Ethernet loop protection method and apparatus
An Ethernet and ring protection technology, applied in the Ethernet field, can solve problems such as difficult to achieve fault recovery, and achieve the effect of simple implementation and strong compatibility
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
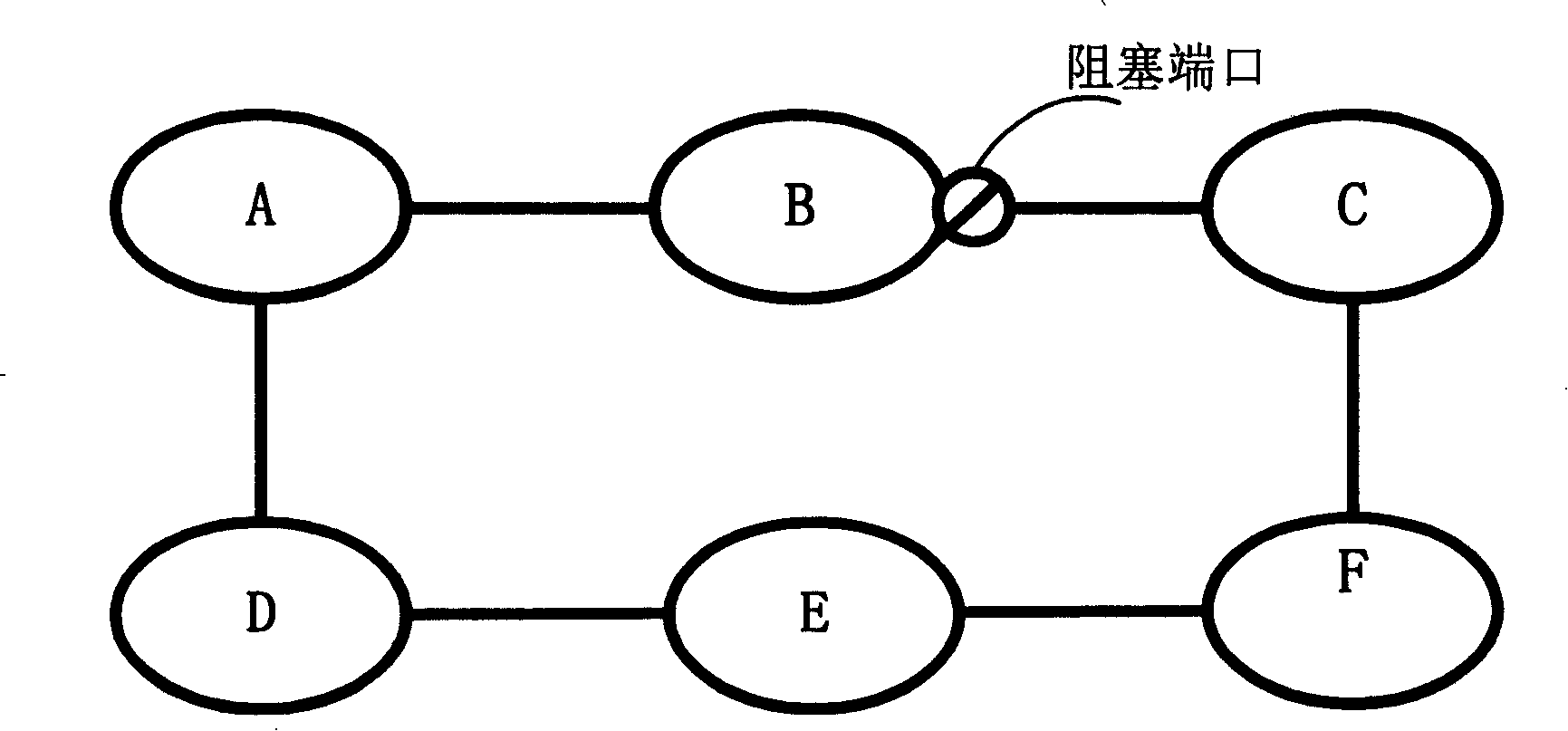
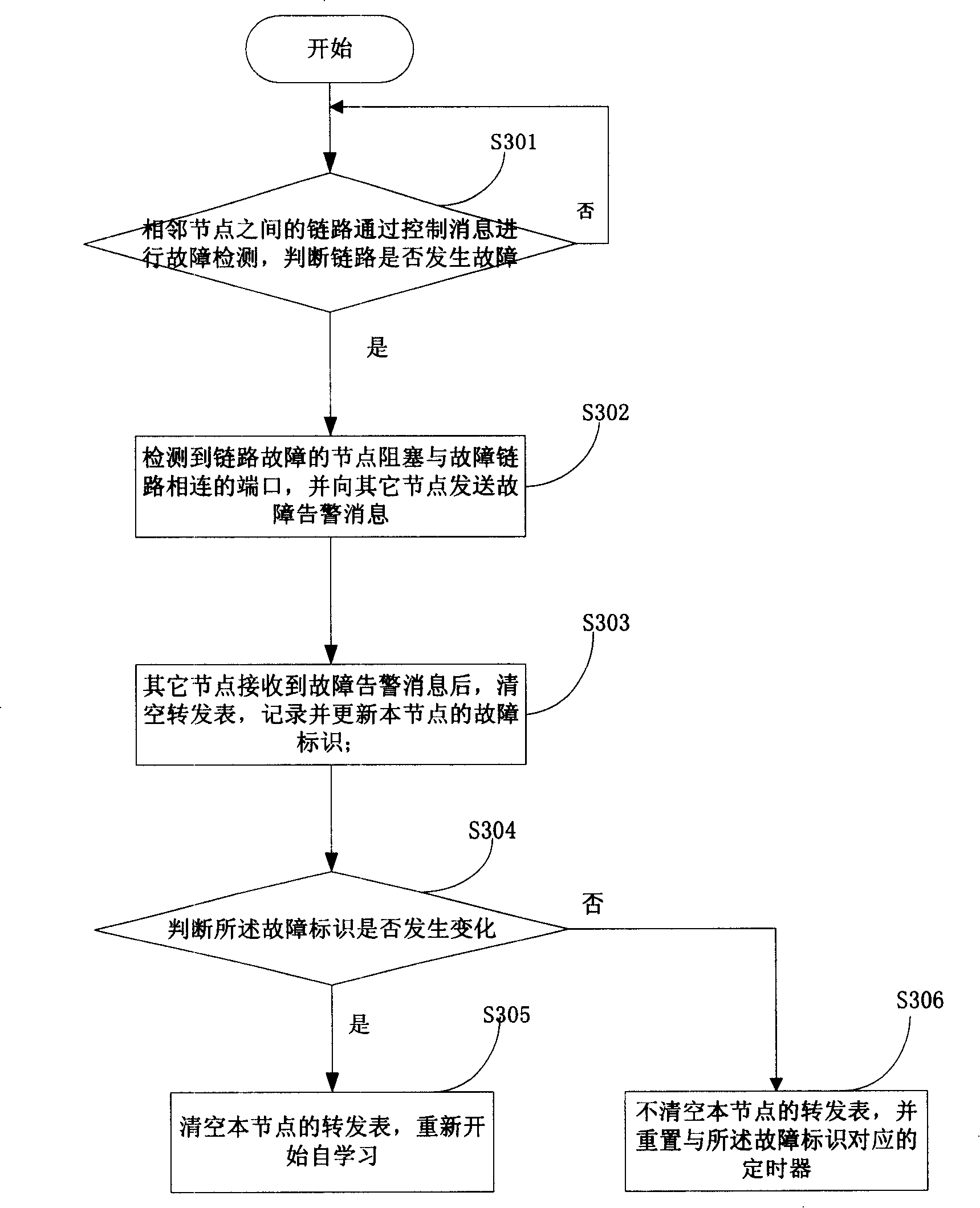
[0063] Please see image 3 , image 3 It is a specific flowchart of the Ethernet ring protection method disclosed in Embodiment 1 of the present invention. Such as image 3 As shown, the method includes:
[0064] Step S301, the link between the adjacent nodes performs fault detection through the control message, and judges whether the link has a fault, if yes, execute step S302, otherwise continue to execute step S301;
[0065] In this step, the control message may be a CC message, and CC messages may be used to detect faults between nodes on the Ethernet ring network. Each node periodically sends a CC message to its adjacent nodes, and the node that receives the CC message directly terminates the message and does not continue to forward it to other nodes. When the node does not receive the CC message within a predetermined time period, it can be determined that the link between the node and the adjacent node fails. The specific process of using the CC message to detect l...
