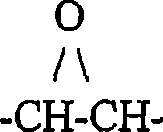Surfacing and/or joining method
A technology for polymers and products, applied in chemical instruments and methods, thin material handling, transportation and packaging, etc., can solve problems such as reduced performance of structural adhesives, undesired moisture absorption characteristics, etc., to reduce expensive costs, reliable and consistent production. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0072] Preparation of Curable Compositions
[0073] The curable composition of the method of the present invention can be prepared by combining at least one modifier in particulate form, at least one resin, and any other ingredients, optionally with stirring or agitation. The resin may be liquid, solid or a combination thereof, and the composition thus obtained may, for example, be in the form of a paste or a film, for example. Depending on the specific formulation and viscoelastic properties, such membranes may be handled with or without support materials (eg, built-in gauze or removable liners).
[0074] Preferably, the particulate modifier is well dispersed in the resin so that aggregation does not substantially occur. If desired, a solvent can be used to assist in binding and dispersion, provided that the selected solvent is one that does not significantly react with the ingredients of the composition, and does not significantly dissolve or swell the particulate modifier ...
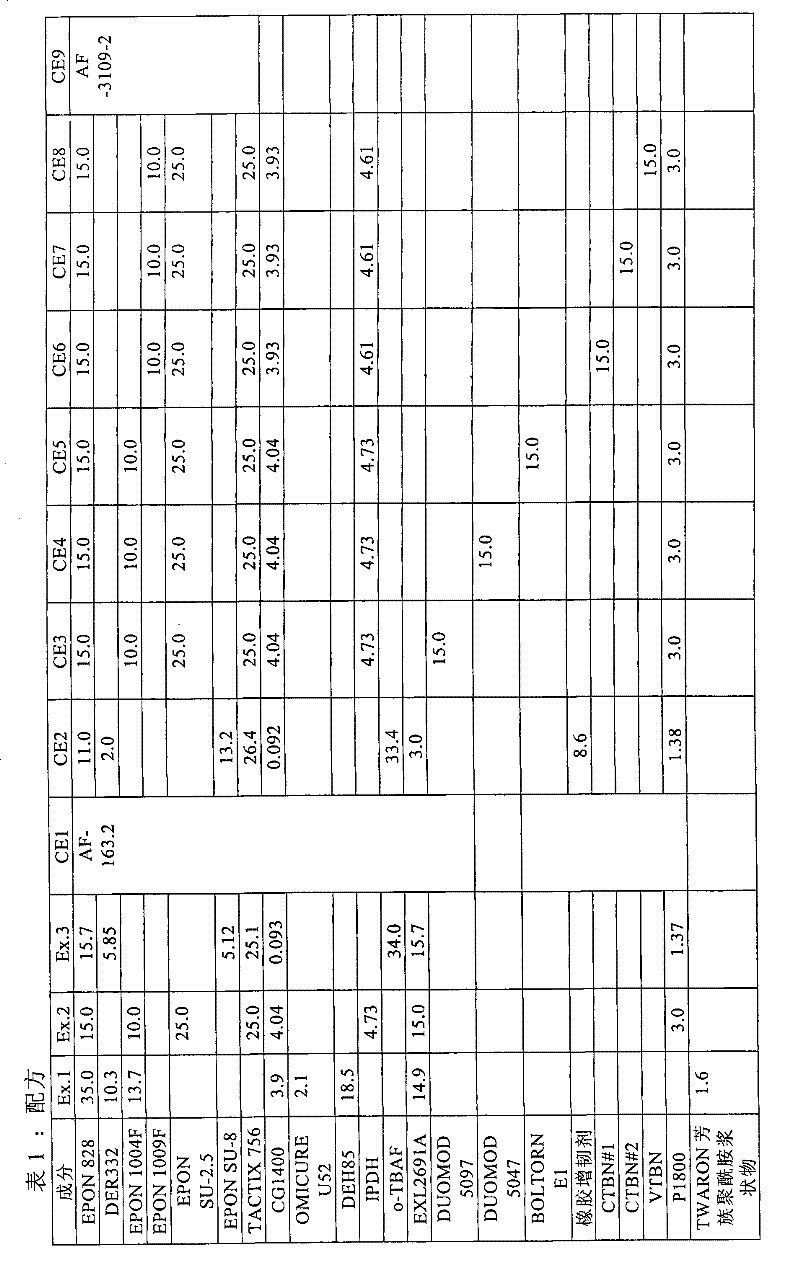
Embodiment 1—3 and comparative Embodiment 1—9
[0156]Examples 1-3 and Comparative Examples (CE) 1-9 in Tables 1, 3, and 4 below illustrate the role of various toughening modifiers in linking environmentally modified cured polymer-based composite articles together to provide Effects in connected structures. The stated amounts are provided in parts by weight (pbw), wherein the combined amount of all ingredients is between 99 and 102 pbw.
Embodiment 1
[0157] Example 1 and Comparative Example 1 were prepared as described above under "Preparing Cured Joints" using a cure cycle of 250°F (121°C) and then evaluated for Overlap Shear Strength (OLS) at 200°F (93°C). Examples 2 and 3 and Comparative Examples 2-9 were prepared as described above under "Preparing Cured Joints" using a cure cycle of 350°F (177°C) and then evaluated for overlap shear strength at 277°F (136°C) .
[0158]
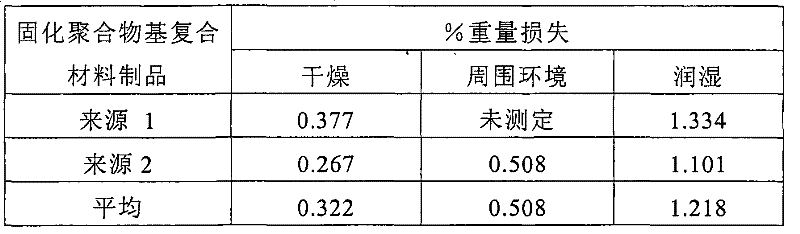
[0159] Moisture Content of Cured Polymer Matrix Composites Articles
[0160] Cured polymer matrix composite articles are provided in two ways as previously described. After environmental conditioning, they were evaluated as described in the test method "weight loss". The words "dry", "ambient" and "wet" in the tables refer to the environmental conditions to which the cured polymer matrix composite article is exposed. The results are listed in Table 2 below.
[0161] Table 2
[0162]
[0163] Overlap Shear Strength (OLS) of Cured Joints
[...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| epoxy equivalent | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| epoxy equivalent | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com