Amplification type solid state imaging device
A solid-state imaging device, a large-scale technology, applied in the direction of electric solid-state devices, semiconductor devices, electrical components, etc., can solve the problems of image quality degradation, noise removal performance, etc., and achieve the effect of suppressing the degradation of image quality
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 approach
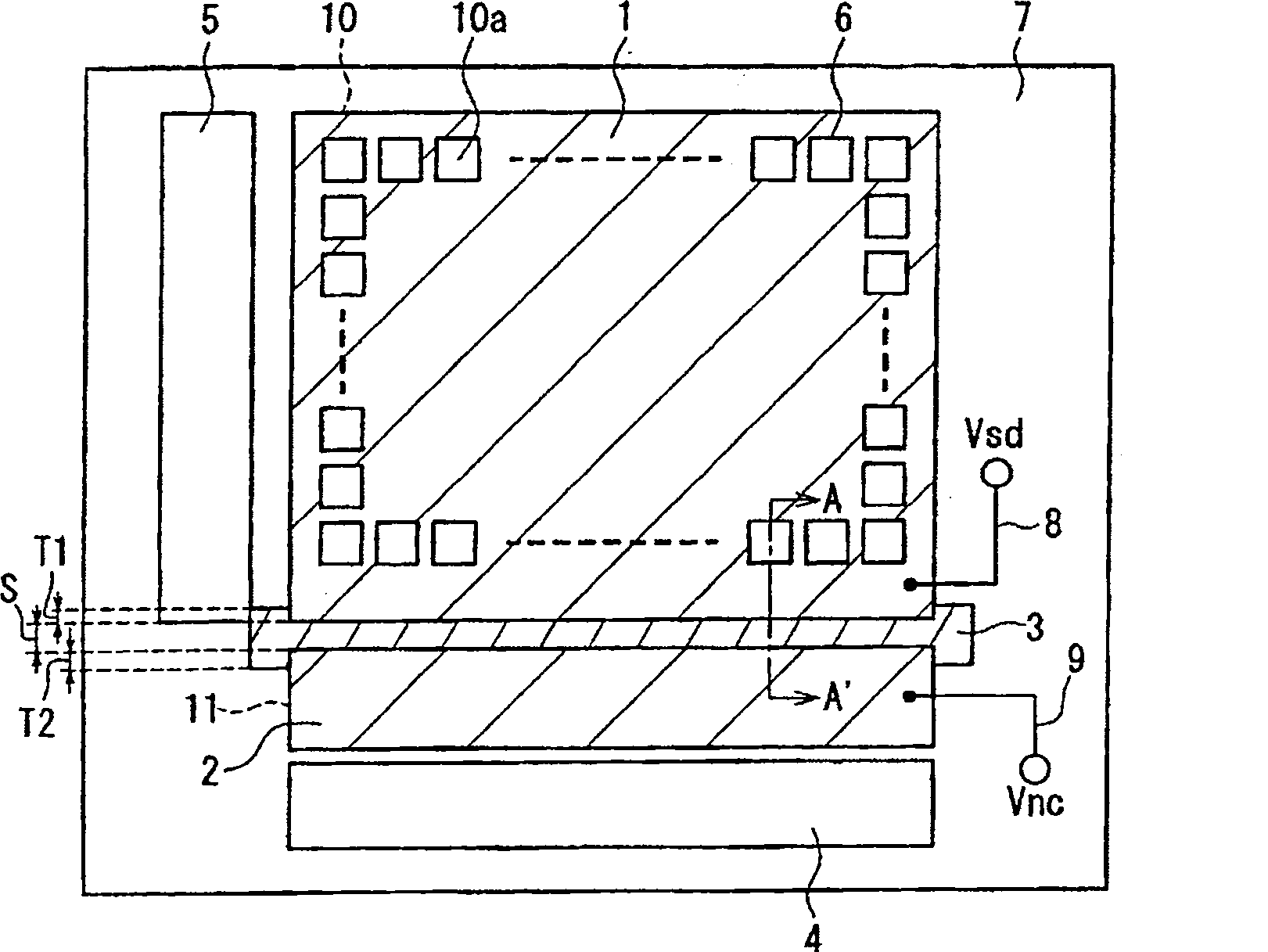
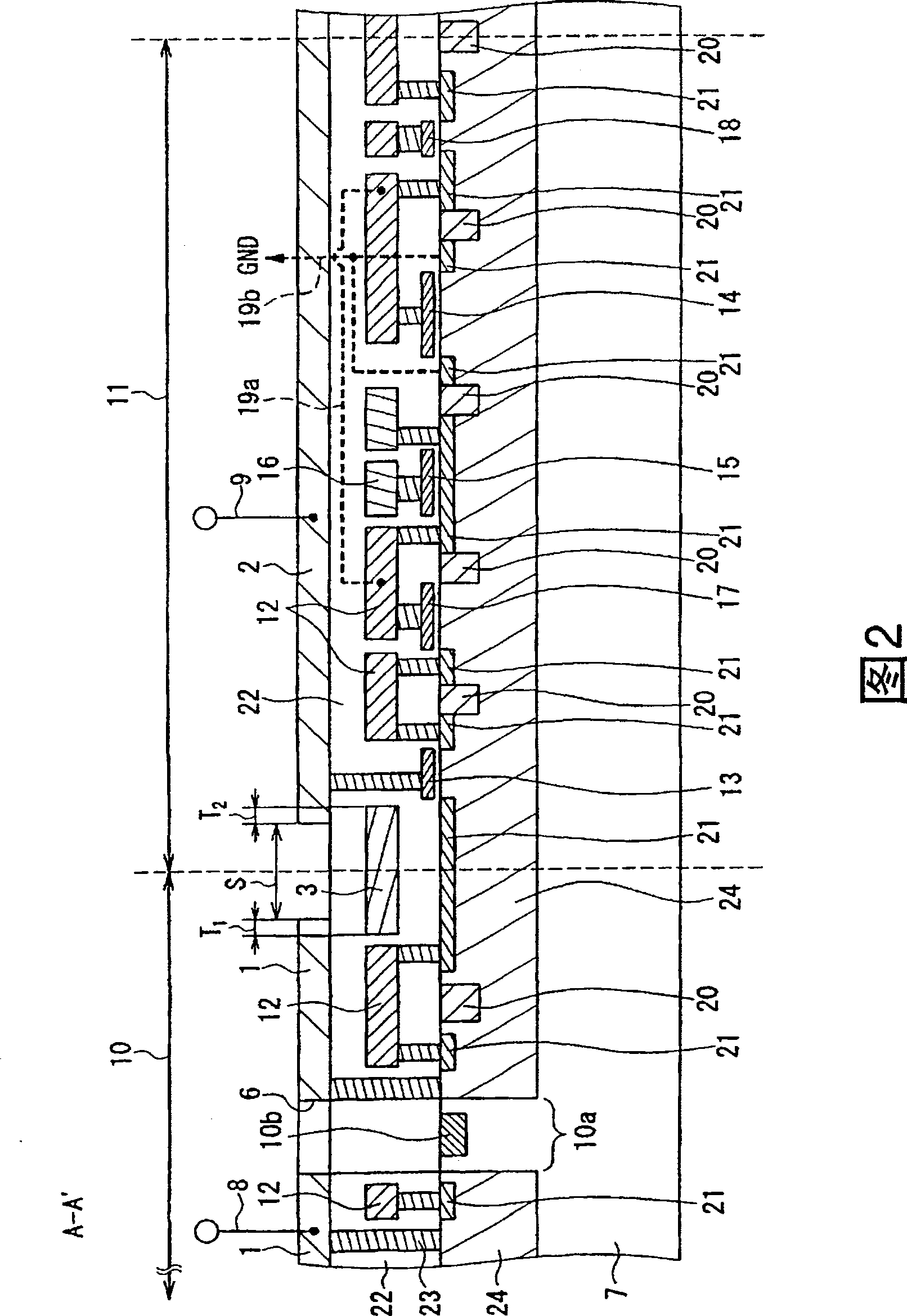
[0046] Below, refer to figure 1 2, the amplifying solid-state imaging device according to the first embodiment of the present invention will be described. figure 1 It is a schematic diagram showing the layout of the amplifying solid-state imaging device according to the first embodiment of the present invention. Figure 2 is a representation of figure 1 A cross-sectional view of a part of the enlarged solid-state imaging device shown, and shows along the figure 1 The state where the section line A-A' in the section is cut. Note that, in FIG. 2 , hatching is omitted for the main portion of the semiconductor substrate 7 and the insulating layer 22 .
[0047] Such as figure 1 As shown, the amplifying solid-state imaging device includes: a light receiving unit 10 , a reading unit, and a noise removal circuit 11 , all of which are provided on a semiconductor substrate 7 . The light receiving unit 10 is formed by arranging a plurality of pixels one-dimensionally or two-dime...
