Novel plasmid autonomously replicable in enterobacteriaceae family
A kind of Enterobacteriaceae, plasmid technology, applied in the field of using the plasmid and microorganisms containing the plasmid
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
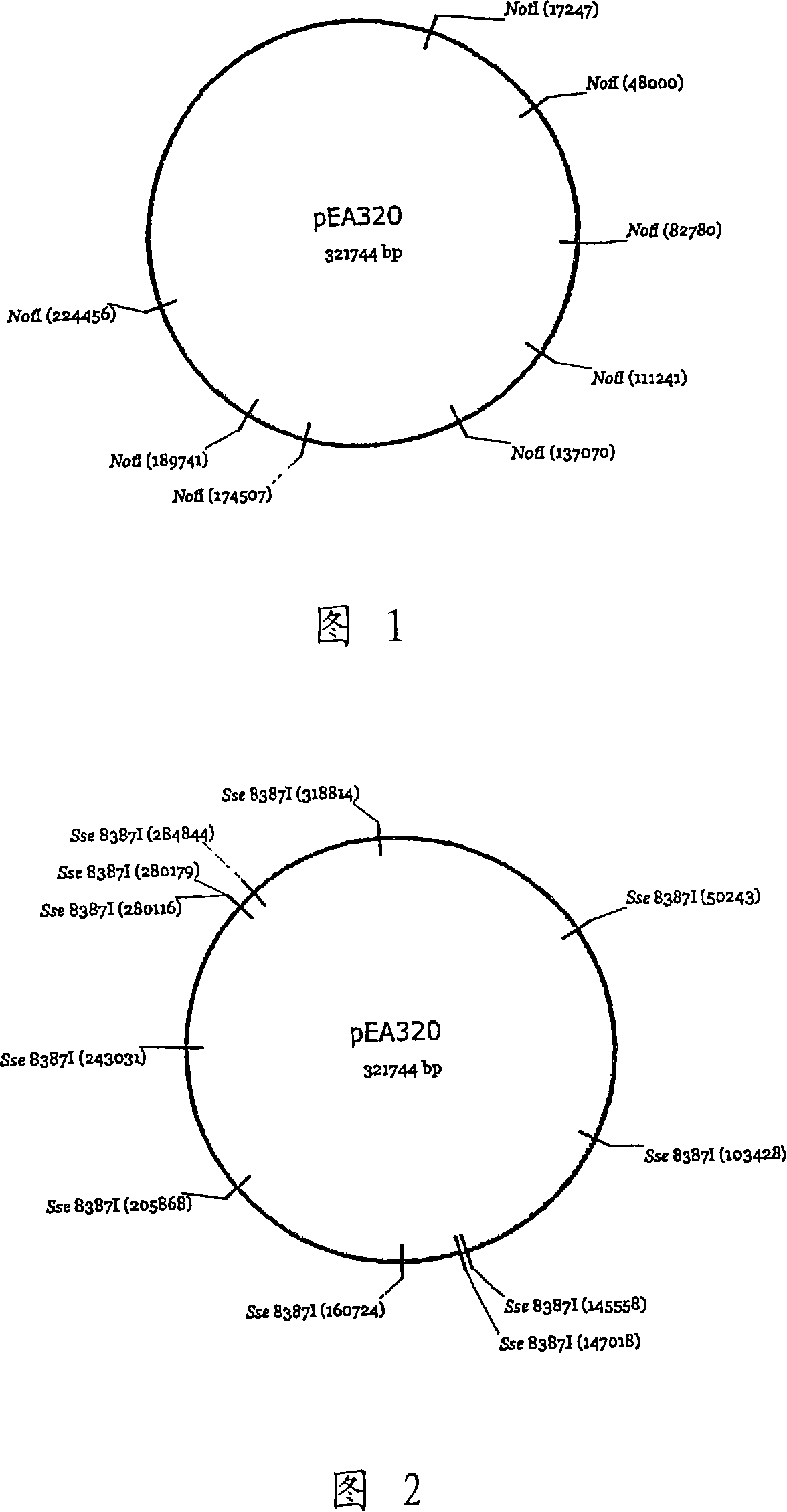
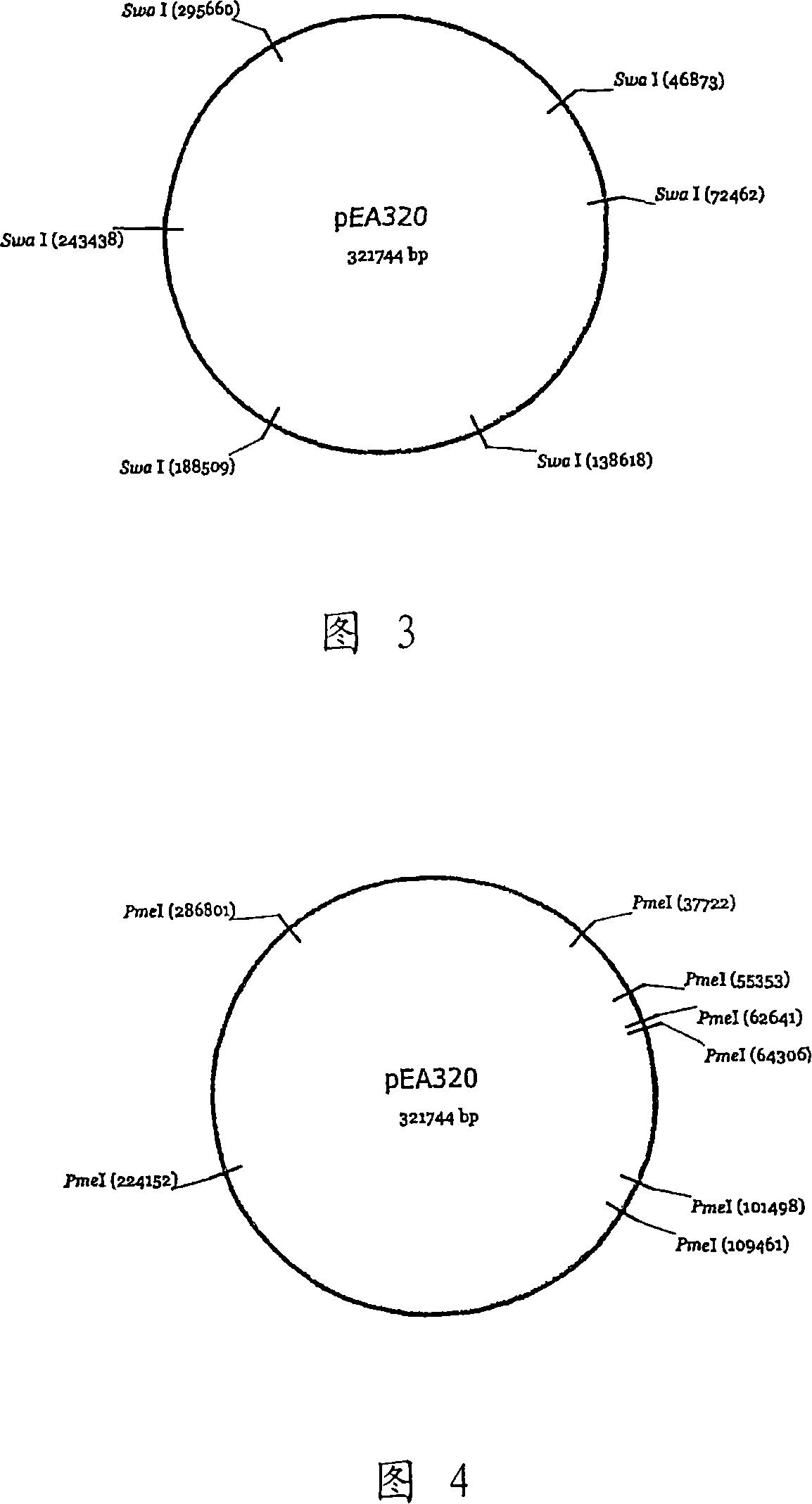
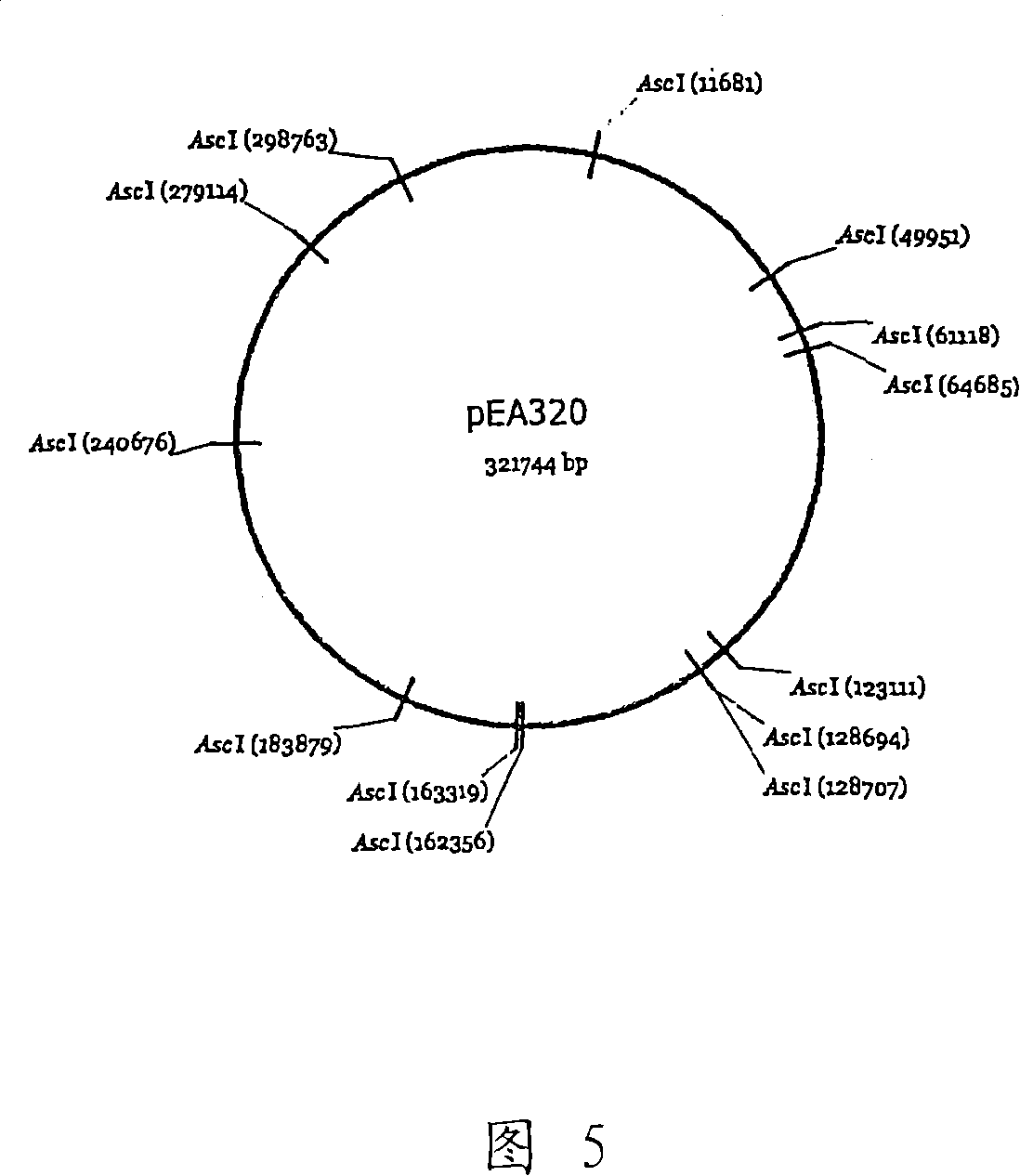
[0120] Because pEA320 is very large (approximately 320 kbs), it is difficult to isolate as circular DNA and difficult to use to transform strains. In addition, since neither a drug resistance gene nor a marker capable of dominant selection exists on the plasmid, it is necessary to introduce a marker gene to make dominant selection possible. Therefore, pUT399 was constructed to enable homologous recombination to occur, and thus, the strain could be selected using chloramphenicol (US Patent Application Publication No. 20040180404).
[0121] pUT399 was constructed as follows. The origin of replication of R6K and the mob of RP4 were amplified by PCR using pUT-miniTn5-Cm (which can be purchased from Biomedal) as template and P7 (SEQ ID NO: 9) and P8 (SEQ ID NO: 10) as primers Gene. In addition, when pHSG399 (TaKaRa) was used as template, and P9 (SEQ ID NO: 11) and P10 (SEQ ID NO: 12) were used as primers, a gene containing chloramphenicol resistance and a multiple cloning site we...
Embodiment 2
[0126]
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com