Multi-address access method for supporting service quality
An access method and quality of service technology, applied in the field of multi-access access that supports quality of service, can solve problems such as hindering high-priority service startup and restricting QoS performance, and achieve simple transceiver equipment requirements and ensure conflict-free transmission , reduce the effect of group collision
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
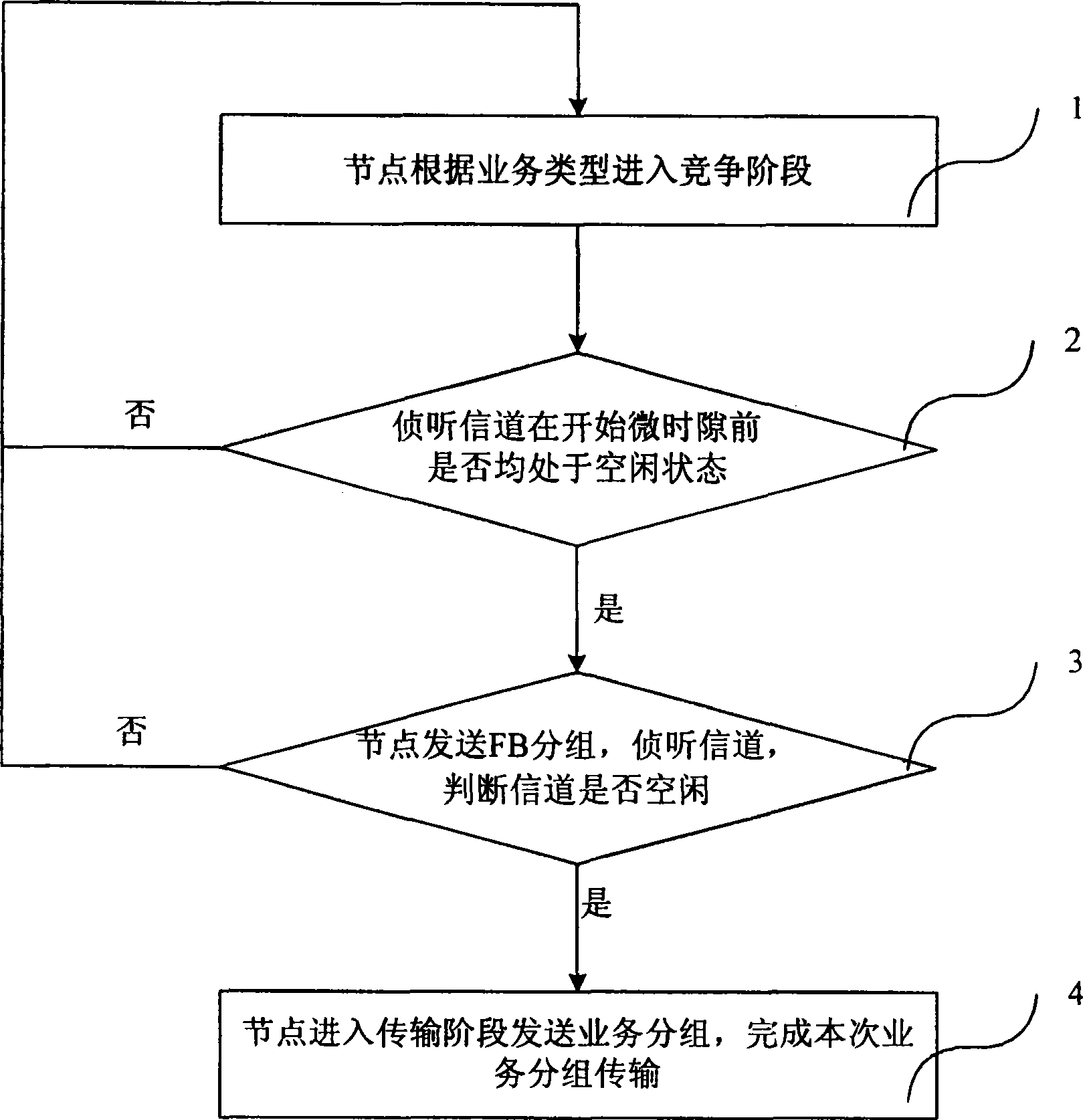
[0023] figure 1 It is a flow chart of Embodiment 1 of the multiple access method supporting quality of service in the present invention, as shown in figure 1 As shown, it specifically includes the following steps:
[0024] Step 1. The node judges the service type according to the service group to be sent. If it is a real-time service, the node sends an FB packet declaring the real-time service type. Packet length, the above-mentioned nodes enter the competition stage, and perform step 2; if it is a non-real-time service, the node continues to listen to a mini-slot of the FB packet length, if it does not hear the FB packet declaring the real-time service type sent by the real-time service node , the above-mentioned nodes enter the competition stage and execute step 2;
[0025] Wherein, the above competition stage is a stage before the node obtains the channel access right, and in this stage, the node sends one or more FB packets to obtain the channel access right. After the ...
