Programmable optical component for spatially controlling the intensity of beam of radiation
A technology for controlling radiation and optical components, which is applied in the field of photolithography and optical scanning devices, can solve the problems of high cost, trouble, and time-consuming photomask, and achieve the effect of small field intensity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
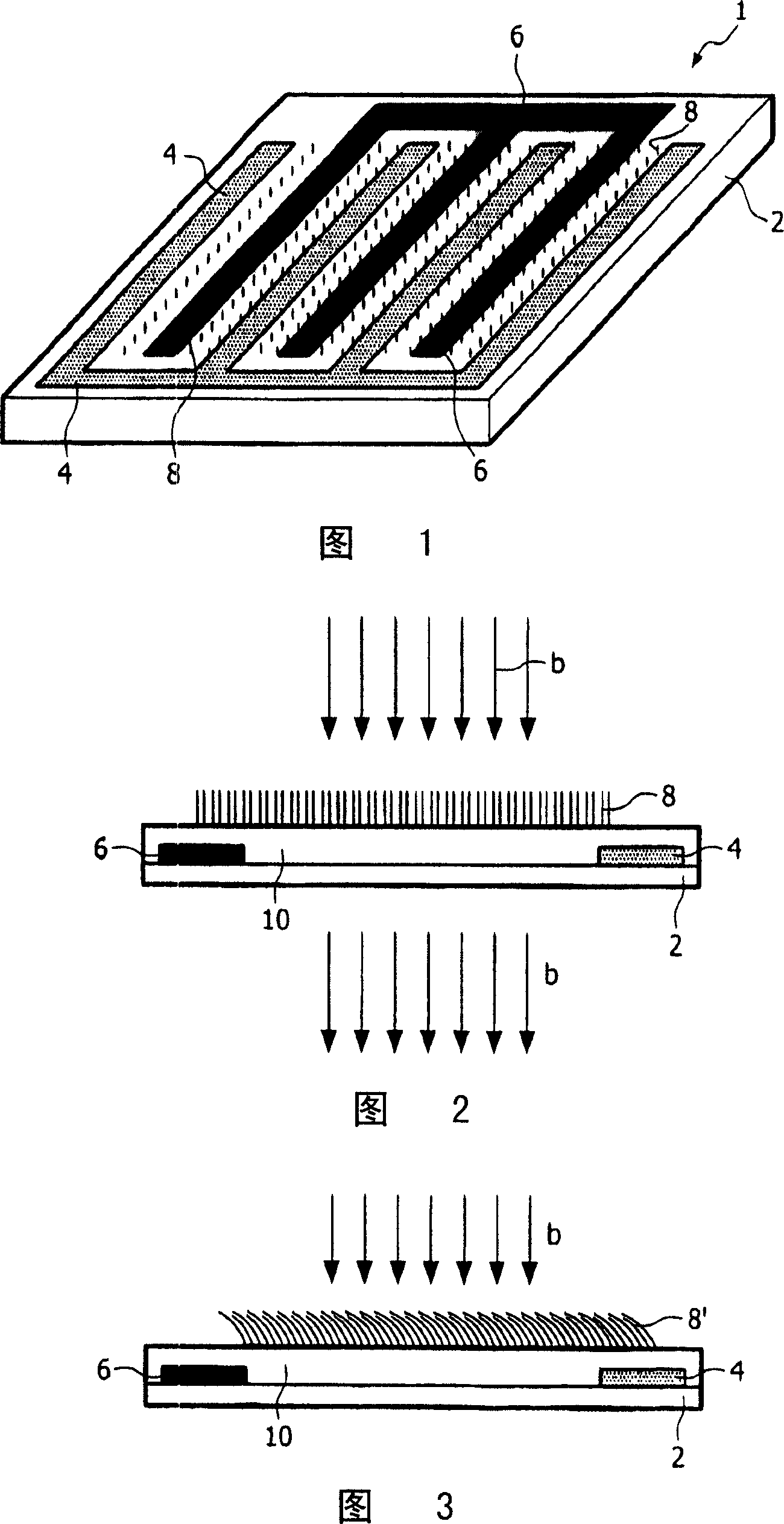
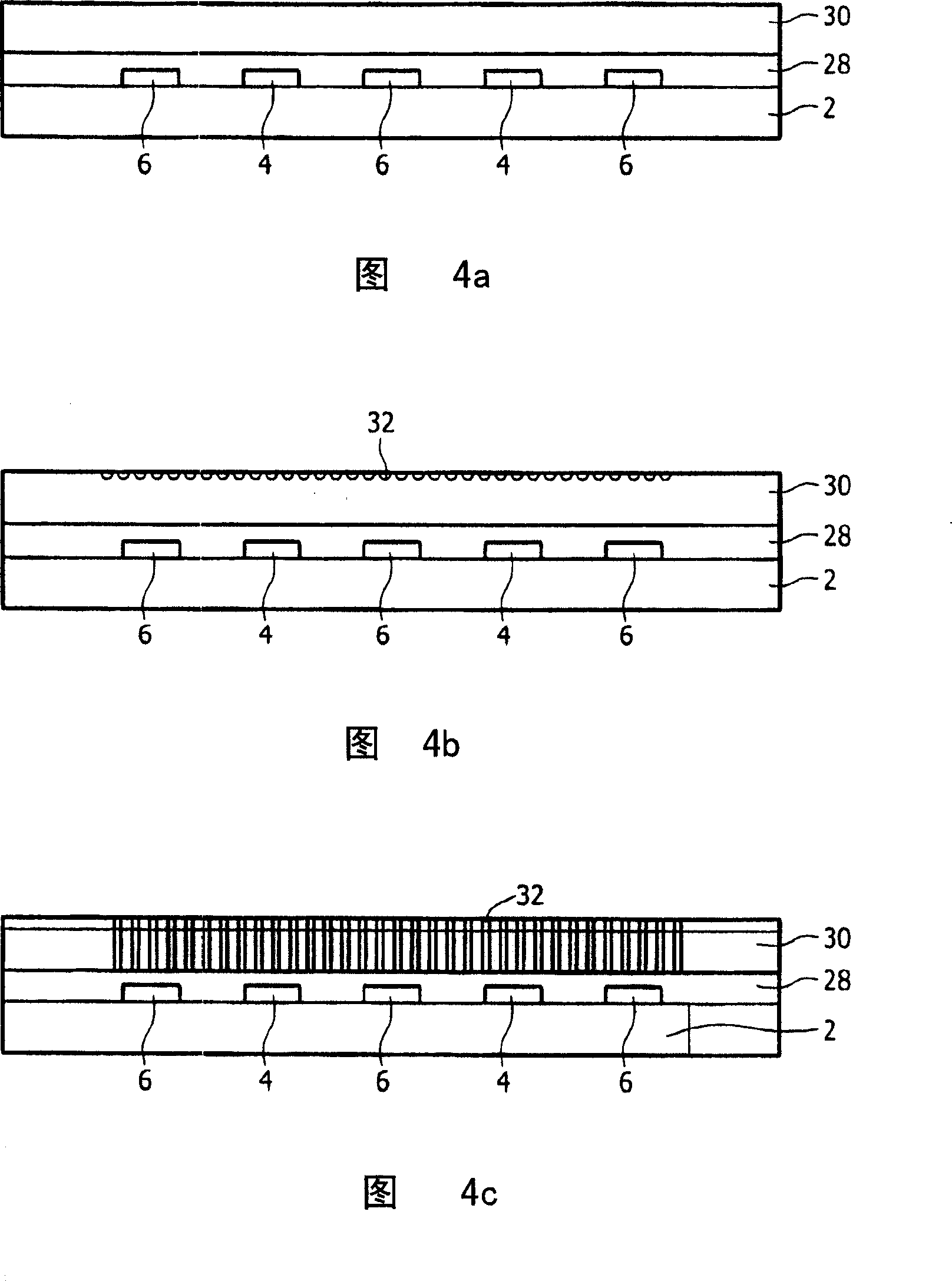
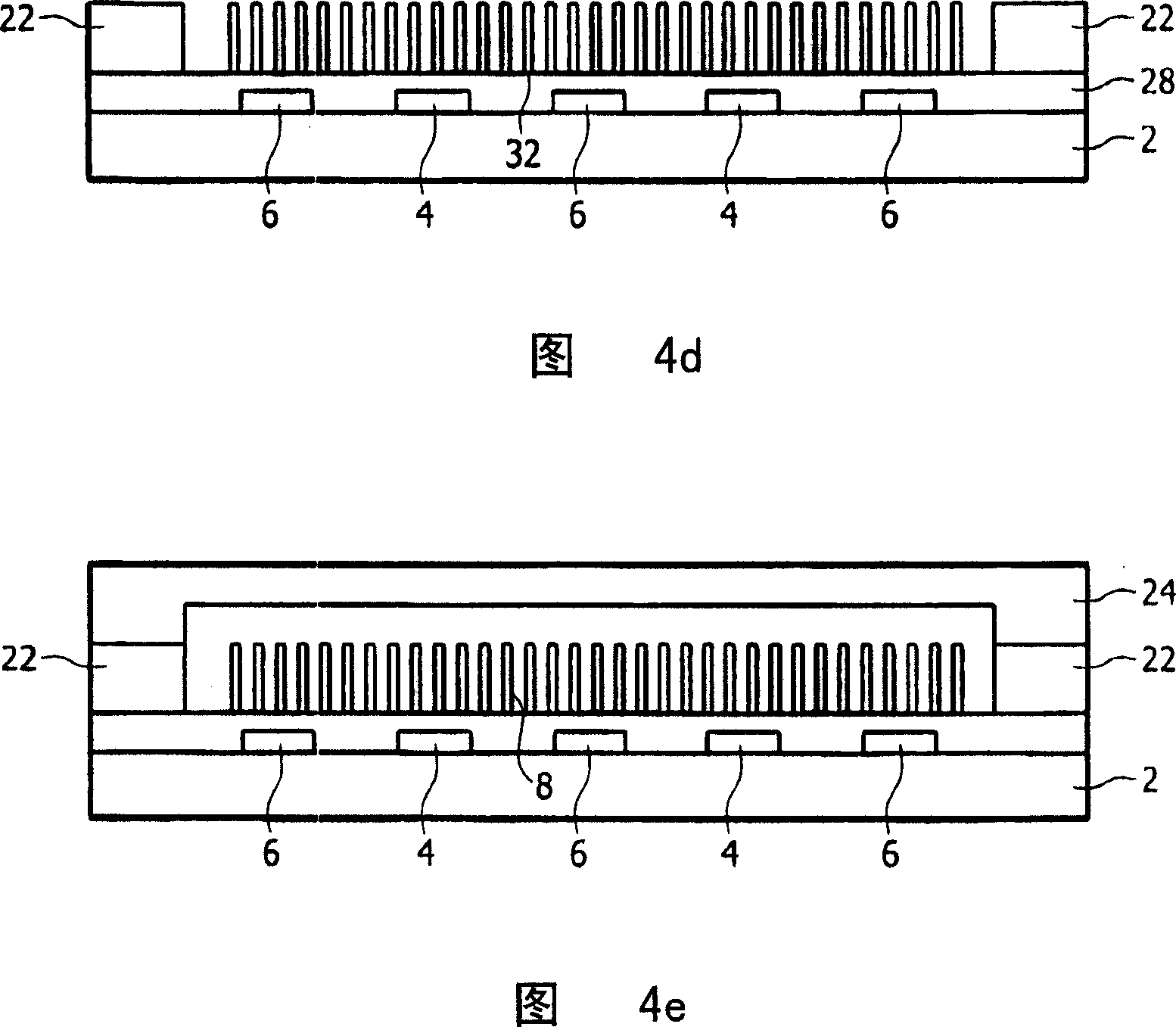
[0076] The part shown in Fig. 1 comprises a substrate 2, for example a transparent substrate such as a glass or transparent plastic substrate. The upper side of the substrate is provided with first and second electrodes 4 and 6, respectively, and with bendable nano-elements 8 arranged between the electrodes. The electrodes 4 and 6 may be interdigitated, ie parts of a first electrode are arranged between parts of a second electrode. This electrode structure is very suitable for the manufacture of diffraction gratings, whereby the stripes with bendable nano-elements form the grating stripes and the electrode part forms the middle stripes. The electrodes 4 and 6 shown in FIG. 1 have four fingers and three fingers, respectively. However, the number of fingers can be chosen freely, and in practice the number of fingers can be higher for a diffraction grating. The electrodes are transparent and can be fabricated, for example, from indium tin oxide (ITO).
[0077] As shown in the ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com