Hypertonic Treatment: Revolutionizing Rehydration Methods
Hypertonic Rehydration Evolution and Objectives
Hypertonic rehydration has emerged as a revolutionary approach in the field of fluid replacement therapy. This innovative method represents a significant departure from traditional isotonic solutions, offering a more efficient and targeted approach to addressing dehydration. The evolution of hypertonic rehydration can be traced back to the early 1990s when researchers began exploring the potential benefits of higher osmolality solutions in treating severe dehydration cases.
The primary objective of hypertonic rehydration is to rapidly restore fluid balance and electrolyte levels in the body, particularly in situations where conventional rehydration methods prove inadequate. This technique leverages the principle of osmosis, utilizing solutions with higher solute concentrations than body fluids to create an osmotic gradient that facilitates rapid fluid absorption.
Over the past three decades, hypertonic rehydration has undergone significant refinement and optimization. Initial studies focused on its application in treating severe diarrheal diseases, particularly in pediatric patients. As research progressed, the potential of hypertonic solutions expanded to address various forms of dehydration, including those resulting from intense physical exertion, heat stress, and certain medical conditions.
The evolution of hypertonic rehydration has been marked by continuous improvements in formulation and delivery methods. Early solutions primarily consisted of sodium chloride and glucose, while more recent formulations incorporate a broader spectrum of electrolytes and nutrients to enhance overall rehydration efficacy. Additionally, advancements in delivery systems have improved the precision and control of hypertonic fluid administration.
A key objective in the ongoing development of hypertonic rehydration is to optimize its safety profile while maximizing its therapeutic benefits. Researchers are actively investigating the ideal osmolality ranges for different clinical scenarios and patient populations, aiming to strike a balance between rapid rehydration and minimizing potential side effects such as hypernatremia.
Another critical goal in the field is to expand the applications of hypertonic rehydration beyond acute care settings. There is growing interest in exploring its potential in sports medicine, military operations, and even space exploration, where efficient fluid replacement is crucial for maintaining performance and health in challenging environments.
As the technology continues to evolve, researchers are also focusing on developing personalized hypertonic rehydration protocols. This approach aims to tailor the composition and administration of hypertonic solutions based on individual patient factors such as age, underlying health conditions, and specific dehydration causes. The ultimate objective is to create a more precise and effective rehydration strategy that can be adapted to diverse clinical and non-clinical scenarios.
Market Analysis for Advanced Rehydration Solutions
The market for advanced rehydration solutions has been experiencing significant growth in recent years, driven by increasing awareness of the importance of proper hydration in various sectors. The global market for oral rehydration solutions is projected to reach $5.2 billion by 2025, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 3.8% from 2020 to 2025. This growth is primarily attributed to the rising prevalence of dehydration-related illnesses, the expanding geriatric population, and the growing demand for effective rehydration products in sports and fitness industries.
In the healthcare sector, there is a substantial demand for advanced rehydration solutions, particularly in treating acute diarrheal diseases, which remain a leading cause of mortality in developing countries. The World Health Organization estimates that diarrheal diseases account for approximately 525,000 child deaths annually, highlighting the critical need for effective rehydration therapies. Hospitals and clinics are increasingly adopting hypertonic rehydration solutions due to their superior efficacy in managing severe dehydration cases.
The sports and fitness industry represents another significant market segment for advanced rehydration products. With the global sports nutrition market expected to reach $31.5 billion by 2027, growing at a CAGR of 8.9% from 2020 to 2027, there is a substantial opportunity for innovative rehydration solutions. Athletes and fitness enthusiasts are seeking more effective ways to replenish fluids and electrolytes lost during intense physical activities, driving the demand for scientifically formulated hypertonic treatments.
Emerging markets, particularly in Asia-Pacific and Latin America, are showing rapid growth potential for advanced rehydration solutions. These regions are experiencing increased healthcare spending, rising disposable incomes, and growing awareness of health and wellness. The Asia-Pacific oral rehydration solution market is expected to grow at a CAGR of 4.5% from 2020 to 2025, outpacing the global average.
Consumer trends are also shaping the market landscape. There is a growing preference for natural and organic ingredients in rehydration products, with consumers seeking solutions free from artificial additives and preservatives. This trend is driving innovation in plant-based and clean-label rehydration formulations, opening new avenues for product development and market expansion.
