In-situ data collection architecture for computer-aided diagnosis
A technology of measured data and medical data, applied in the field of data collection, it can solve problems such as difficulty in obtaining enough data or known cases, high cost, and the reluctance of hospitals to disclose
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
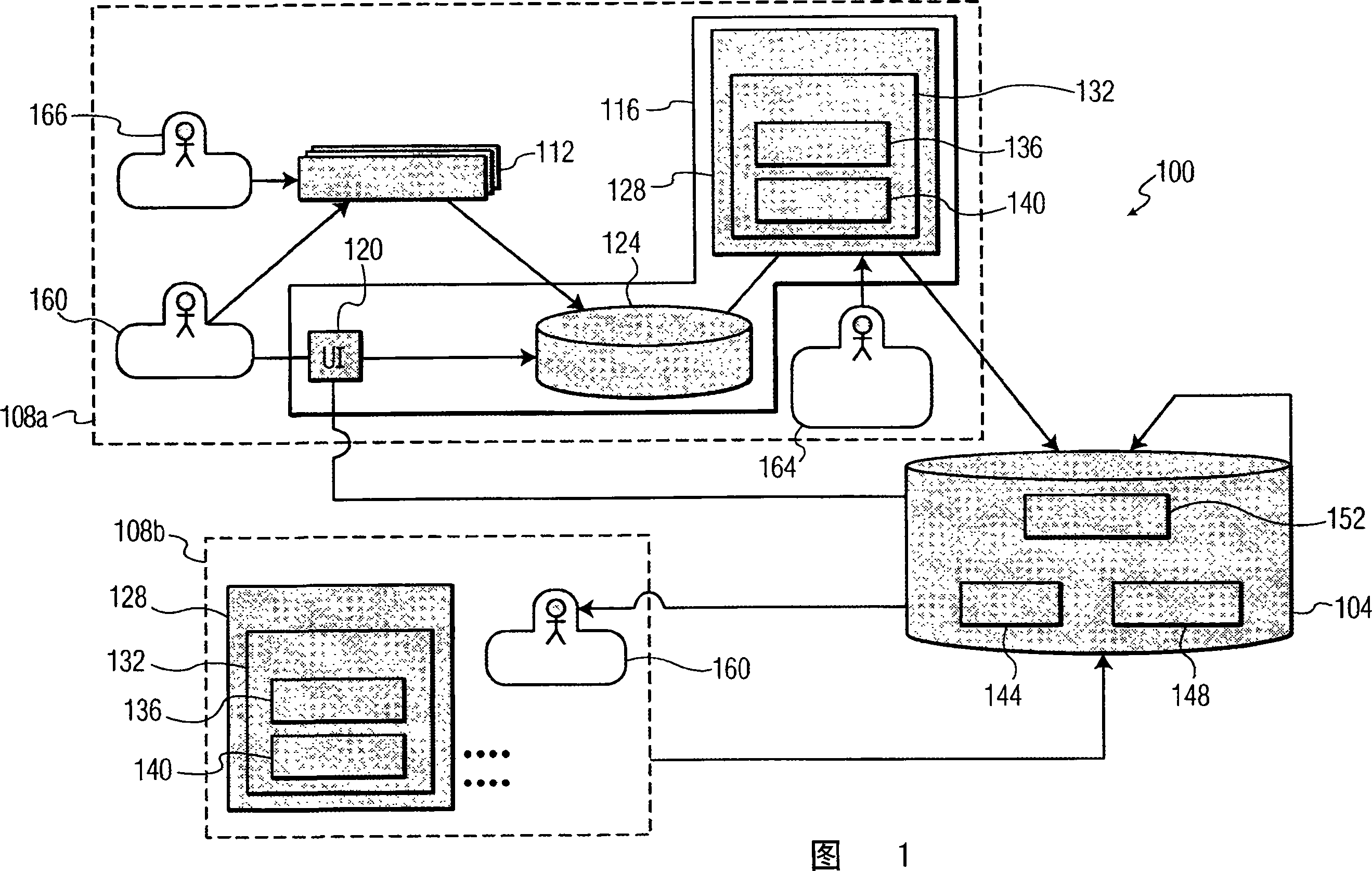
[0017] FIG. 1 depicts, by way of an illustrative and non-limiting example, a CAD input information collection system 100 according to the present invention. System 100 includes diagnostic decision support server 104 and customer site hospitals (or customer sites) 108a and 108b. There may be only one client site hospital or more than two client site hospitals (not shown), preferably more than two client site hospitals.
[0018] Within the customer site hospital 108a are an imaging device 112 and a data collection device 116, which are interconnected. Imaging by the imaging device 112 may be of any type, such as ultrasound and computed tomography (CT), magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
[0019] Data collection device 116 includes user interface (UI) 120 , patient database 124 , memory 128 including software agent 132 . Memory 128 preferably includes random access memory (RAM) and read only memory (ROM), in any form.
[0020] The software agent 132 has a segmentation algorithm...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com