Control method of induction motor
A technology for induction motors and control methods, which is applied in the direction of AC motor control, starters of single multi-phase induction motors, motor generators/starters, etc., and can solve the problem of complex circuit structures, frequency and circuit speed dependent on commercial power supply 1 Complex structure and other issues
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
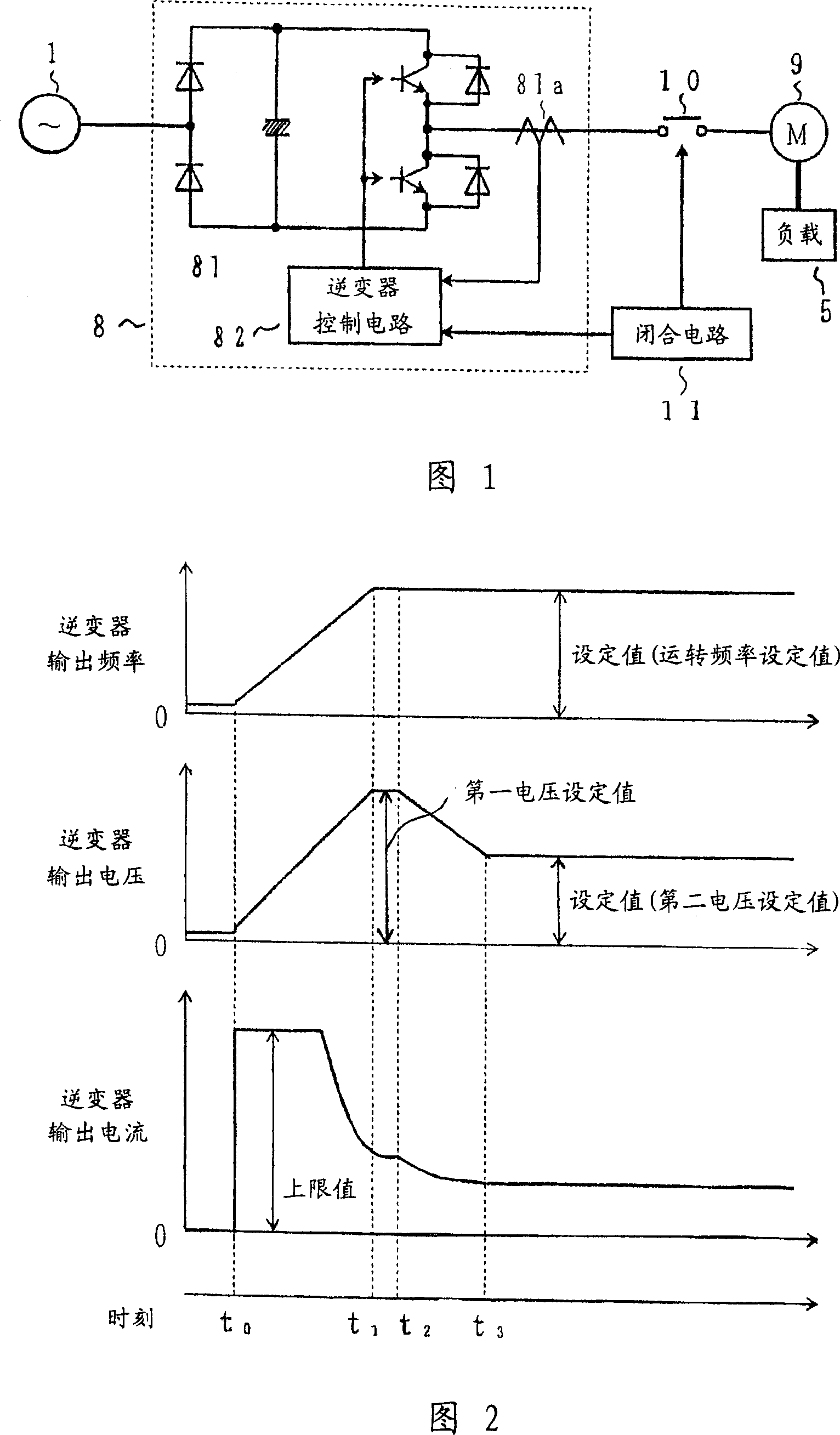
[0042] 1 is a circuit configuration diagram showing a first embodiment of a method for controlling an induction motor according to the present invention, and components having the same functions as those in the conventional configuration shown in FIG. 9 are assigned the same reference numerals.