Embodiment 2
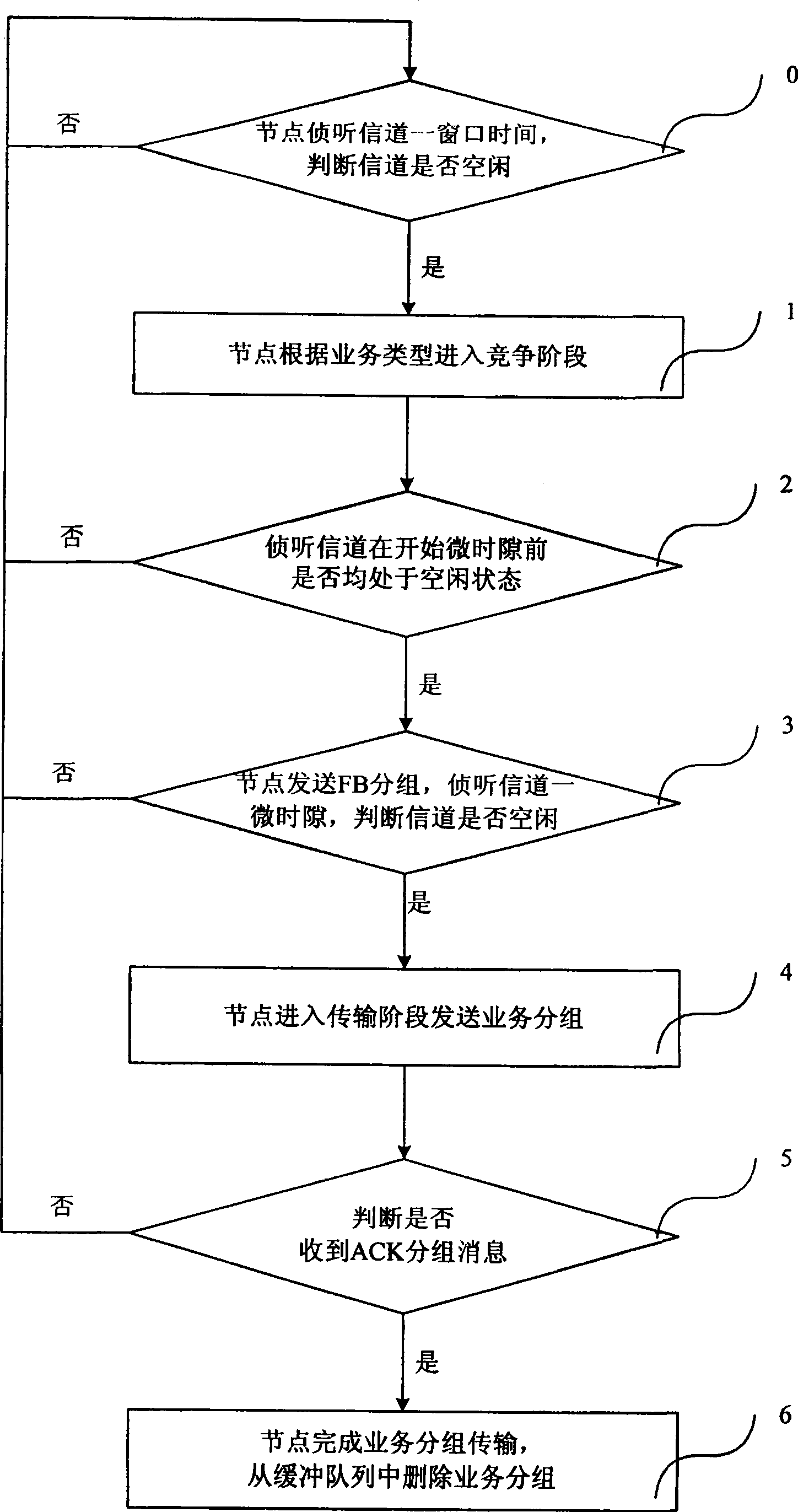
[0033] Such as figure 2 As shown, it is a flow chart of embodiment 2 of the multiple access method supporting quality of service of the present invention. Compared with the previous embodiment, it also includes before step 1:
[0034] Step 0. When a node has a service and needs to access the channel, the node first monitors the channel for a window time, and judges whether the channel is in an idle state at this time. If the channel is in an idle state during the listening window time, then perform step 1; If the channel is busy within the listening window, the node repeats step 0.
[0035] Compared with the previous embodiment, the return step 1 in steps 2 and 3 is replaced by return step 0; in step 3, it is judged whether the channel is in an idle state at this time by listening to a mini-slot of the channel . In addition, compared with the previous embodiment, the following steps are also included after step 4:
[0036] Step 5, wait to receive the message of feedback ac...
