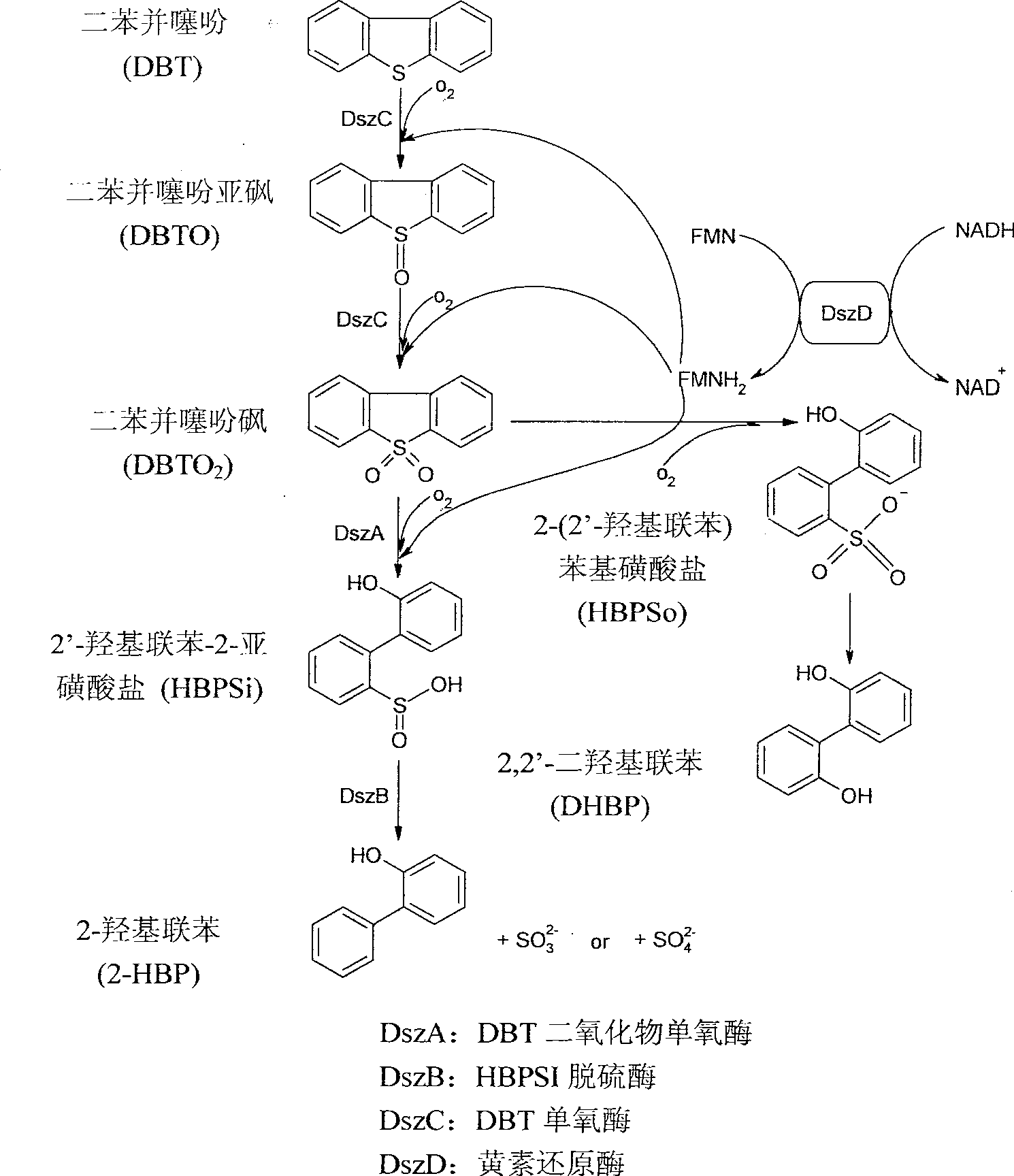
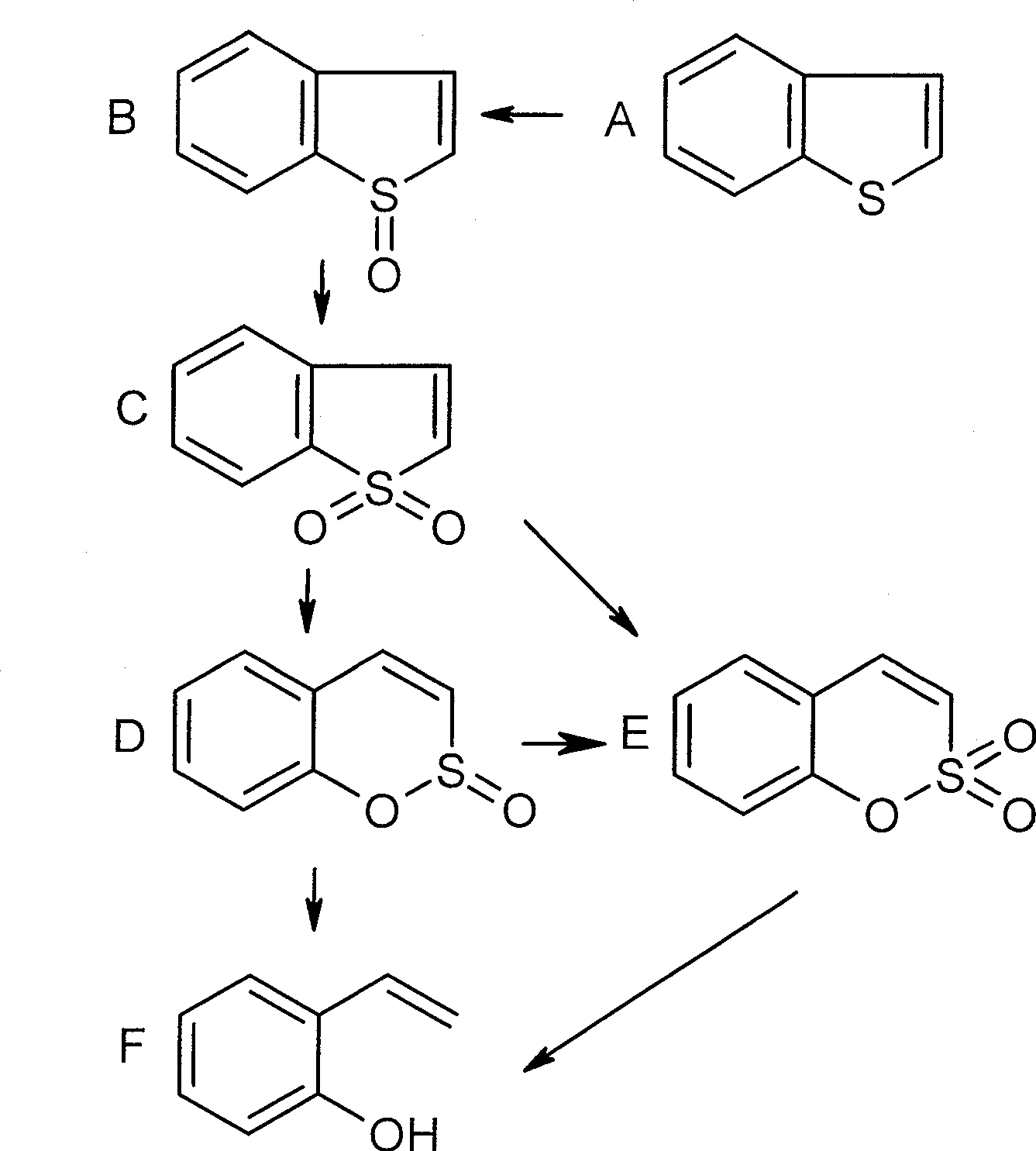
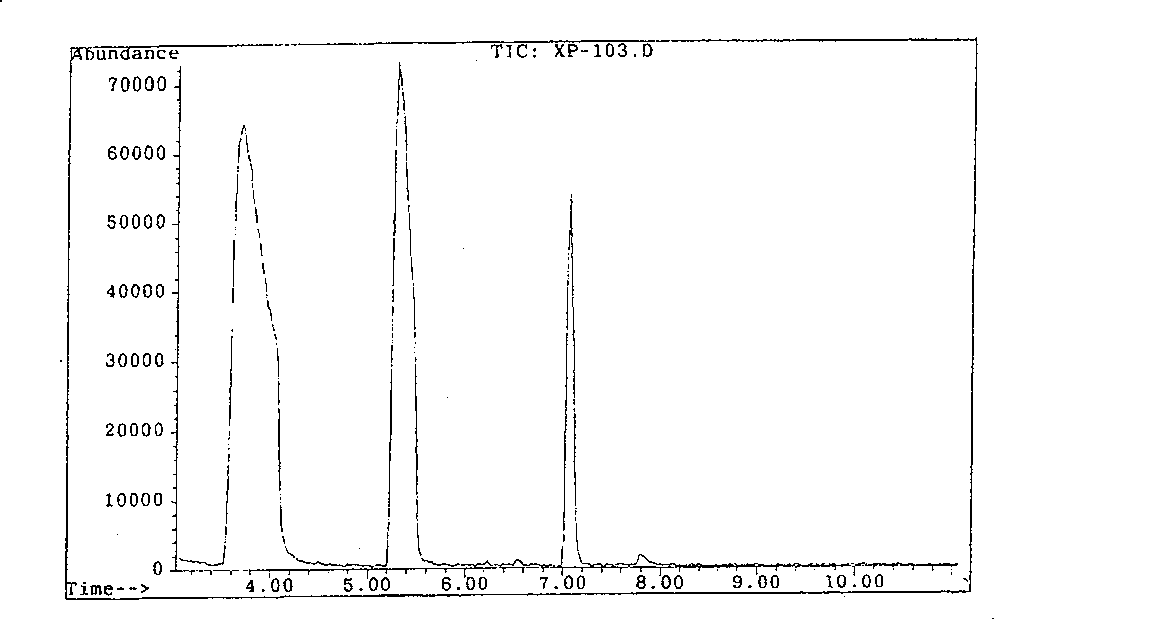
Sulfate-resistant Rhodococcus erythropolis and use thereof
A technology for Rhodococcus erythropolis and strains, which can be applied in the biological field and can solve the problems of narrow substrate range and low desulfurization activity.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0059] Example 1: Screening of Rhodococcus erythropolis SDUZAWQ strain
[0060] Strain screening Obtain soil samples and water samples from places such as refinery sewage outlets, use basic inorganic salt medium (medium composition: 1 liter of distilled water contains: 2.44g of KH 2 PO 4 , 5.57 g Na 2 HPO 4 , 2g NH 4 Cl, 0.2 g MgCl 2 , 2g of glycerin, 1mL of trace element mixture. The composition of the trace element mixture is: 1 liter of distilled water contains: 1g of CuCl 2 2H 2 O, 4 g CoCl 2 ·6H 2 O, 2g ZnCl 2 , 40g CaCl 2 , 0.5 