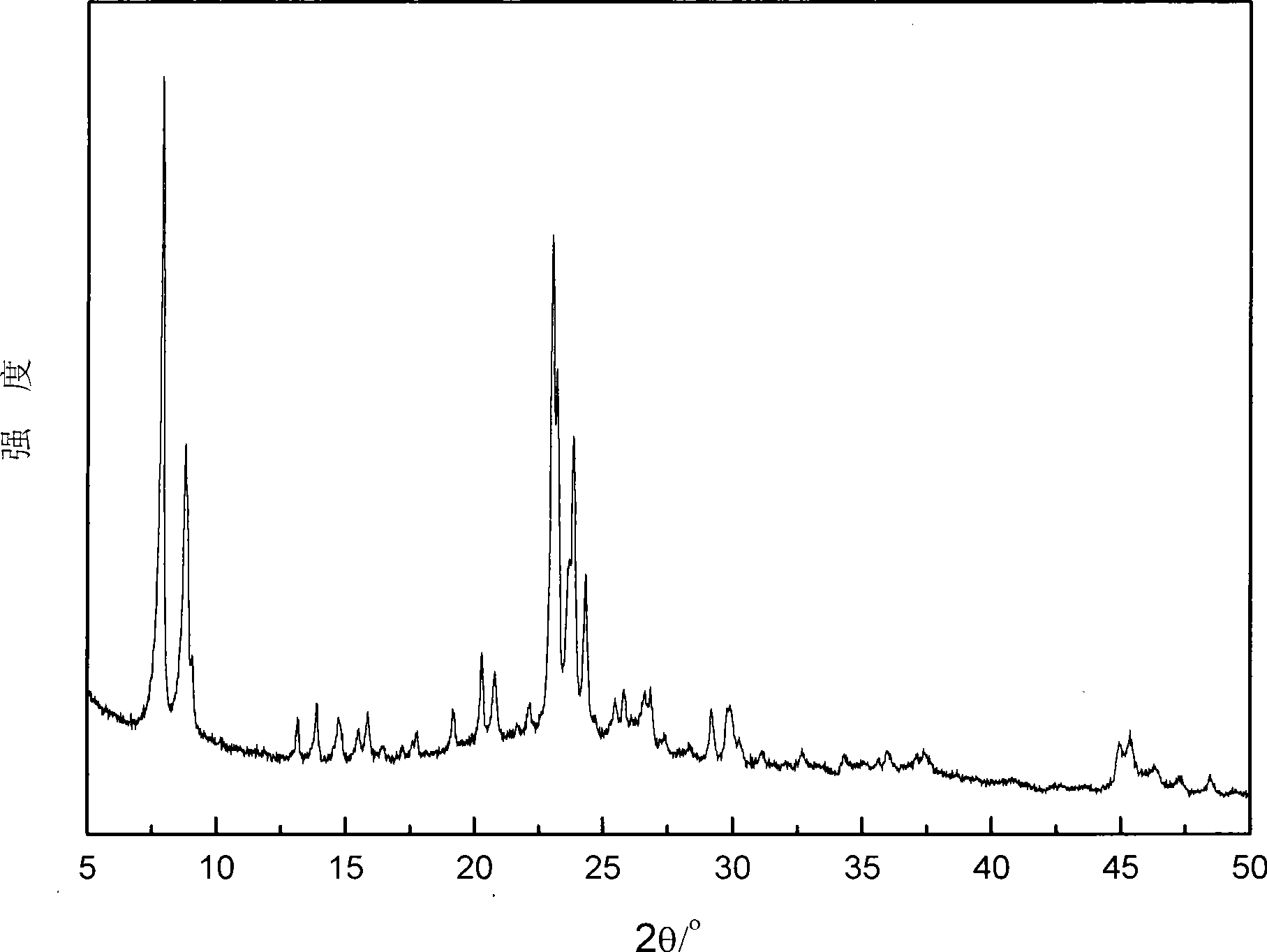
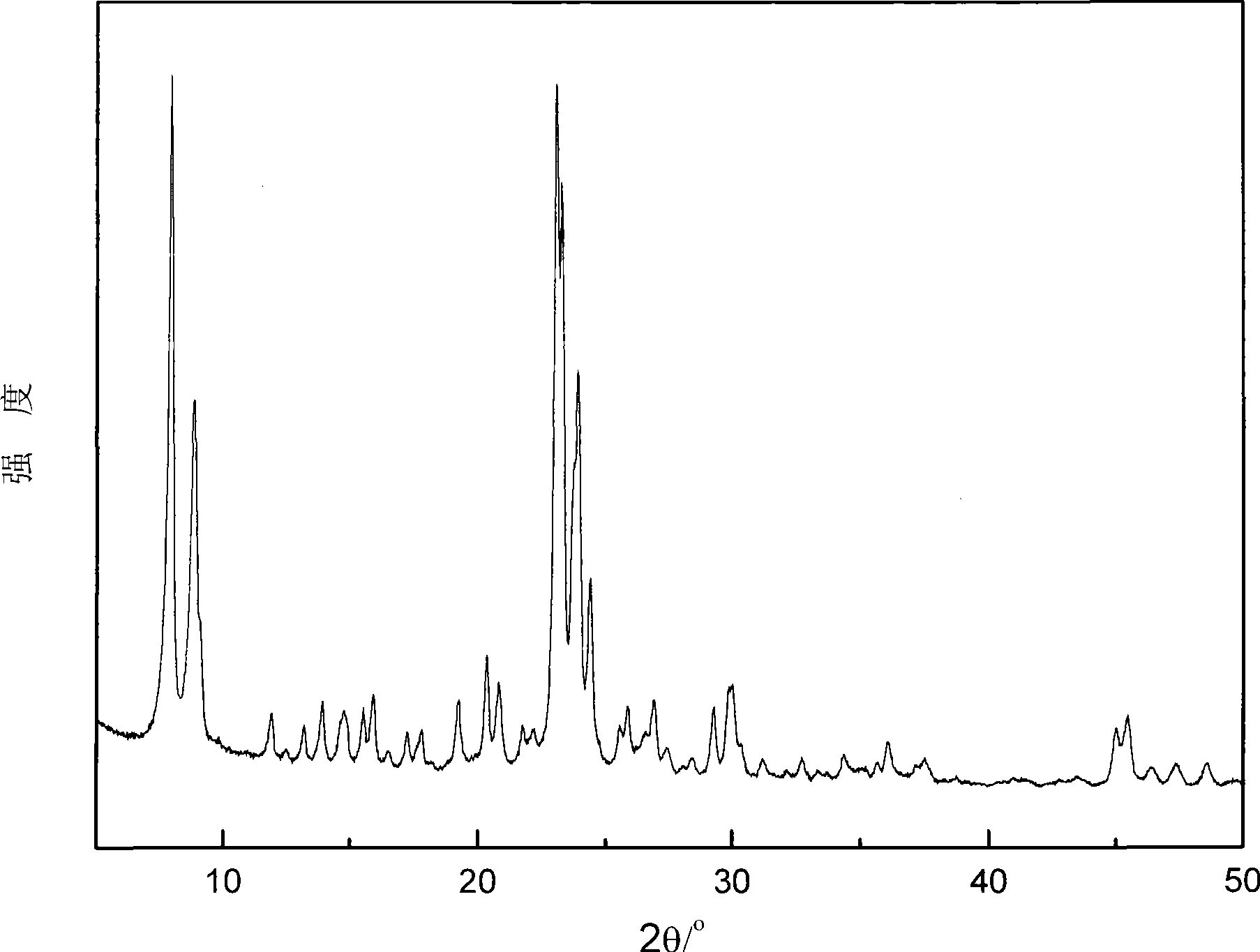
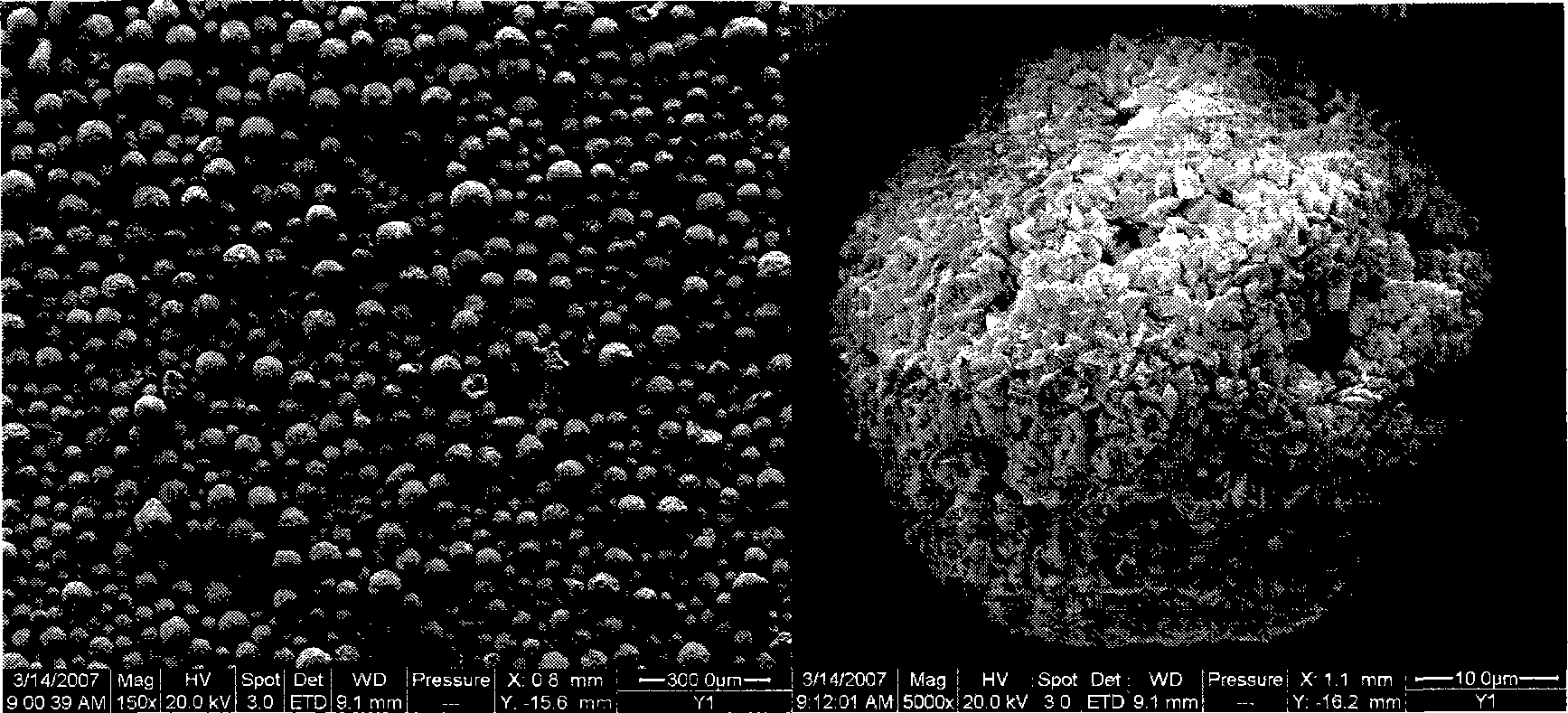
Method for preparing ZSM-5 zeolite by in situ crystallization
An in-situ crystallization, ZSM-5 technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, crystalline aluminosilicate zeolite, borocarbane silicone crystalline aluminum silicate zeolite, etc., can solve the problem of small micropore area and micropore volume , Complicated methods, low ZSM-5 zeolite content, etc., to achieve the effect of rich mesopores, increased micropore volume, and high zeolite content
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0038] 1. Preparation of microspheres
[0039] Add kaolin, diatomite, bentonite, silica sol and water into a gel tank and mix homogeneously so that the solid content of the slurry is 30% by weight. The slurry is spray-dried to obtain microspheres with an average particle diameter of 50 μm. The microspheres were washed twice with decationized water of pH=2-4 at a mass ratio of 10:1 to the microspheres. The properties of raw materials are shown in Table 1, and the composition content of each component in the slurry is calculated on a dry basis in Table 2.
