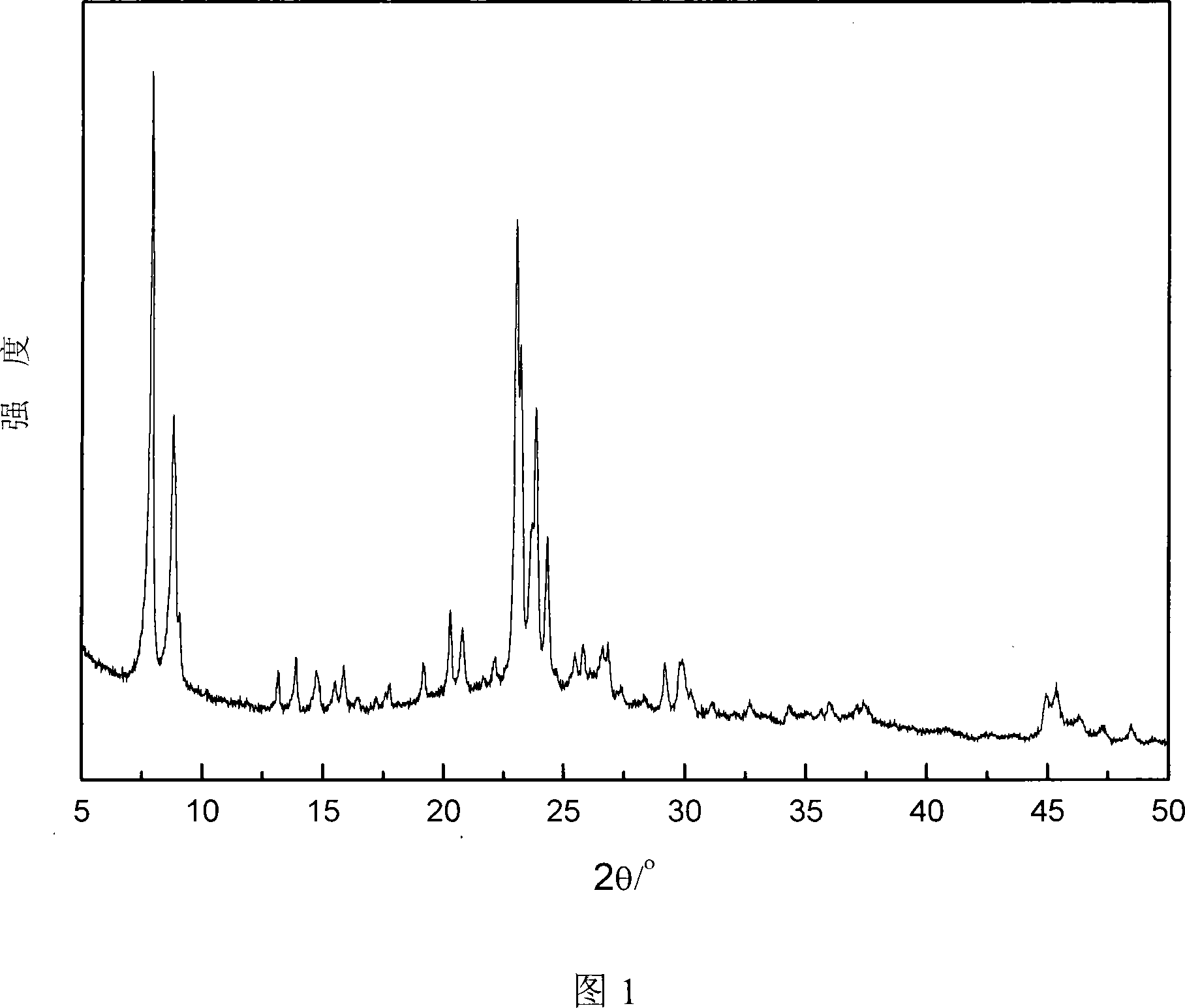
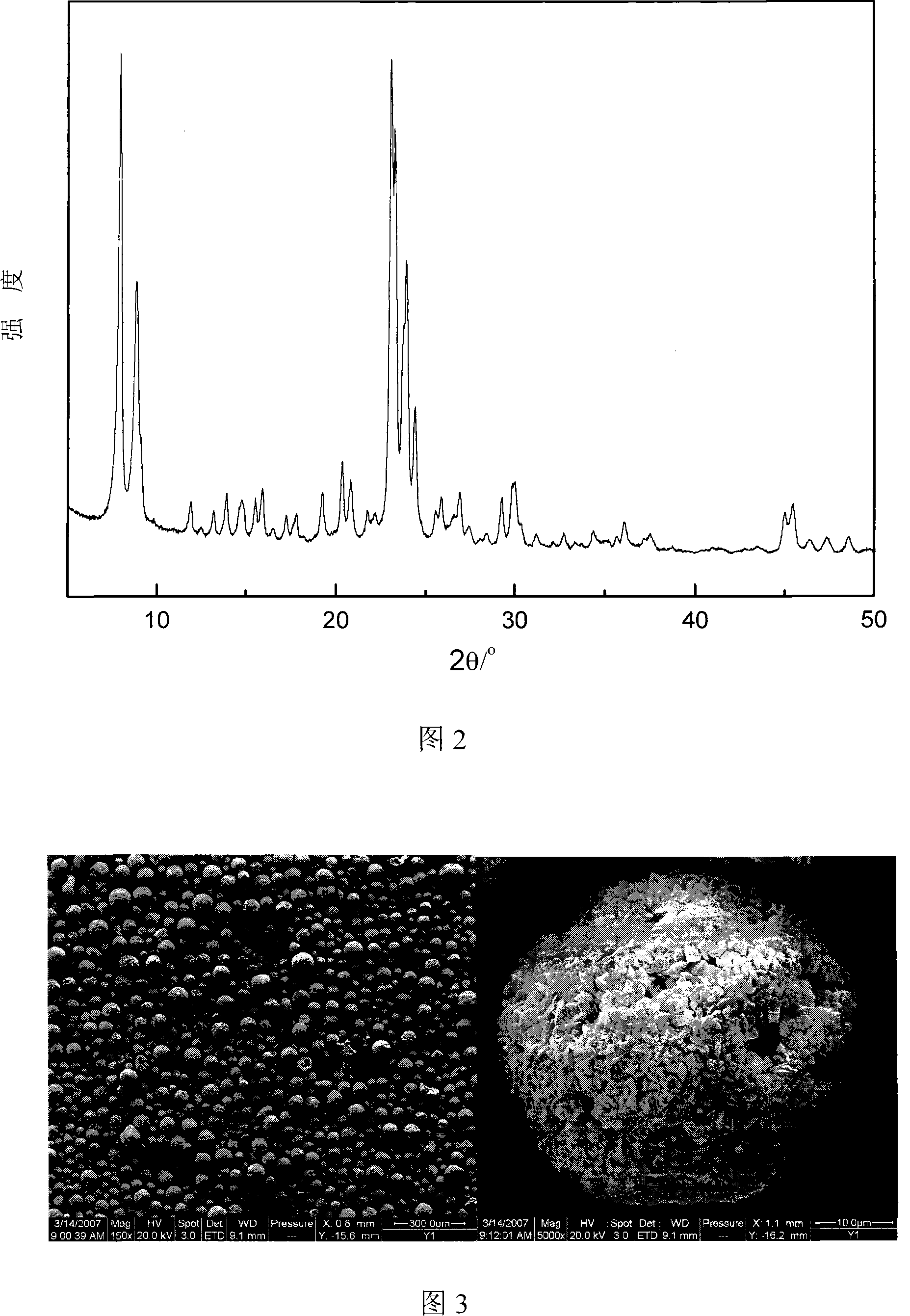
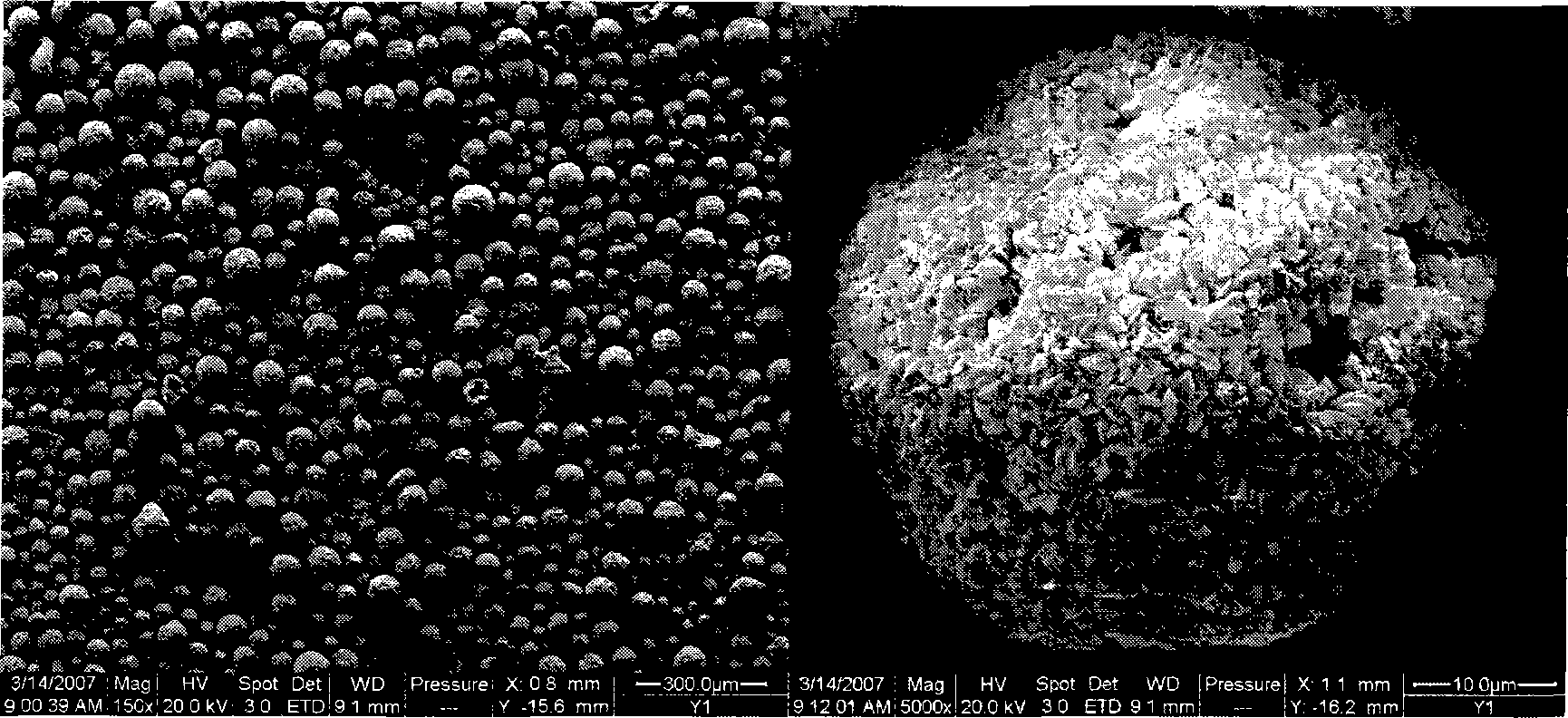
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0038] 1. Preparation of microspheres
[0039] Add kaolin, diatomite, bentonite, silica sol and water into a gel tank and mix homogeneously so that the solid content of the slurry is 30% by weight. The slurry is spray-dried to obtain microspheres with an average particle diameter of 50 μm. The microspheres were washed twice with decationized water of pH=2-4 at a mass ratio of 10:1 to the microspheres. The properties of raw materials are shown in Table 1, and the composition content of each component in the slurry is calculated on a dry basis in Table 2.
[0040] Table 1
[0041] raw material
place of origin
Chemical composition (dry basis, mass%)
SiO 2
Al 2 o 3
Na 2 o
K 2 o
MgO
CaO
Fe 2 o 3
TiO 2
Kaolin
China Kaolin Company
52.8
44.3
0.07
0.42
0.07
0.26
0.70
0.66
Guangxi Baolixi Quarry Co., Ltd.
limited company
51
...
Embodiment 2
