No dead lock plane self-adapted routing method in 3-D mesh
An adaptive, deadlock-free technology, applied in data exchange networks, digital transmission systems, electrical components, etc., can solve the problem of not being used, and achieve the effect of reducing transmission delay, improving transmission performance, and increasing actual traffic.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
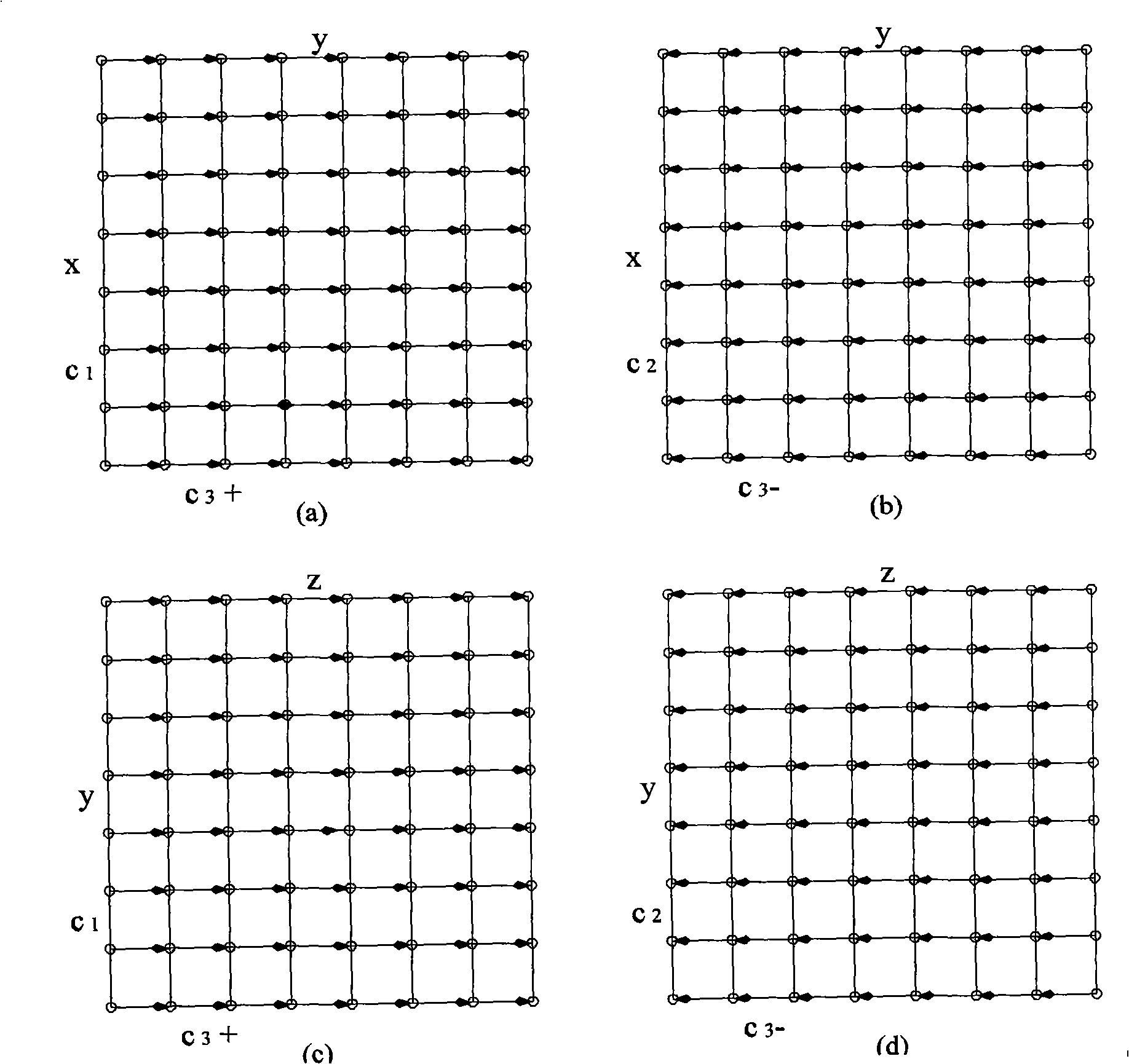
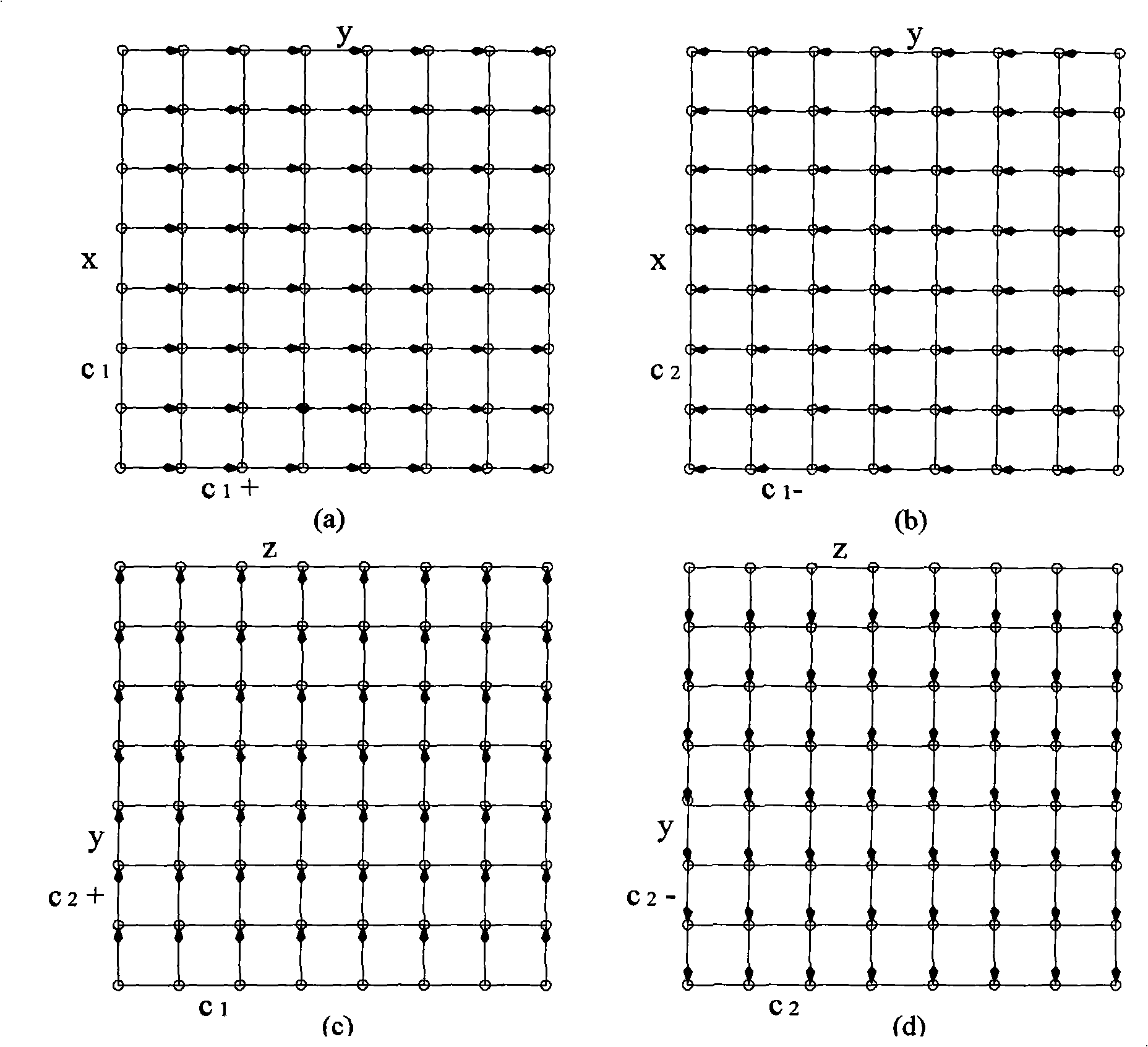
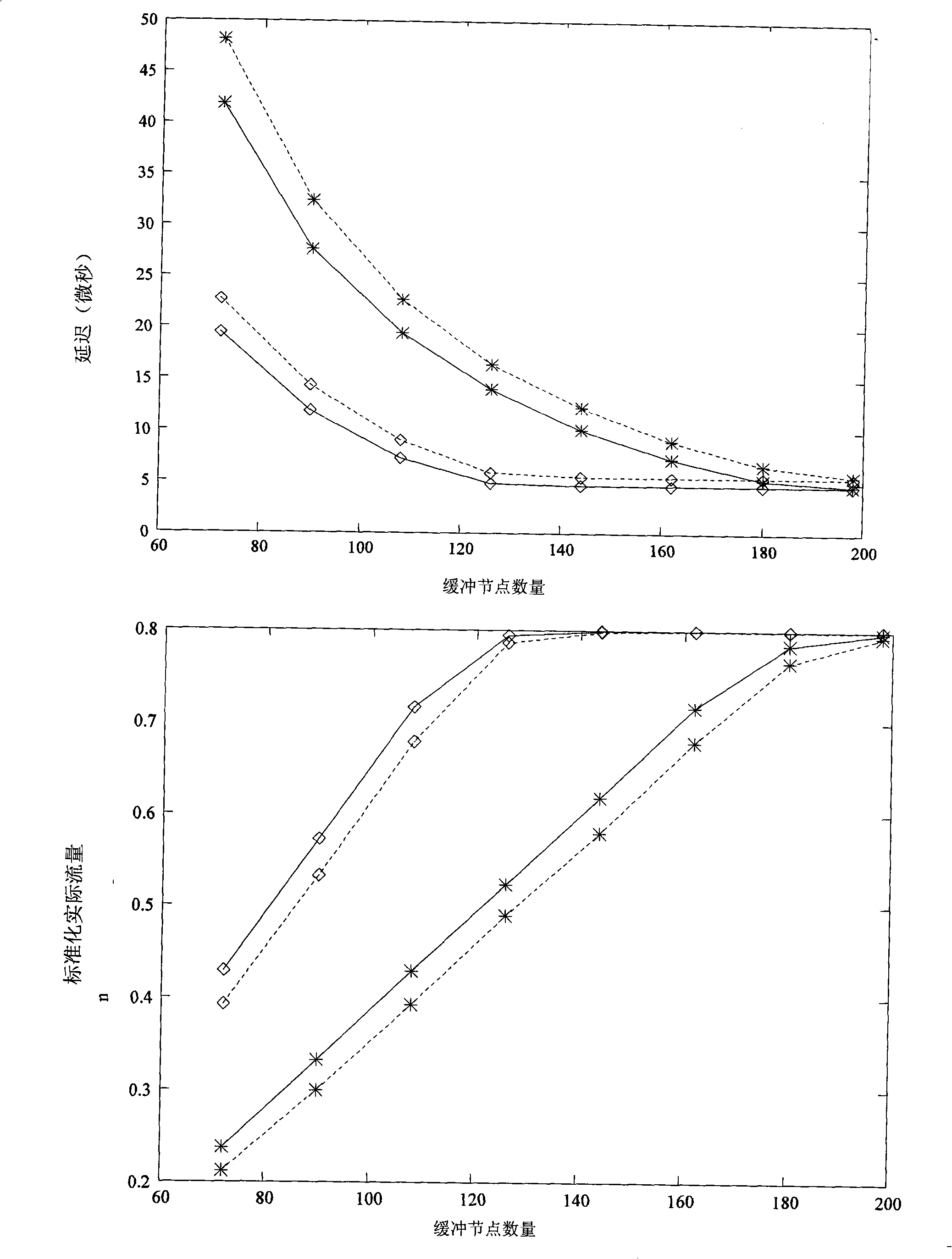
[0053] Based on the above virtual channel allocation strategy, we propose a new adaptive deadlock-free routing method. In general, the routing message is first routed on the x-y plane, and when the offset in the x direction becomes 0, it jumps to the y-z plane. Continue routing. When starting x-y plane routing, according to the offset direction in the y direction between the source node and the target node, choose to insert the message into the ascending subnet or the descending subnet, and always keep routing in this subnet. When jumping to the y-z plane, the ascending or descending subnet is also selected according to the offset direction in the y-direction and the routing in this subnet is maintained in the y-z plane. The routing methods in the x-y ascending subnet, x-y descending subnet and y-z plane ascending subnet are described as follows. The routing method of the descending subnet in the y-z plane is similar to the method in the ascending subnet, and the channel in t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com