Hypertonic Application in Wound Care: A Technical Overview
Hypertonic Wound Care Evolution and Objectives
Hypertonic wound care has evolved significantly over the past few decades, driven by advancements in medical science and a deeper understanding of wound healing processes. The journey began with the recognition of osmotic pressure's role in wound management, leading to the development of hypertonic solutions for wound cleansing and debridement.
Initially, simple saline solutions were used, but as research progressed, more complex formulations emerged. These included hypertonic saline, glucose solutions, and eventually, specialized dressings impregnated with hypertonic agents. The evolution of hypertonic wound care has been marked by a shift from basic osmotic effects to more sophisticated approaches that combine osmosis with other therapeutic mechanisms.
A key milestone in this evolution was the introduction of honey-based dressings, which leverage the natural hypertonic properties of honey along with its antimicrobial effects. This paved the way for multi-functional hypertonic solutions that not only draw out excess fluid but also provide additional healing benefits.
The objectives of hypertonic wound care have expanded over time. While the primary goal remains effective debridement and moisture management, modern hypertonic treatments aim to achieve several additional outcomes. These include reducing bacterial load, promoting granulation tissue formation, and creating an optimal wound healing environment.
Current research in hypertonic wound care focuses on developing smart dressings that can adapt to the wound environment, releasing hypertonic agents in a controlled manner. There is also a growing interest in combining hypertonic solutions with growth factors and other bioactive substances to enhance wound healing.
The future objectives of hypertonic wound care include minimizing pain during dressing changes, reducing the frequency of dressing applications, and improving overall patient comfort. There is also a push towards personalized wound care, where hypertonic treatments can be tailored to individual patient needs and wound characteristics.
As we look ahead, the field of hypertonic wound care aims to integrate with emerging technologies such as nanotechnology and smart materials. The goal is to develop advanced wound care systems that can actively respond to changes in the wound environment, adjusting their hypertonic properties as needed throughout the healing process.
Market Analysis for Hypertonic Wound Solutions
The global market for hypertonic wound solutions has been experiencing significant growth in recent years, driven by the increasing prevalence of chronic wounds and the rising demand for advanced wound care products. The market is characterized by a diverse range of products, including hypertonic saline solutions, honey-based dressings, and other osmotic agents designed to promote wound healing through osmosis and moisture management.
Key factors contributing to market growth include the aging population, rising incidence of diabetes and obesity, and the growing awareness of advanced wound care techniques among healthcare professionals. The market is also benefiting from technological advancements in wound care products and the increasing adoption of evidence-based practices in wound management.
Geographically, North America and Europe currently dominate the hypertonic wound solutions market, owing to their well-established healthcare infrastructure and higher healthcare expenditure. However, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the fastest growth in the coming years, driven by improving healthcare access, rising disposable incomes, and increasing investment in healthcare infrastructure.
The market is segmented based on product type, application, end-user, and region. Hypertonic saline solutions hold a significant market share due to their widespread use in various wound care applications. Chronic wounds, including diabetic foot ulcers, pressure ulcers, and venous leg ulcers, represent the largest application segment for hypertonic wound solutions.
Hospitals and clinics are the primary end-users of hypertonic wound solutions, followed by home healthcare settings. The increasing trend towards outpatient and home-based care is expected to drive growth in the home healthcare segment in the coming years.
The competitive landscape of the hypertonic wound solutions market is characterized by the presence of both established players and innovative start-ups. Key market players are focusing on product innovation, strategic partnerships, and geographical expansion to strengthen their market position. The market is also witnessing a trend towards the development of combination products that incorporate hypertonic solutions with other wound care technologies to enhance healing outcomes.
Despite the positive growth outlook, the market faces challenges such as the high cost of advanced wound care products, reimbursement issues in some regions, and the need for clinical evidence to support the efficacy of hypertonic solutions in various wound types. Overcoming these challenges will be crucial for sustained market growth and wider adoption of hypertonic wound care solutions across different healthcare settings.