Embodiment 2
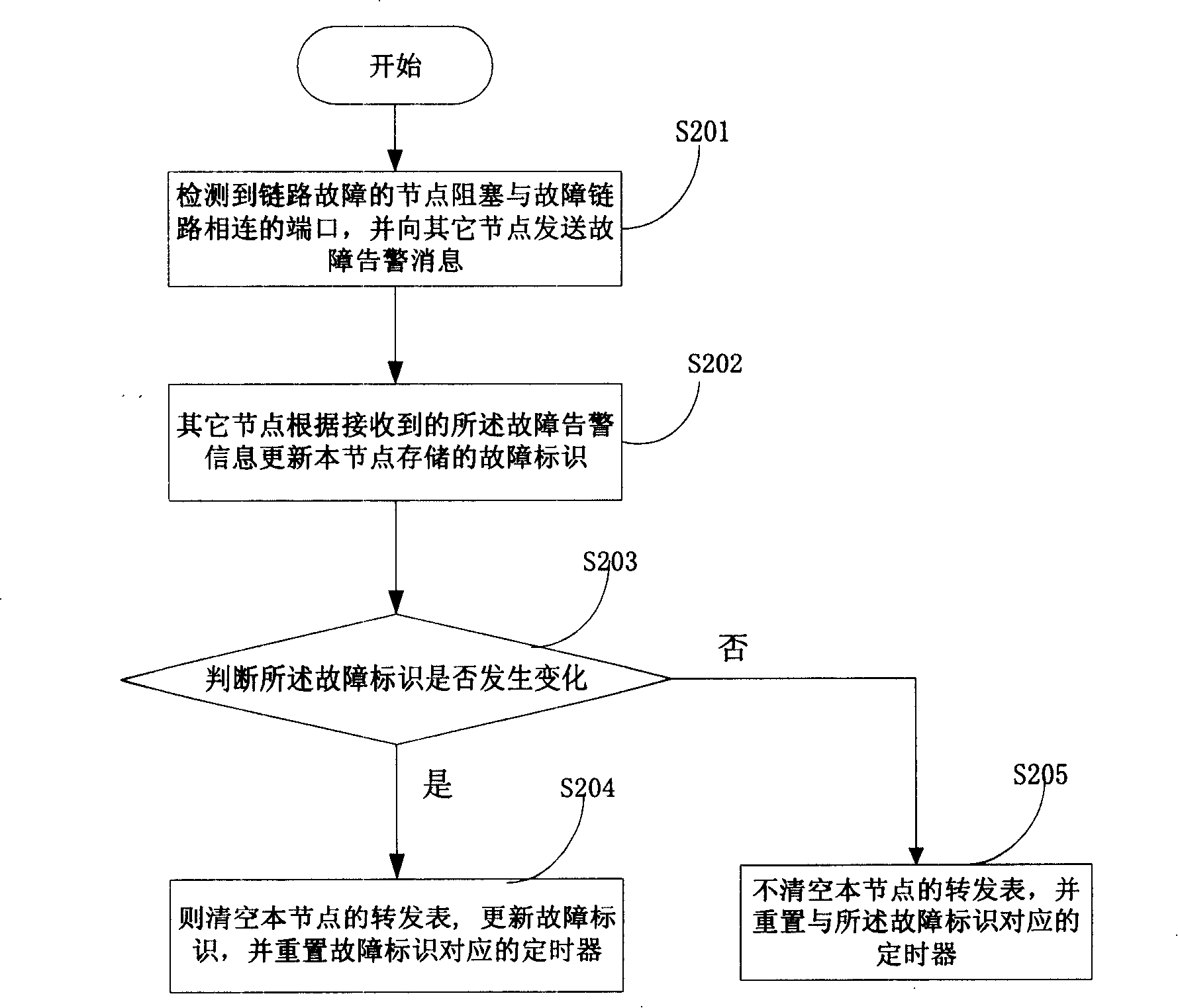
[0085] Embodiment 1 describes the specific implementation of the present invention when a single link fails on the Ethernet ring network. This embodiment further illustrates the specific implementation of the present invention by taking multiple faults on the Ethernet ring network and fault recovery as an example.
[0086] In this embodiment, when a node detects a link, its specific method flow is the same as that in Embodiment 1, and will not be repeated here. The difference between embodiment 2 and embodiment 1 is: when the link failure in embodiment 1 has not been recovered, when other links fail again, after the nodes on the ring network receive the AIS alarm information, they judge that the fault identification has changed, then Empty the forwarding table and re-learn. This process will be described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
[0087] Please see Image 6 , Image 6 It is a schematic diagram when multiple faults occur on the Ethernet ...
Embodiment 3
[0090] The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 and Embodiment 2 is that each node receiving the fault information in this embodiment no longer stores and updates the fault identification composed of the source address of the alarm information, but each node only confirms the normal state and fault status. When the node that receives the fault alarm information receives the fault alarm information in the normal state, it clears the forwarding table and restarts self-learning; when the node that receives the fault alarm information receives the fault alarm information in the fault state, it does not clear the idling Instead, the timer corresponding to the fault condition is reset.
[0091] Further, if other nodes do not receive the control message again within a predetermined time, then change the state of this node from the fault state to a normal state, and clear the forwarding table of this node.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com