Embodiment 3
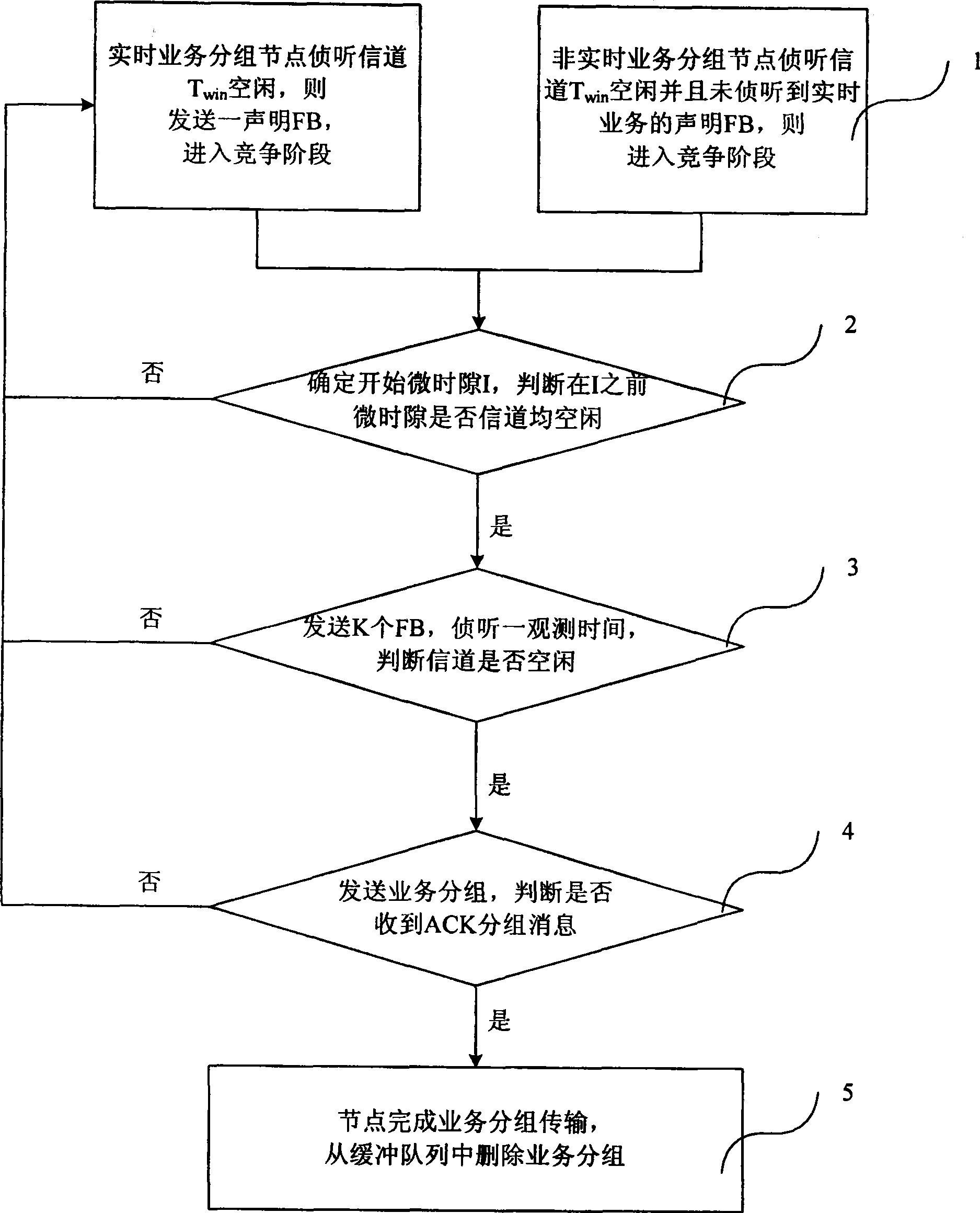
[0040] image 3 It is a flow chart of Embodiment 3 of the multiple access method supporting quality of service in the present invention, as shown in image 3 As shown, it specifically includes the following steps:
[0041] Step 1. Nodes with real-time services and non-real-time services are distinguished by statements: before the node accesses the channel, it listens to the channel for a window time Twin. If the channel is idle within this time, the node judges the service type according to the service group to be sent, that is, , the nodes (real-time service nodes) that have real-time service packets to be sent are at T win Immediately after being idle, send a FB packet declaring the business type and enter the competition stage; the nodes (non-real-time business nodes) that have non-real-time business packets to be sent are in T win Continue to listen to a micro-slot of FB length after being idle. If there is no statement from a real-time service node, the non-real-time se...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com