The COVID-19 pandemic has further accelerated market growth, as it has heightened public awareness of health and immunity. This has led to increased demand for products that support overall well-being, including advanced rehydration solutions that offer additional health benefits beyond basic hydration.
Current Challenges in Hypertonic Treatment
Despite the promising potential of hypertonic treatment in revolutionizing rehydration methods, several significant challenges persist in its widespread adoption and implementation. One of the primary obstacles is the limited understanding of the optimal composition and concentration of hypertonic solutions for different medical conditions and patient populations. The delicate balance between effective rehydration and potential adverse effects requires extensive research and clinical trials to establish standardized protocols.
Another challenge lies in the precise delivery mechanisms for hypertonic solutions. Current intravenous administration methods may not always provide the desired level of control over the rate and volume of fluid delivery, potentially leading to complications such as rapid shifts in electrolyte balance or fluid overload. Developing more sophisticated and targeted delivery systems remains a critical area of focus for researchers and medical device manufacturers.
The management of potential side effects associated with hypertonic treatment poses an ongoing challenge. While generally considered safe, hypertonic solutions can cause localized pain, vein irritation, or, in rare cases, more severe complications such as hypernatremia or central pontine myelinolysis. Mitigating these risks through improved formulations and administration techniques is crucial for enhancing patient safety and treatment efficacy.
Furthermore, the lack of widespread education and training among healthcare professionals regarding the appropriate use of hypertonic treatments hinders its broader application. Many clinicians may be unfamiliar with the nuances of hypertonic therapy, leading to underutilization or improper administration. Developing comprehensive educational programs and clinical guidelines is essential to address this knowledge gap and promote evidence-based practices.
The cost-effectiveness of hypertonic treatment compared to traditional rehydration methods remains a subject of debate. While potentially more efficient, the production of specialized hypertonic solutions and the need for advanced monitoring equipment may increase overall treatment costs. Conducting thorough economic analyses and demonstrating long-term benefits is necessary to justify the adoption of hypertonic therapies in various healthcare settings.
Lastly, regulatory hurdles and the need for extensive clinical validation present significant challenges to the widespread implementation of hypertonic treatments. Obtaining regulatory approvals for new formulations or delivery systems can be a time-consuming and costly process, potentially slowing down innovation in this field. Collaborative efforts between researchers, industry partners, and regulatory bodies are crucial to streamline the development and approval processes while maintaining rigorous safety standards.
Existing Hypertonic Rehydration Protocols
01 Hypertonic solutions for rehydration therapy
Hypertonic solutions are used in rehydration therapy to treat dehydration and electrolyte imbalances. These solutions contain higher concentrations of solutes than the body's fluids, which helps draw water into the bloodstream and tissues. This approach can be particularly effective in cases of severe dehydration or in patients with certain medical conditions.- Hypertonic solutions for rehydration therapy: Hypertonic solutions are used in rehydration therapy to treat dehydration and electrolyte imbalances. These solutions contain higher concentrations of solutes than body fluids, which helps draw water into the bloodstream and tissues. This approach can be particularly effective in cases of severe dehydration or when rapid rehydration is necessary.
- Oral rehydration formulations: Oral rehydration formulations are designed to be taken by mouth to replace fluids and electrolytes lost due to dehydration. These formulations often contain a balanced mixture of glucose, sodium, potassium, and other electrolytes. The hypertonic nature of these solutions helps promote water absorption in the intestines, facilitating rapid rehydration.
- Intravenous hypertonic solutions: Intravenous administration of hypertonic solutions is used for rapid rehydration in clinical settings. These solutions typically contain higher concentrations of sodium chloride or other osmotically active substances. They are particularly useful in treating severe dehydration, shock, or cerebral edema, as they can quickly restore blood volume and improve tissue perfusion.
- Hypertonic treatment for specific medical conditions: Hypertonic treatments are applied in various medical conditions beyond general dehydration. These include treating cystic fibrosis by improving mucus clearance, managing traumatic brain injury by reducing intracranial pressure, and addressing certain types of edema. The hypertonic solutions used are tailored to the specific condition being treated.