g H 3 BO 3 , 2 g NaMoO 4 2H 2 O, 40g FeCl 3 ·7H 2 O, 1 g of AlGl 3 ·6H 2 O, 8g MnCl 2 4H 2 O) Soak overnight, culture at 30° C. with shaking at 200 rpm for 48 hours. The culture medium was centrifuged to remove the soil sample, and then the bacteria were obtained by centrifugation. The bacteria were washed twice with 0.85% physiological saline, and suspended in the pH7.0 potassium phosphate buffer. Add 1 mL of this bacterial ...
Embodiment 2
[0061] Embodiment 2: Preparation of cell liquid culture of Rhodococcus erythropolis SDUZAWQ bacterial strain:
[0062]Pick a nutrient agar slant to culture a ring of Rhodococcus erythropolis SDUZAWQ strain and inoculate it in a 300ml Erlenmeyer flask containing 50ml of sterilized basic inorganic salt medium, add sterilized DBT-dimethylformamide stock solution , the DBT concentration was 0.5mM, and cultured on a shaker at 30°C and 180 rpm for 36-48h. Take 5ml of the cultured bacterial solution and inoculate it into a 500ml Erlenmeyer flask filled with 100ml of basic inorganic salt medium, and then add sterilized DBT-dimethylformamide stock solution to make the DBT concentration 0.1-0.5mM. The Erlenmeyer flask was placed in a shaker and cultured at 30° C. and 180 rpm for 48 hours to prepare a liquid culture solution of Rhodococcus erythropolis SDUZAWQ cells.
Embodiment 3
[0063] Embodiment 3: Preparation of Rhodococcus erythropolis SDUZAWQ strain resting cell liquid:
[0064] The liquid culture solution of the cells of the strain SDUZAWQ obtained by the method of Example 2 was centrifuged at 5000 rpm for 10 min, and the supernatant was poured off. Wash and centrifuge three times with an appropriate amount of normal saline, suspend the obtained centrifuged sediment in normal saline, and then freeze and store in a refrigerator to obtain resting cells of the Rhodococcuserythropolis SDUZAWQ strain.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com