no. 2 approach
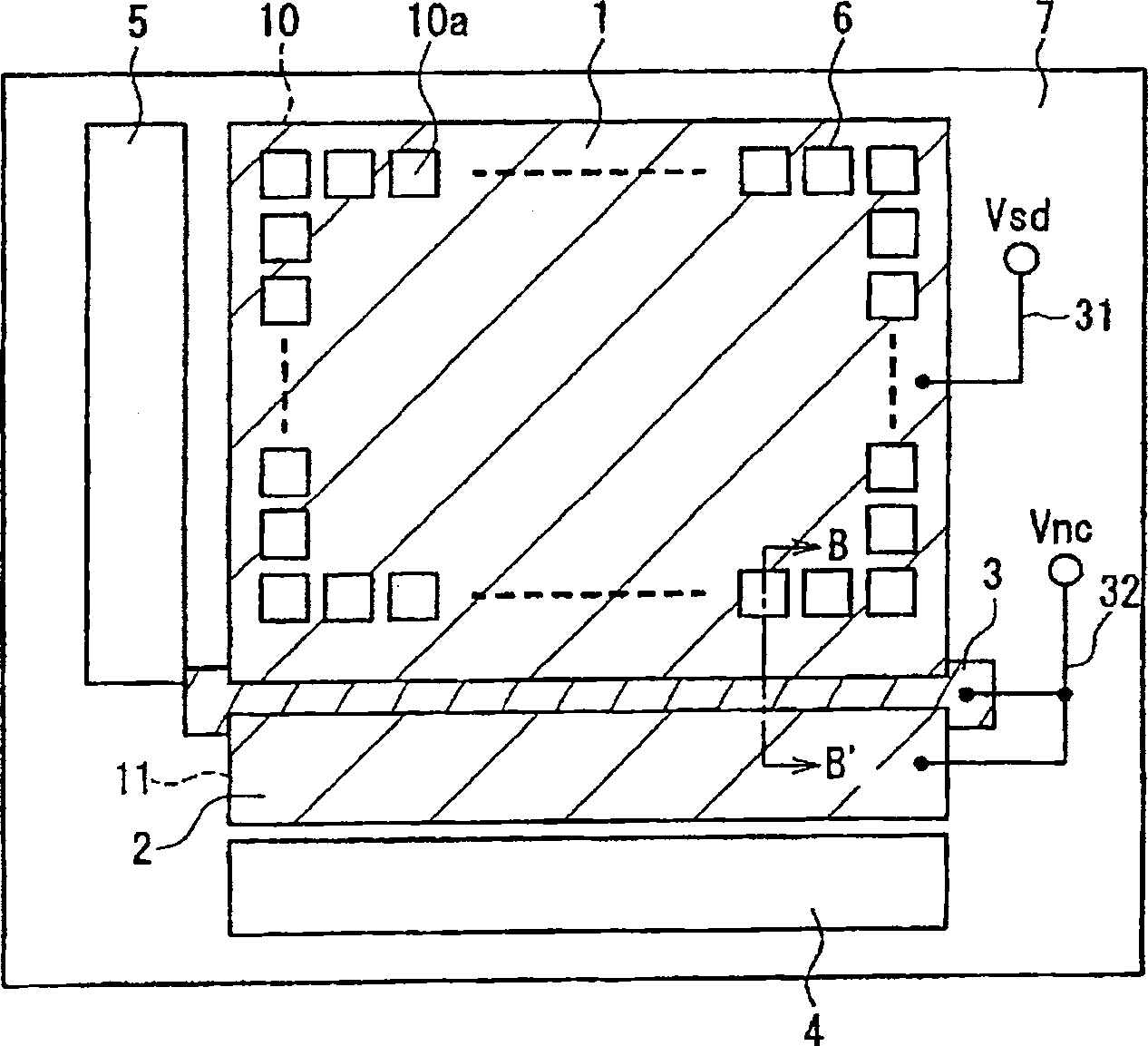
[0072] Next, refer to image 3 4, an amplifying solid-state imaging device in a second embodiment of the present invention will be described. image 3 It is a schematic diagram showing the layout of the amplifying solid-state imaging device according to the second embodiment of the present invention. Figure 4 is a representation of image 3 A cross-sectional view of a part of the enlarged solid-state imaging device shown, and shows along the image 3 The cutting line B-B' in the state.
[0073] again, in image 3 and Figure 4, given the figure 1 or the marked part shown in Figure 2 is with the figure 1 Or the same part as the part given the same mark in FIG. 2 . In addition, in FIG. 4 , hatching is omitted for the main part of the semiconductor substrate 7 and the insulating layer 22 . Also, the parts given the same hatching in FIG. 4 are parts having the same function.
[0074] Such as image 3 As shown in FIG. 4 , the second embodiment is also the same as the firs...
no. 3 approach
[0081] Next, refer to Figure 5 , the amplifying solid-state imaging device in the third embodiment of the present invention will be described. Figure 5 It is a schematic diagram showing the layout of the amplifying solid-state imaging device according to the third embodiment of the present invention. again, in Figure 5 in, endowed with figure 1 The marked parts shown are the same as in the figure 1 The same part as the part assigned the same mark.
[0082] Such as Figure 5 As shown, in this third embodiment, with image 3 Unlike the illustrated example, the second light-shielding layer 2 and the third light-shielding layer 3 are electrically connected by wiring 33 other than the second wiring 32 . Again, for structures other than this, Figure 5 The amplified solid-state imaging device shown has the same image 3 The amplified solid-state imaging device shown has the same structure.
[0083] Specifically, at one side (right side in the figure) end of the second ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com