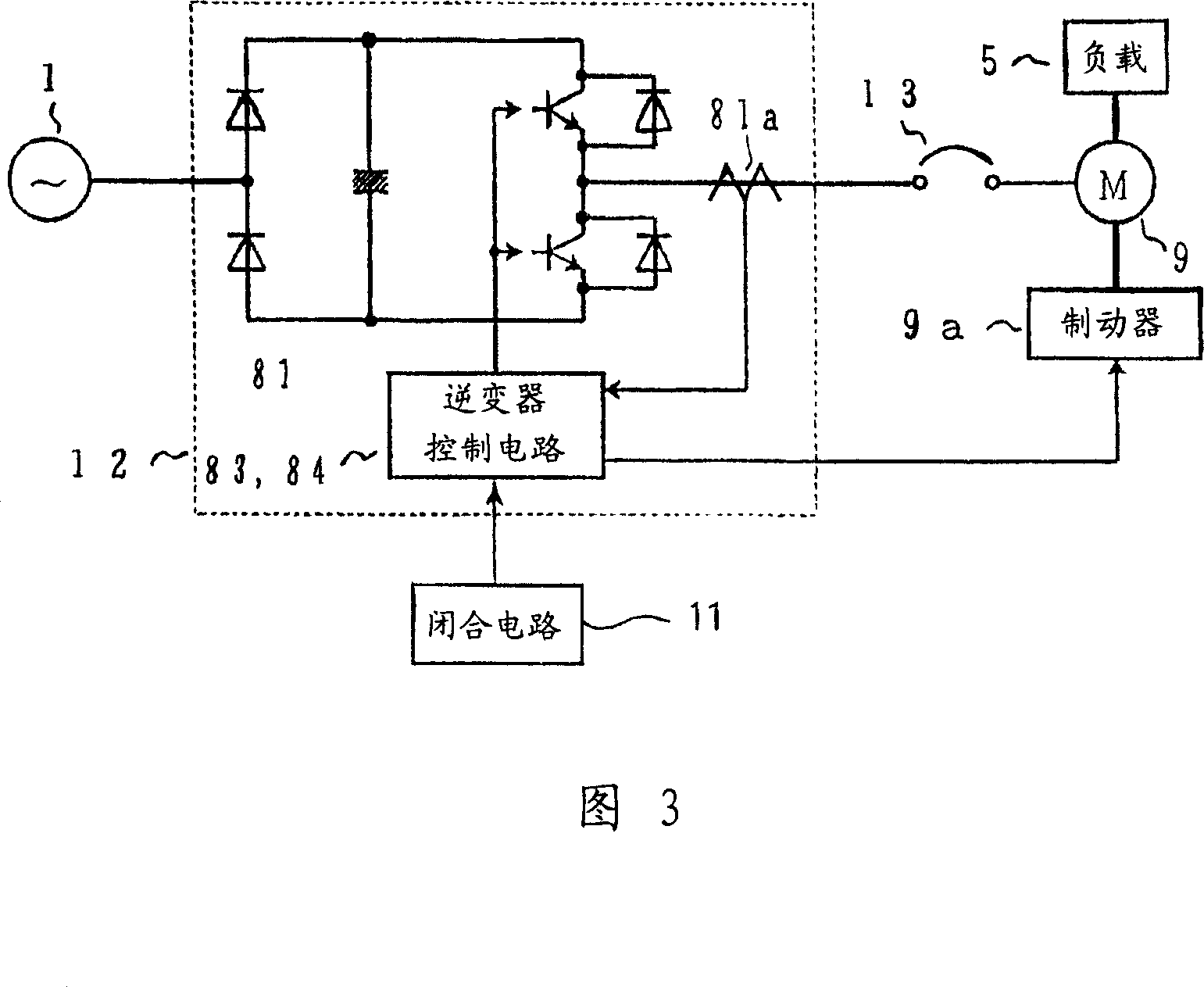
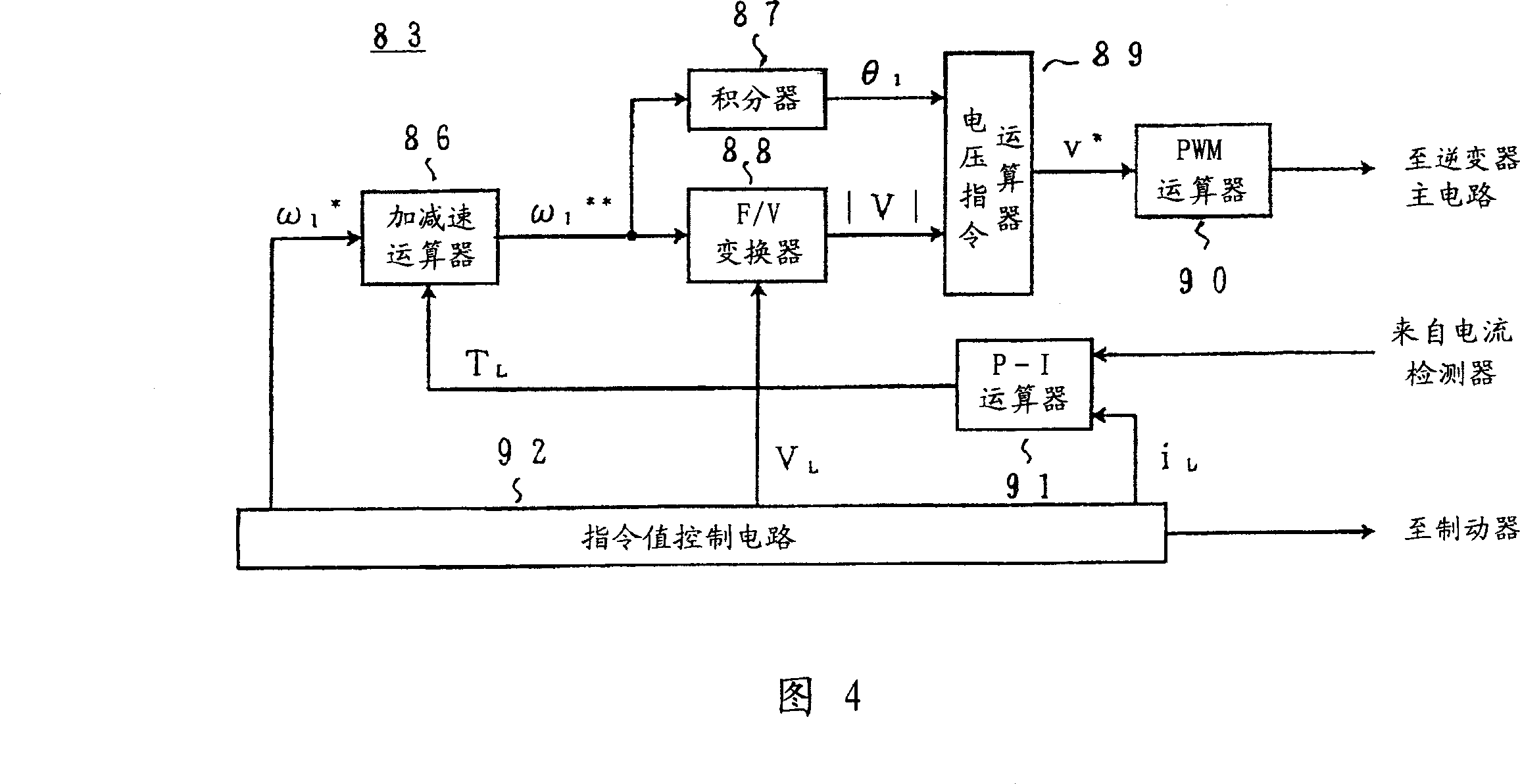
[0043] That is, in the circuit structure shown in FIG. 1, in addition to the commercial power supply 1 and the load 5, it also includes: a VVVF inverter 8, an induction motor 9 connected in a delta connection with primary coils, an electromagnetic relay 10, and a closed circuit of the electromagnetic relay 10 11. The VVVF inverter 8 includes an inverter main circuit 81 and an inverter control circuit 82 . The inverter main circuit 81 converts the AC voltage of the commercial power supply 1 into a DC voltage with a diode rectifier and a smoothing capacitor, and connects an antiparallel circuit of transistors and diodes that convert the DC voltage into an AC voltage in a bridge. The in...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com