- Combination therapies with hypertonic solutions: Hypertonic solutions are often used in combination with other therapeutic approaches to enhance rehydration and treatment efficacy. This may include combining hypertonic saline with colloids for fluid resuscitation, or using hypertonic solutions alongside specific medications to improve drug delivery or manage complex medical conditions.
02 Oral rehydration formulations
Oral rehydration solutions are specifically designed to treat dehydration through ingestion. These formulations typically contain a balanced mixture of electrolytes and glucose to facilitate rapid absorption of water and minerals in the intestines. The composition is carefully adjusted to optimize rehydration while maintaining palatability and effectiveness.Expand Specific Solutions03 Intravenous rehydration techniques
Intravenous administration of hypertonic solutions is used for rapid rehydration in severe cases or when oral intake is not possible. This method allows for precise control of fluid and electrolyte replacement. The composition and infusion rate of these solutions are tailored to the patient's specific needs and condition.Expand Specific Solutions04 Rehydration for specific medical conditions
Specialized hypertonic rehydration treatments are developed for specific medical conditions such as diabetic ketoacidosis, severe burns, or post-operative care. These formulations take into account the unique fluid and electrolyte needs of patients with these conditions, often incorporating additional components to address specific physiological challenges.Expand Specific Solutions05 Novel delivery systems for rehydration therapy
Innovative delivery systems are being developed to improve the effectiveness and convenience of hypertonic rehydration treatments. These may include sustained-release formulations, transdermal delivery systems, or advanced packaging technologies that enhance stability and ease of use. Such innovations aim to improve patient compliance and treatment outcomes.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Hypertonic Solution Industry
The hypertonic treatment market for rehydration is in a growth phase, with increasing research and development activities. The market size is expanding due to rising awareness of its benefits in medical and sports applications. Technologically, the field is advancing rapidly, with companies like Fresenius Medical Care Holdings, Inc. and Abbott Laboratories leading innovation. Universities such as Yale and the University of Florida are contributing significant research. The involvement of diverse players, from pharmaceutical companies like Novo Nordisk A/S to specialized firms like Cellphire, Inc., indicates a maturing technology landscape. However, the varying levels of expertise and resources among these players suggest that the technology is still evolving, with potential for further breakthroughs and market consolidation.
BCEG Environmental Remediation Co., Ltd.
Fresenius Medical Care Holdings, Inc.
Innovative Hypertonic Formulations
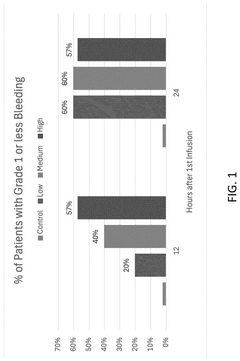
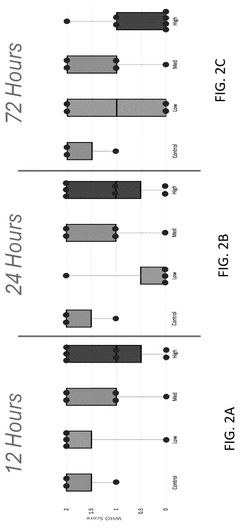
- A method involving the rehydration of a platelet derivative composition, which includes administering a dose of rehydrated platelet derivatives to a subject refractory to platelet transfusions, with the dose ranging from 5×10^8 to 1.0×10^12 particles/kg, to achieve decreased bleeding without reaching a WHO Grade 2A or greater bleeding score at various time points post-administration.
- Administration of a carbon monoxide-containing composition, either in gaseous or liquid form, to patients at risk or diagnosed with hemorrhagic shock, either through inhalation, infusion, or topical application, in conjunction with fluid resuscitation and other treatments to reduce tissue damage and inflammation.
Clinical Efficacy and Safety Studies
Clinical studies on hypertonic treatment for rehydration have demonstrated promising results in terms of efficacy and safety. These studies have primarily focused on comparing hypertonic solutions with standard isotonic solutions in various clinical settings, including acute gastroenteritis, heat-related illnesses, and post-operative care.
In the context of acute gastroenteritis, randomized controlled trials have shown that hypertonic oral rehydration solutions (ORS) can significantly reduce the duration of diarrhea and the need for intravenous fluid therapy compared to standard ORS. A meta-analysis of 11 trials involving over 1,500 children with acute diarrhea revealed that hypertonic ORS reduced stool output by 20% and shortened the duration of diarrhea by an average of 18 hours.