[0040] Table 1
[0041]
[0042] Table 2
[0043] Composition (dry basis, parts by weight, adhesive is SiO 2 count) Example 1 Kaolin 5, diatomaceous earth 35, bentonite 45, silica sol 15 Example 2 Kaolin 45, diatomaceous earth 35, water glass 20 Example 3 Kaolin 20, pyrophyllite 60, silica sol 20 Example 4 Kaolin 70, diatomaceous earth 1, ZSM-5 zeolite variety 5, silica sol 24 ...
Embodiment 2
[0049] 1. Preparation of microspheres
[0050] Microspheres were prepared according to the method for preparing microspheres described in Example 1, except that the slurry was prepared according to the formula in Example 2 in Table 2.
[0051] 2. Calcination of microspheres and in situ hydrothermal crystallization
[0052] The obtained microspheres were calcined at a temperature of 800° C. for 3 hours to obtain calcined microspheres, and the active SiO2 in the calcined microspheres 2 The content is 65% by weight.
[0053] Get the microsphere after 23.8g roasting, mix with 1.42g sodium hydroxide and 67.5g water, wherein the active SiO in the microsphere 2 with OH - The molar ratio is 1:0.14. The mixture was moved into a stainless steel kettle with a polytetrafluoroethylene liner, and was subjected to static constant temperature crystallization at a temperature of 170° C. for 12 hours, and then the solid product was separated, filtered with suction, washed and dried to obtai...
Embodiment 3
[0056] 1. Preparation of microspheres
[0057] Microspheres were prepared according to the method for preparing microspheres described in Example 1, except that the slurry was prepared according to the formula in Example 3 in Table 2.
[0058] 2. Calcination of microspheres and in situ hydrothermal crystallization
[0059] The obtained microspheres were calcined at a temperature of 700° C. for 4 hours to obtain calcined microspheres, and the active SiO2 in the calcined microspheres 2 The content is 53% by weight.
[0060] Get 14.3g calcined microspheres, mix with 1.95g sodium hydroxide, 3.51g n-butylamine and 108g water, wherein the active SiO in the microspheres 2 with OH - The molar ratio is 1:0.39, the active SiO 2 The molar ratio with n-butylamine is 1:0.38. Move the mixture into a stainless steel kettle with a polytetrafluoroethylene liner, raise the temperature from room temperature to 110°C within 1 hour, dynamically crystallize at a temperature of 110°C for 20 hou...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com