Anti-resonance vibrating sifter
An anti-resonance, vibrating screen technology, applied in the direction of filter screen, solid separation, grille, etc., can solve the problems of heavy machine weight, easy fatigue damage of screen box, high noise, etc., and achieve the effect of reducing motor power
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0061] The detailed structure of the present invention is described in conjunction with the following examples and accompanying drawings.
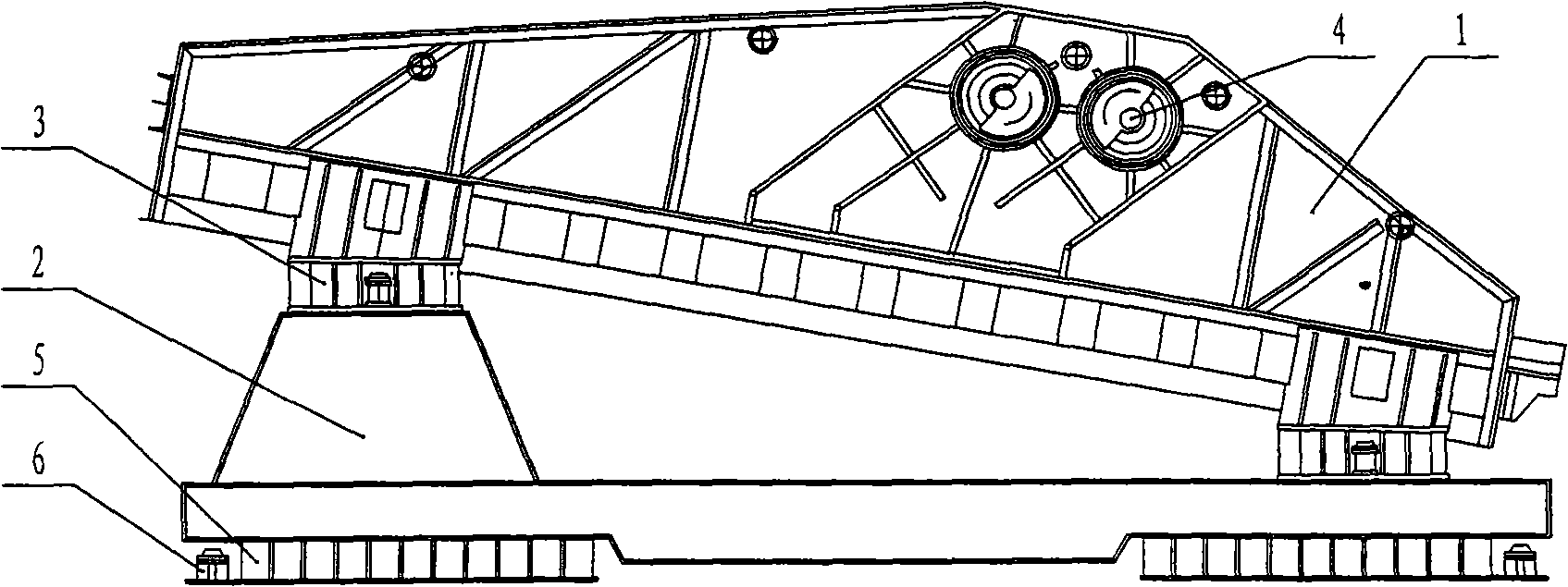
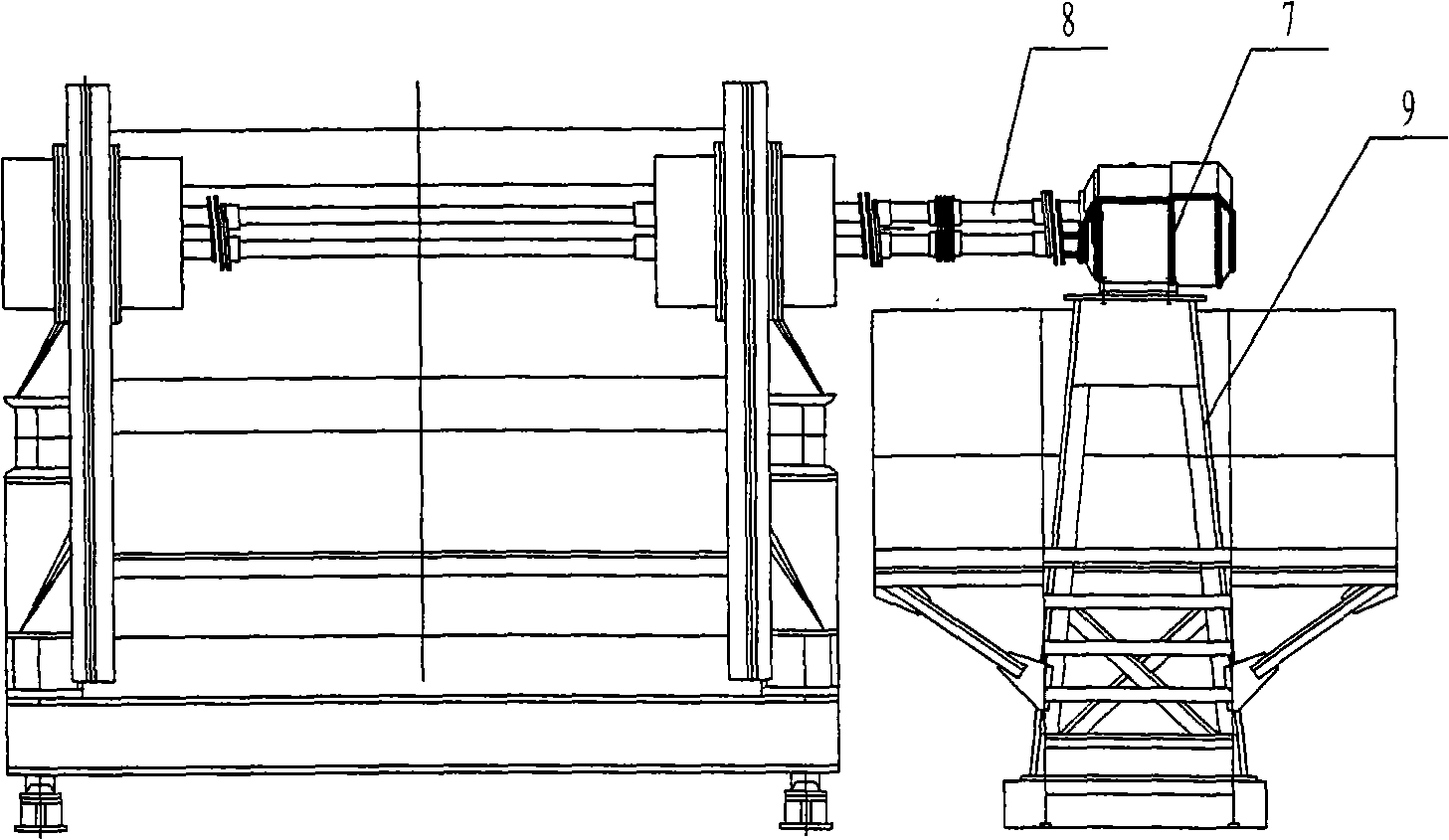
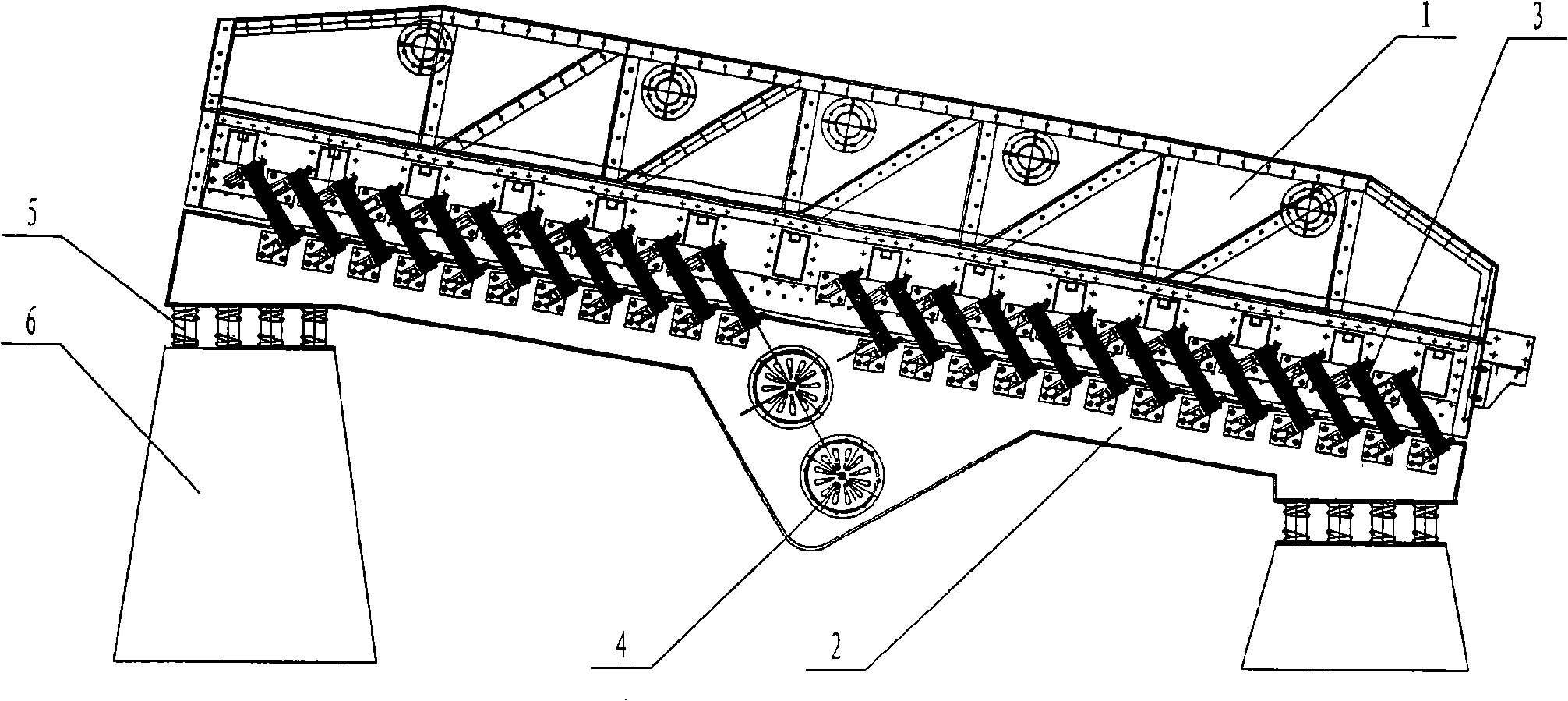
[0062] The structure of the present invention is as image 3 As shown, the upper plastid of the screen box (1) is the working part of the anti-resonance vibrating screen, the lower plastid of the exciter (2) is the driving part, and the exciter (4) is installed on the exciter (2). The screen box (1) and the vibrating body (2) are connected through the main vibration spring (3), the vibrating body (2) is seated on the foundation (6) through the vibration isolation spring (5), and the motor (7) is installed on the on the motor bracket (9), and connected to the exciter (4) through the transmission shaft (8); the main vibration spring in this embodiment is a leaf spring, which is divided into multiple groups, each group has multiple pieces, and the total stiffness of the main vibration spring is easy to adjust. Mass ratio of upper and lower p...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com