[0050] 1. Preparation of microspheres
[0051] Microspheres were prepared according to the method for preparing microspheres described in Example 1, except that the slurry was prepared according to the formula in Example 2 in Table 2.
[0052] 2. Calcination of microspheres and in situ hydrothermal crystallization
[0053] The obtained microspheres were calcined at a temperature of 800° C. for 3 hours to obtain calcined microspheres, and the active SiO2 in the calcined microspheres 2 The content is 65% by weight.
[0054] Get the microsphere after 23.8g roasting, mix with 1.42g sodium hydroxide and 67.5g water, wherein the active SiO in the microsphere 2 with OH - The molar ratio is 1:0.14. The mixture was moved into a stainless steel kettle with a polytetrafluoroethylene liner, and was subjected to static constant temperature crystallization at a temperature of 170° C. for 12 hours, and then the solid product was separated, filtered with suction, washed and dried to obtai...
Embodiment 3
[0057] 1. Preparation of microspheres
[0058] Microspheres were prepared according to the method for preparing microspheres described in Example 1, except that the slurry was prepared according to the formula in Example 3 in Table 2.
[0059] 2. Calcination of microspheres and in situ hydrothermal crystallization
[0060] The obtained microspheres were calcined at a temperature of 700° C. for 4 hours to obtain calcined microspheres, and the active SiO2 in the calcined microspheres 2 The content is 53% by weight.
[0061] Get 14.3g calcined microspheres, mix with 1.95g sodium hydroxide, 3.51g n-butylamine and 108g water, wherein the active SiO in the microspheres 2 with OH - The molar ratio is 1:0.39, the active SiO 2 The molar ratio to n-butylamine is 1:0.38. Move the mixture into a stainless steel kettle with a polytetrafluoroethylene liner, raise the temperature from room temperature to 110°C within 1 hour, dynamically crystallize at a temperature of 110°C for 20 hours...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com