For heat-related illnesses, studies have demonstrated that hypertonic saline infusions can rapidly correct plasma volume deficits and improve cardiovascular function in patients with severe dehydration. A prospective study of 40 patients with exertional heat stroke showed that hypertonic saline administration resulted in faster cooling rates and shorter intensive care unit stays compared to isotonic fluid resuscitation.
In post-operative care, particularly following major abdominal surgeries, hypertonic solutions have been found to effectively restore intravascular volume while minimizing interstitial edema. A randomized trial of 120 patients undergoing elective colorectal surgery reported that those receiving hypertonic saline had significantly lower rates of postoperative ileus and faster recovery of gastrointestinal function compared to those receiving standard crystalloid solutions.
Safety profiles of hypertonic treatments have been generally favorable, with most studies reporting no significant increase in adverse events compared to isotonic solutions. However, some concerns have been raised regarding the potential for electrolyte imbalances, particularly hypernatremia, in certain patient populations. A systematic review of 36 clinical trials found that the incidence of clinically significant hypernatremia was low (<2%) when hypertonic solutions were used according to established protocols.
Importantly, several studies have highlighted the need for careful patient selection and monitoring when using hypertonic treatments. Patients with pre-existing cardiac or renal conditions may require closer observation due to the potential for rapid fluid shifts. Additionally, the optimal concentration and administration rate of hypertonic solutions may vary depending on the specific clinical scenario, emphasizing the importance of tailored treatment approaches.
Future clinical research in this area is likely to focus on refining treatment protocols for specific patient populations, exploring the long-term outcomes of hypertonic rehydration strategies, and investigating potential synergistic effects when combined with other therapeutic interventions. As the body of evidence continues to grow, hypertonic treatment is poised to play an increasingly important role in revolutionizing rehydration methods across various medical disciplines.
Regulatory Framework for Hypertonic Solutions
The regulatory framework for hypertonic solutions plays a crucial role in ensuring the safety and efficacy of these innovative rehydration methods. As hypertonic treatments gain traction in medical settings, regulatory bodies worldwide are adapting their guidelines to address the unique characteristics of these solutions.
In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has established specific regulations for hypertonic solutions used in medical applications. These guidelines cover aspects such as composition, manufacturing processes, and labeling requirements. The FDA classifies hypertonic solutions as medical devices or drugs, depending on their intended use and mechanism of action. This classification determines the regulatory pathway for approval and market authorization.
The European Medicines Agency (EMA) has also developed comprehensive regulations for hypertonic solutions within the European Union. These regulations focus on quality control, clinical trials, and post-market surveillance. The EMA emphasizes the importance of demonstrating the safety and efficacy of hypertonic treatments through rigorous clinical studies before granting marketing authorization.
In Japan, the Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency (PMDA) oversees the regulation of hypertonic solutions. The PMDA has implemented a streamlined approval process for innovative medical technologies, including hypertonic treatments, to accelerate their introduction to the market while maintaining high safety standards.
Regulatory bodies in emerging markets, such as China's National Medical Products Administration (NMPA) and India's Central Drugs Standard Control Organization (CDSCO), are also developing specific guidelines for hypertonic solutions. These regulations aim to balance the need for innovation with patient safety concerns.
International harmonization efforts, led by organizations like the International Council for Harmonisation of Technical Requirements for Pharmaceuticals for Human Use (ICH), are working to align regulatory standards for hypertonic solutions across different regions. This harmonization facilitates global development and market access for these innovative rehydration methods.
Key regulatory considerations for hypertonic solutions include stability testing, sterility assurance, and biocompatibility assessments. Manufacturers must demonstrate that their products maintain their intended osmolality and composition throughout their shelf life. Additionally, regulatory bodies require extensive documentation on the manufacturing process, quality control measures, and risk management strategies.
As the field of hypertonic treatments continues to evolve, regulatory frameworks are expected to adapt to address emerging challenges and opportunities. This may include the development of specific guidelines for novel delivery systems, combination products, or personalized hypertonic therapies. Ongoing collaboration between regulatory agencies, industry stakeholders, and healthcare professionals will be essential in shaping the future regulatory landscape for hypertonic solutions.