Current Challenges in Hypertonic Wound Therapy
Despite the promising potential of hypertonic wound therapy, several challenges currently hinder its widespread adoption and optimal efficacy in clinical practice. One of the primary obstacles is the lack of standardized protocols for hypertonic solution application. The concentration, frequency, and duration of hypertonic treatments vary widely across different healthcare settings, making it difficult to establish consistent best practices and compare outcomes effectively.
Another significant challenge is the potential for tissue irritation and pain associated with hypertonic solutions, particularly in patients with sensitive or compromised skin. The high osmolarity of these solutions can cause discomfort and, in some cases, lead to further tissue damage if not managed properly. This necessitates careful patient selection and monitoring, which can be resource-intensive for healthcare providers.
The limited understanding of the optimal osmolarity range for different wound types presents another hurdle. While hypertonic solutions are generally effective in reducing edema and promoting wound healing, the ideal concentration may vary depending on the wound etiology, depth, and healing stage. This variability complicates treatment decisions and may lead to suboptimal outcomes in some cases.
Furthermore, the interaction between hypertonic solutions and other wound care products, such as dressings and topical medications, is not fully elucidated. This can result in reduced efficacy or unexpected side effects when combining therapies, necessitating further research to establish compatible treatment regimens.
The cost-effectiveness of hypertonic wound therapy compared to conventional treatments remains a point of contention. While some studies suggest improved healing rates and reduced treatment duration, the higher cost of specialized hypertonic solutions and the potential need for more frequent dressing changes can offset these benefits in certain healthcare systems.
Lastly, there is a notable gap in long-term follow-up studies assessing the sustained effects of hypertonic wound therapy. This lack of comprehensive data on long-term outcomes, including recurrence rates and quality of life measures, makes it challenging for clinicians and policymakers to fully endorse the therapy for widespread use.
Addressing these challenges will require concerted efforts in clinical research, standardization of protocols, and improved education for healthcare providers. As the field of wound care continues to evolve, overcoming these obstacles will be crucial in realizing the full potential of hypertonic wound therapy and improving patient outcomes.
Existing Hypertonic Wound Treatment Approaches
01 Hypertonic solutions for wound healing
Hypertonic solutions are used in wound healing to create an osmotic gradient that draws fluid from the wound, reducing edema and promoting healing. These solutions can contain various osmotic agents such as sodium chloride or glucose, which help to cleanse the wound and create an environment conducive to tissue repair.- Hypertonic solutions for wound healing: Hypertonic solutions are used in wound healing to promote tissue repair and reduce inflammation. These solutions create an osmotic gradient that draws excess fluid from the wound, reducing edema and promoting a favorable environment for healing. The high osmolarity also helps to inhibit bacterial growth, potentially reducing the risk of infection.
- Composition of hypertonic wound healing solutions: Hypertonic wound healing solutions typically contain high concentrations of solutes such as sodium chloride, glucose, or other osmotically active agents. These compositions may also include additional components like antimicrobial agents, growth factors, or other bioactive molecules to enhance the wound healing process.
- Application methods for hypertonic solutions: Hypertonic solutions can be applied to wounds through various methods, including direct application, impregnated dressings, or irrigation systems. The choice of application method depends on the wound type, location, and severity. Continuous or intermittent application may be used to maintain the osmotic gradient and promote optimal healing conditions.
- Combination therapies with hypertonic solutions: Hypertonic solutions may be used in combination with other wound healing therapies to enhance overall treatment efficacy. This can include combining hypertonic solutions with negative pressure wound therapy, growth factor treatments, or other advanced wound care techniques to address complex or chronic wounds.
- Monitoring and adjusting hypertonic therapy: Effective use of hypertonic solutions in wound healing requires careful monitoring of wound progress and adjustment of treatment parameters. This may involve assessing wound characteristics, measuring osmolarity, and evaluating the wound environment to optimize the concentration and application of hypertonic solutions throughout the healing process.
02 Composition of hypertonic wound healing solutions
Hypertonic wound healing solutions often contain a combination of osmotic agents, antimicrobial compounds, and other active ingredients. These may include electrolytes, vitamins, amino acids, and growth factors to support tissue regeneration and prevent infection. The specific composition is tailored to address different types of wounds and stages of healing.Expand Specific Solutions03 Application methods for hypertonic solutions
Hypertonic solutions can be applied to wounds through various methods, including direct application, impregnated dressings, or irrigation systems. The choice of application method depends on the wound type, location, and severity. Some advanced delivery systems allow for controlled release of the hypertonic solution over time, optimizing the wound healing process.Expand Specific Solutions04 Combination therapy with hypertonic solutions
Hypertonic solutions are often used in combination with other wound healing therapies. This may include negative pressure wound therapy, debridement techniques, or the application of bioactive dressings. The synergistic effects of these combined approaches can enhance wound healing outcomes and reduce healing time.Expand Specific Solutions05 Novel formulations and delivery systems
Research is ongoing to develop novel formulations and delivery systems for hypertonic wound healing solutions. These innovations aim to improve the efficacy, ease of application, and patient comfort. Some approaches include nanoparticle-based delivery systems, smart hydrogels that respond to wound environment changes, and bioengineered scaffolds that incorporate hypertonic solutions.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players in Hypertonic Wound Care
The hypertonic application in wound care market is in a growth phase, driven by increasing prevalence of chronic wounds and rising demand for advanced wound care solutions. The market size is expanding, with a projected CAGR of 6-8% over the next five years. Technologically, the field is advancing rapidly, with key players like Smith & Nephew plc, KCI Licensing, Inc., and 3M Innovative Properties Co. leading innovation. These companies are developing sophisticated hypertonic solutions and delivery systems, improving efficacy and patient outcomes. Emerging players such as Neodyne Biosciences, Inc. and KLOX Technologies, Inc. are also contributing to technological advancements, focusing on novel approaches to hypertonic wound care. The competitive landscape is characterized by a mix of established medical device companies and specialized wound care firms, with ongoing research and development efforts aimed at enhancing product performance and expanding applications.
Smith & Nephew plc
KCI Licensing, Inc.
Innovative Hypertonic Wound Care Technologies
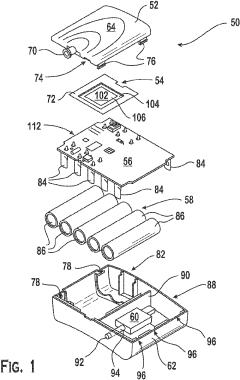
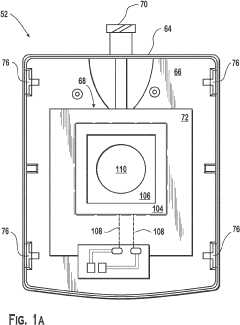
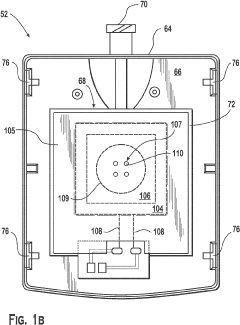
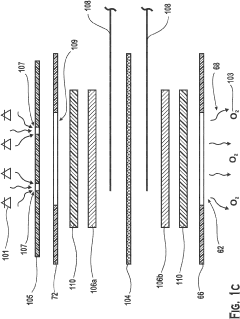
- A bandage comprising a gas-permeable and liquid-impermeable material separating an oxygen storage form, such as hydrogen peroxide, from a perfluorocarbon like Oxycyte®, which facilitates controlled oxygen release to the wound, enhancing tissue oxygenation.
- A device that combines transdermal continuous oxygen therapy with NPWT, utilizing a membrane electrode assembly (MEA) to concentrate oxygen from ambient air and a mechanical pump for vacuum application, allowing for simultaneous or intermittent delivery of oxygen and negative pressure to the wound.
Regulatory Framework for Wound Care Products
The regulatory framework for wound care products, including hypertonic applications, is a complex and evolving landscape that significantly impacts the development, approval, and marketing of these medical devices. In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) is the primary regulatory body overseeing wound care products. The FDA classifies most wound care products as Class II medical devices, which require a 510(k) premarket notification submission to demonstrate substantial equivalence to a legally marketed predicate device.
For hypertonic wound care applications, manufacturers must provide evidence of safety and efficacy through clinical trials and laboratory testing. This includes demonstrating the product's ability to maintain a hypertonic environment, promote wound healing, and prevent infection without causing adverse effects. The FDA also requires manufacturers to implement and maintain quality management systems that comply with Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) regulations.
In the European Union, wound care products fall under the Medical Device Regulation (MDR), which came into full effect in May 2021. The MDR has introduced more stringent requirements for clinical evidence, post-market surveillance, and traceability. Manufacturers must obtain CE marking to market their products in the EU, which involves a conformity assessment procedure and, in some cases, review by a notified body.
Internationally, many countries have their own regulatory frameworks for wound care products, often influenced by FDA and EU regulations. For example, Japan's Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency (PMDA) and China's National Medical Products Administration (NMPA) have specific requirements for the approval of wound care devices, including those utilizing hypertonic solutions.
Regulatory compliance also extends to labeling and marketing claims. Manufacturers must ensure that product labels and promotional materials accurately reflect the approved indications and do not make unsubstantiated claims about the product's effectiveness. This is particularly important for hypertonic wound care applications, as the mechanism of action and benefits must be clearly and accurately communicated.
As the field of wound care continues to advance, regulatory bodies are adapting their frameworks to address new technologies and treatment modalities. This includes the development of guidance documents specific to advanced wound care products and the consideration of real-world evidence in regulatory decision-making. Manufacturers of hypertonic wound care applications must stay abreast of these evolving regulations to ensure continued compliance and market access for their products.
Safety and Efficacy of Hypertonic Applications
The safety and efficacy of hypertonic applications in wound care have been extensively studied, demonstrating promising results in various clinical settings. Hypertonic solutions, typically containing high concentrations of sodium chloride or other osmotically active agents, have shown significant potential in promoting wound healing and managing infection.
Safety considerations for hypertonic applications are generally favorable. When used appropriately, these solutions have minimal adverse effects on healthy tissue. However, care must be taken to avoid prolonged exposure to extremely high concentrations, which may cause temporary discomfort or irritation. Proper dilution and application techniques are crucial to maximize benefits while minimizing potential risks.
Efficacy studies have revealed several mechanisms by which hypertonic applications contribute to wound healing. The osmotic effect draws excess fluid from the wound bed, reducing edema and promoting a more favorable healing environment. This action also helps to remove debris and contaminants, facilitating the natural cleansing process of the wound.
Furthermore, hypertonic solutions have demonstrated antimicrobial properties, effectively reducing bacterial load in infected wounds. This is particularly beneficial in managing chronic wounds or those at high risk of infection. The osmotic stress induced by these solutions can disrupt bacterial cell membranes, leading to cell death or inhibition of growth.
Clinical trials have shown that hypertonic applications can accelerate wound closure rates compared to standard saline solutions. This is attributed to enhanced granulation tissue formation and improved epithelialization. The osmotic gradient created by hypertonic solutions also stimulates local blood flow, promoting the delivery of oxygen and nutrients to the wound site.
In terms of pain management, hypertonic applications have shown promise in reducing wound-related pain. The mechanism is thought to involve the modulation of nerve endings and the reduction of inflammatory mediators in the wound environment. This analgesic effect can significantly improve patient comfort and compliance with wound care regimens.
Long-term studies have demonstrated the sustained efficacy of hypertonic applications in chronic wound management. Regular use has been associated with reduced healing times, decreased incidence of wound complications, and improved overall outcomes. These benefits have been observed across various wound types, including diabetic ulcers, pressure sores, and surgical wounds.
While the overall safety profile is favorable, it is important to note that individual patient factors should be considered when implementing hypertonic wound care regimens. Factors such as wound type, location, and the patient's overall health status may influence the appropriateness and efficacy of hypertonic applications.